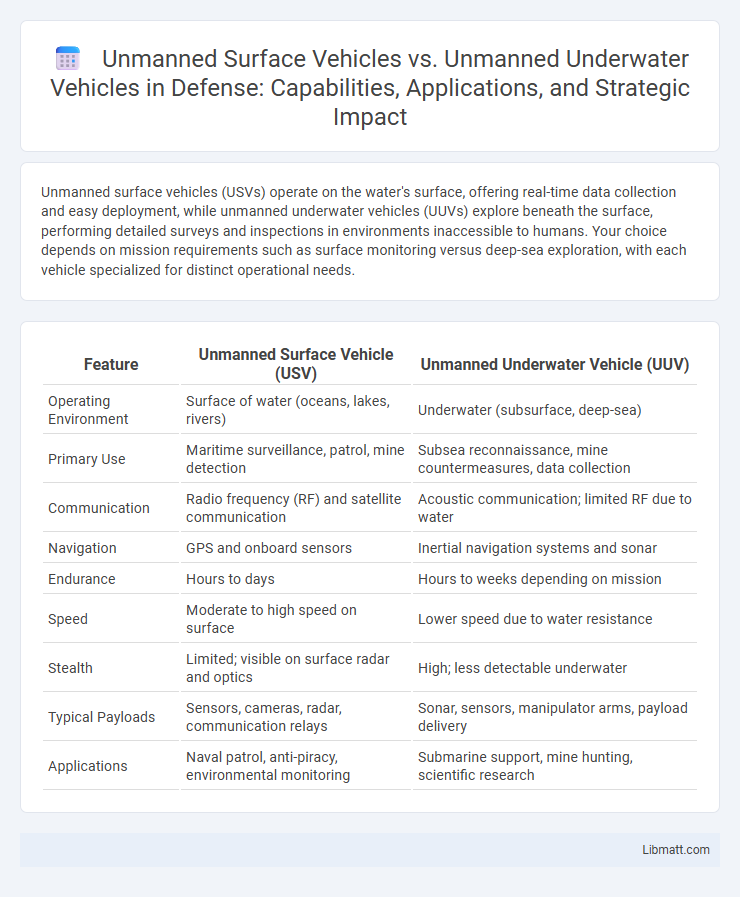
Unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) operate on the water's surface, offering real-time data collection and easy deployment, while unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) explore beneath the surface, performing detailed surveys and inspections in environments inaccessible to humans. Your choice depends on mission requirements such as surface monitoring versus deep-sea exploration, with each vehicle specialized for distinct operational needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Unmanned Surface Vehicle (USV) | Unmanned Underwater Vehicle (UUV) |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Environment | Surface of water (oceans, lakes, rivers) | Underwater (subsurface, deep-sea) |
| Primary Use | Maritime surveillance, patrol, mine detection | Subsea reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, data collection |
| Communication | Radio frequency (RF) and satellite communication | Acoustic communication; limited RF due to water |
| Navigation | GPS and onboard sensors | Inertial navigation systems and sonar |
| Endurance | Hours to days | Hours to weeks depending on mission |
| Speed | Moderate to high speed on surface | Lower speed due to water resistance |
| Stealth | Limited; visible on surface radar and optics | High; less detectable underwater |
| Typical Payloads | Sensors, cameras, radar, communication relays | Sonar, sensors, manipulator arms, payload delivery |
| Applications | Naval patrol, anti-piracy, environmental monitoring | Submarine support, mine hunting, scientific research |
Introduction to Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs) and Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs)
Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs) operate on the water's surface, equipped with advanced navigation sensors and communication systems for applications in maritime surveillance, environmental monitoring, and naval defense. Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) function beneath the waterline, utilizing sonar, pressure sensors, and autonomous navigation to conduct underwater inspections, scientific research, and mine countermeasures. Both USVs and UUVs leverage autonomous technologies, but their differing operational environments demand specialized design considerations for surface buoyancy and underwater pressure resistance.
Key Differences Between USVs and UUVs
Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs) operate on the water's surface, equipped with GPS and radar for navigation, while Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) function beneath the surface using sonar and inertial navigation systems. USVs are primarily used for surface surveillance, maritime security, and environmental monitoring, whereas UUVs excel in underwater exploration, mine detection, and subsea data collection. The physical design differences include buoyancy and hull structure, with USVs designed to withstand surface conditions and UUVs engineered for pressure resistance at varying depths.
