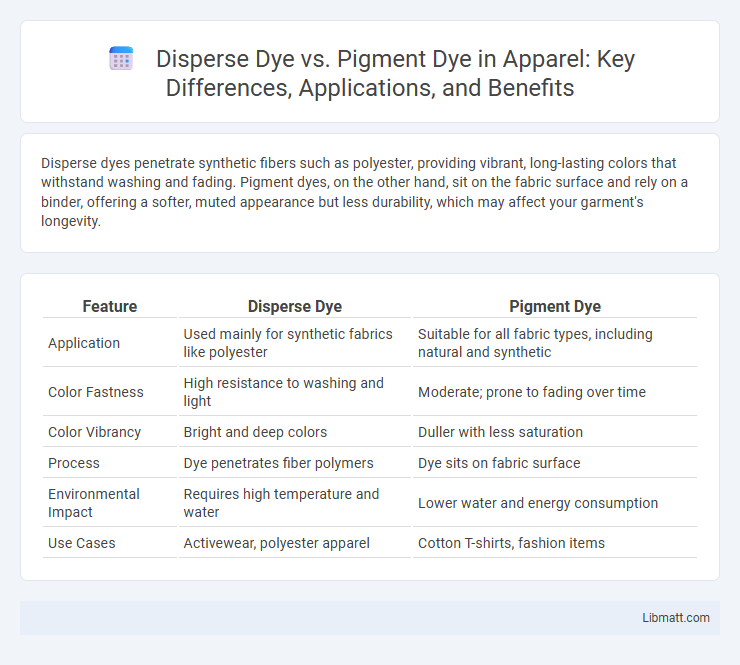
Disperse dyes penetrate synthetic fibers such as polyester, providing vibrant, long-lasting colors that withstand washing and fading. Pigment dyes, on the other hand, sit on the fabric surface and rely on a binder, offering a softer, muted appearance but less durability, which may affect your garment's longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Disperse Dye | Pigment Dye |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Used mainly for synthetic fabrics like polyester | Suitable for all fabric types, including natural and synthetic |
| Color Fastness | High resistance to washing and light | Moderate; prone to fading over time |
| Color Vibrancy | Bright and deep colors | Duller with less saturation |
| Process | Dye penetrates fiber polymers | Dye sits on fabric surface |
| Environmental Impact | Requires high temperature and water | Lower water and energy consumption |
| Use Cases | Activewear, polyester apparel | Cotton T-shirts, fashion items |
Introduction to Disperse and Pigment Dyes
Disperse dyes are synthetic dyes primarily used for coloring synthetic fibers such as polyester, offering excellent fastness and vibrant shades through a process of dye diffusion. Pigment dyes, in contrast, consist of insoluble color particles that adhere to the surface of fibers like cotton or leather via binders, resulting in durable, colorfast finishes without fiber penetration. Understanding these distinct dyeing mechanisms is crucial for selecting appropriate textile applications and achieving desired color effects.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Disperse dyes are small, non-ionic molecules with low water solubility, primarily composed of azo, anthraquinone, and other heterocyclic compounds, designed to penetrate synthetic fibers like polyester through physical diffusion. Pigment dyes consist of larger, insoluble organic or inorganic particles with complex molecular structures that do not chemically bond to fibers but adhere to surfaces using binders. The fundamental chemical difference lies in disperse dyes' solubility and fiber affinity versus pigment dyes' particulate nature and reliance on mechanical adhesion.
Dyeing Mechanisms: How Each Dye Works
Disperse dyes penetrate synthetic fibers like polyester by sublimation, allowing molecules to diffuse directly into the fiber's polymer matrix through heat, resulting in vibrant and durable coloration. Pigment dyes, on the other hand, adhere to fabric surfaces via binding agents without penetrating fibers, creating a color layer that sits on top and offers less wash-fastness but exceptional brightness. Your choice between these dyeing mechanisms influences fabric feel, longevity, and color intensity based on the interaction of dye particles with fiber structure.
Substrate Compatibility: Applicable Fabrics
Disperse dyes are specifically designed for synthetic fibers such as polyester, nylon, and acetate, offering excellent colorfastness and vibrant hues by penetrating the fiber molecularly. Pigment dyes, in contrast, are non-soluble and adhere to the fabric surface, making them compatible with a wider range of substrates including cotton, wool, and blends, but often resulting in less durability. The choice between disperse and pigment dyes largely depends on the fabric composition and desired durability, with disperse dyes favored for synthetic textiles and pigment dyes used for diverse materials requiring surface-level coloration.
Color Fastness and Durability
Disperse dyes exhibit superior color fastness and durability on synthetic fibers such as polyester, maintaining vibrant hues through repeated washing and exposure to sunlight. Pigment dyes, which adhere to fabric surfaces rather than penetrating fibers, often show lower wash fastness and may fade or crack over time, especially on cotton and other natural fibers. The inherent chemical bonding of disperse dyes to synthetic fibers ensures longer-lasting color retention compared to the more surface-level attachment of pigment dyes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Disperse dyes generally have a lower environmental impact compared to pigment dyes due to their higher substantivity to synthetic fibers, resulting in less dye waste and water pollution during the dyeing process. Pigment dyes, often used in waterless or low-water printing techniques, can reduce water consumption but may involve binders and chemicals that complicate biodegradability and recyclability. Sustainable dyeing practices prioritize disperse dyes with eco-friendly formulations and closed-loop systems to minimize resource use and toxic effluents, supporting circularity in textile manufacturing.
Application Techniques and Processes
Disperse dyes are primarily applied through high-temperature dyeing processes such as thermosol and high-pressure jet dyeing, which enable deep penetration into synthetic fibers like polyester. Pigment dyes rely on surface application techniques including screen printing and pigment printing, where dyes adhere to the fabric surface through binders rather than fiber absorption. Both methods require specific fixation techniques: disperse dyes depend on heat for diffusion, while pigment dyes necessitate curing to ensure colorfastness and durability on various textiles.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Disperse dyes generally offer a lower cost per unit compared to pigment dyes due to their higher affinity for synthetic fibers and more efficient dyeing process, resulting in less dye waste and lower energy consumption. Pigment dyes, while often pricier initially, provide advantages in color fastness and versatility across fabric types, potentially reducing long-term replacement or reprocessing costs. Economic considerations must weigh the balance between upfront material expenses and operational efficiencies to determine the most cost-effective option for specific textile production needs.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Dye
Disperse dye offers excellent colorfastness and vibrant shades, making it ideal for polyester fabrics but may have limitations in environmental impact and application on natural fibers. Pigment dye provides versatility for various fabric types and imparts a soft, vintage look, though it can suffer from lower wash durability and potential color fading over time. Understanding your fabric choice and desired durability helps determine whether disperse or pigment dye suits your needs best.
Choosing Between Disperse and Pigment Dyes
Choosing between disperse and pigment dyes depends on fabric type and desired colorfastness; disperse dyes are ideal for synthetic fibers like polyester due to their excellent penetration and vibrant hues, while pigment dyes work best on natural fibers and offer superior versatility in surface coloration. Disperse dyes chemically bond with fibers, ensuring durability and resistance to washing, whereas pigment dyes rely on a binder to adhere to the fabric, which can affect wash and light fastness. For applications requiring bright, long-lasting colors on synthetic textiles, disperse dyes are preferable, but for broader compatibility and ease of application on various materials, pigment dyes provide a practical solution.
Disperse dye vs pigment dye Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com