Rib knit fabric offers superior stretch and elasticity, making it ideal for cuffs, collars, and form-fitting garments, while flat knit fabric provides a smoother surface and better drape, suitable for sweaters and lightweight clothing. Understanding the differences helps you choose the best knit type based on durability, texture, and garment fit.
Table of Comparison
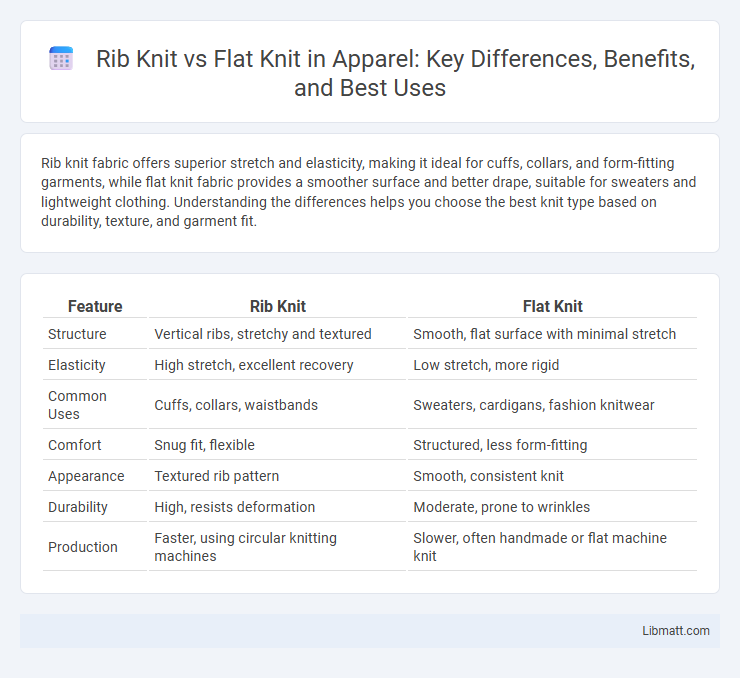
| Feature | Rib Knit | Flat Knit |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Vertical ribs, stretchy and textured | Smooth, flat surface with minimal stretch |
| Elasticity | High stretch, excellent recovery | Low stretch, more rigid |
| Common Uses | Cuffs, collars, waistbands | Sweaters, cardigans, fashion knitwear |
| Comfort | Snug fit, flexible | Structured, less form-fitting |
| Appearance | Textured rib pattern | Smooth, consistent knit |
| Durability | High, resists deformation | Moderate, prone to wrinkles |
| Production | Faster, using circular knitting machines | Slower, often handmade or flat machine knit |
Introduction to Rib Knit and Flat Knit
Rib knit fabric features vertical ridges created by alternating knit and purl stitches, offering exceptional elasticity and shape retention. Flat knit fabric is produced on a flat knitting machine, resulting in a smooth, uniform texture ideal for detailed patterns and less stretch compared to rib knit. Both knitting types serve unique purposes in garment construction, with rib knit commonly used for cuffs and collars, while flat knit suits body panels and intricate designs.
Key Differences Between Rib Knit and Flat Knit
Rib knit fabric features vertical textured lines created by alternating knit and purl stitches, offering high elasticity and a snug fit, ideal for cuffs and collars. Flat knit fabric is produced on a flat knitting machine, resulting in a smooth, consistent surface that is less stretchy and commonly used for sweaters and structured garments. The primary differences lie in texture, stretchability, and typical applications, with rib knit providing flexibility and flat knit emphasizing stability and uniformity.
Structure and Texture Comparison
Rib knit features vertical ridges formed by alternating knit and purl stitches, creating a textured, stretchy fabric ideal for cuffs and collars. Flat knit produces a smooth, even surface with less elasticity, making it suitable for structured garments and detailed patterns. Your choice depends on whether you prefer the flexible, tactile feel of rib knit or the sleek, stable finish of flat knit.
Production Methods: Rib Knit vs Flat Knit
Rib knit fabric is produced by alternating knit and purl stitches on the same row, creating vertical textured ribs that enhance elasticity and stretch. Flat knit fabric is made using a flatbed knitting machine producing a smooth, uniform surface, ideal for structured and less stretchable garments. The production method of rib knit allows for greater flexibility, while flat knit emphasizes precision and stability in fabric construction.
Stretch and Elasticity Characteristics
Rib knit fabric exhibits superior stretch and elasticity due to its alternating knit and purl stitches, allowing it to expand and recover efficiently, ideal for form-fitting garments. Flat knit fabric offers less stretch and elasticity as its smooth, uniform texture provides more stability and structure with minimal give. Your choice between rib knit and flat knit will depend on whether you prioritize flexible, stretchy material or a firmer, more stable knit for your project.
Common Uses in Apparel and Textiles
Rib knit fabric is predominantly used in cuffs, collars, and waistbands due to its excellent elasticity and recovery, making it ideal for garments requiring stretch and shape retention. Flat knit fabric is commonly employed in body panels, sweaters, and cardigans where a smooth, uniform texture and dimension stability are desired. Both knit types are essential in apparel manufacturing, offering distinct benefits for diverse textile applications.
Pros and Cons of Rib Knit Fabrics
Rib knit fabrics offer excellent elasticity and recovery, making them ideal for garments that require stretch and shape retention such as cuffs and collars, but they can be prone to curling at the edges. Their textured pattern provides added durability and a snug fit, though rib knits tend to be thicker and heavier compared to flat knit fabrics, which may affect breathability. Your choice should consider the desired garment structure and comfort, as rib knits deliver superior flexibility but may require more careful handling during sewing to avoid distortions.
Pros and Cons of Flat Knit Fabrics
Flat knit fabrics offer a smooth, consistent texture ideal for structured garments and detailed patterns, providing excellent shape retention and minimal stretch. However, they tend to be less flexible and can feel stiffer compared to rib knit fabrics, potentially limiting comfort and ease of movement. Choosing flat knit ensures durability and a polished appearance, making it suitable for your tailored wardrobe pieces.
Care and Maintenance for Rib and Flat Knits
Rib knits require gentle washing in cold water and laying flat to dry to maintain their elasticity and prevent distortion, while flat knits benefit from similar care but often tolerate a bit more stretch without losing shape. Avoiding high heat during washing and drying is crucial for both knit types to preserve fiber integrity and prevent shrinking. Using mild detergents and avoiding bleach help extend the lifespan of rib and flat knit garments by protecting the knit structure.
Choosing Between Rib Knit and Flat Knit
When choosing between rib knit and flat knit fabrics, consider the application and desired texture; rib knit offers superior elasticity and structure, making it ideal for cuffs, collars, and fitted garments, while flat knit provides a smoother surface suitable for lightweight sweaters and scarves. Rib knit features raised vertical lines due to alternating knit and purl stitches, enhancing stretch and recovery, whereas flat knit's uniform rows create a sleek, flexible fabric. Durability and appearance vary, with rib knit maintaining shape over time and flat knit providing a polished, less bulky finish for layering.
rib knit vs flat knit Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com