Core Technologies Powering USVs and UUVs
Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs) rely on advanced navigation systems, real-time communication links, and solar or diesel-electric hybrid propulsion to optimize surface operations, while Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) focus on sonar-based mapping, autonomous underwater navigation, and battery technologies such as lithium-ion for extended submerged endurance. USVs integrate GPS and radar systems for precision surface maneuverability, contrasting with UUVs' acoustic modems and inertial navigation systems designed for deep-sea exploration. Both platforms utilize AI-driven data processing and power management systems to enhance mission efficiency and operational range in maritime environments.
Mission Capabilities and Deployment Environments
Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs) excel in missions requiring real-time data collection, surveillance, and maritime security on open water surfaces, benefiting from easy deployment and retrieval. Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) specialize in underwater exploration, reconnaissance, and subsea maintenance, operating effectively in challenging underwater environments like deep oceans and complex terrain. Your choice depends on mission needs: USVs for surface tasks with extended communication range, and UUVs for stealthy, submerged operations.
Sensor Suites: Above vs. Below Water Detection
Unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) utilize sensor suites optimized for above-water detection, including radar, LiDAR, and electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) cameras for navigation, target identification, and environmental monitoring. In contrast, unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) rely on sonar systems such as side-scan sonar, multibeam echosounders, and acoustic Doppler current profilers to detect and map underwater objects and terrain. USVs excel in line-of-sight sensing and surface communication, while UUVs are specialized for acoustic sensing in low-visibility, high-pressure underwater environments.
Communication Systems and Data Transmission
Unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) utilize radio frequency (RF) communication and satellite links for real-time data transmission over long distances, benefiting from less signal attenuation at the water-air interface. Unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) primarily rely on acoustic communication systems, which offer lower bandwidth and slower data rates due to high signal attenuation and multipath effects underwater. Advances in optical communication are emerging for UUVs, providing higher data rates but limited range, while USVs maintain more robust and continuous communication capabilities for remote operations.
Power Sources and Endurance Comparison
Unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) primarily utilize solar panels and fuel cells as power sources, enabling extended endurance ranging from several days to weeks depending on mission profiles and energy storage capacity. Unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) often rely on high-density lithium-ion batteries or advanced hybrid systems that offer shorter endurance, typically measured in hours to a few days, due to limited opportunities for recharging underwater. The energy demands and operational environments fundamentally influence the power source selection and endurance capabilities of USVs and UUVs, with surface-based recharge options granting USVs longer mission durations.
Commercial and Military Applications of USVs vs. UUVs
Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs) excel in maritime surveillance, environmental monitoring, and cargo transport within commercial sectors, while their military applications include naval reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, and coastal defense. Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) are vital for subsea exploration, pipeline inspection, and underwater infrastructure maintenance commercially, with military uses centered on intelligence gathering, anti-submarine warfare, and underwater mine detection. Both USVs and UUVs enhance operational efficiency by reducing human risk and extending mission capabilities in complex marine environments.
Operational Challenges and Limitations
Unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) face operational challenges such as surface-level weather conditions, wave motion, and limited endurance due to energy constraints, while their communication systems generally benefit from line-of-sight radio transmissions. Unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) encounter significant limitations in underwater navigation due to GPS unavailability, requiring advanced inertial navigation systems and acoustic communications that suffer from low bandwidth and high latency. Both platforms must address power management, environmental interference, and mission-specific constraints, but UUVs are more constrained by depth-related pressure and limited data transmission capabilities.
Future Trends in Unmanned Maritime Robotics
Unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) and unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) are evolving rapidly with advancements in autonomous navigation, sensor integration, and AI-driven decision-making. Future trends highlight enhanced interoperability between USVs and UUVs, enabling more comprehensive maritime surveillance, environmental monitoring, and defense applications. Your investment in these technologies can leverage real-time data fusion and swarm capabilities to improve efficiency and operational scope in unmanned maritime robotics.
Unmanned surface vehicle vs Unmanned underwater vehicle Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com