Rehydration rate measures how quickly a substance absorbs water and returns to its original state, while dissolution rate refers to the speed at which a solid dissolves into a solvent to form a solution. Understanding your product's rehydration and dissolution rates is crucial for optimizing performance in applications like pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Table of Comparison
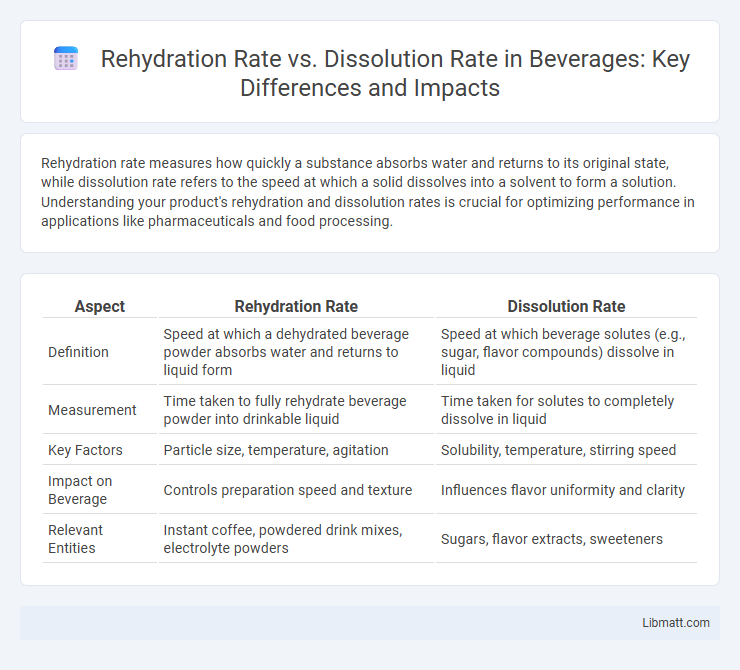
| Aspect | Rehydration Rate | Dissolution Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Speed at which a dehydrated beverage powder absorbs water and returns to liquid form | Speed at which beverage solutes (e.g., sugar, flavor compounds) dissolve in liquid |
| Measurement | Time taken to fully rehydrate beverage powder into drinkable liquid | Time taken for solutes to completely dissolve in liquid |
| Key Factors | Particle size, temperature, agitation | Solubility, temperature, stirring speed |
| Impact on Beverage | Controls preparation speed and texture | Influences flavor uniformity and clarity |
| Relevant Entities | Instant coffee, powdered drink mixes, electrolyte powders | Sugars, flavor extracts, sweeteners |
Understanding Rehydration Rate and Dissolution Rate
Rehydration rate measures the speed at which a dehydrated substance absorbs water and returns to its original state, crucial in food processing and pharmaceuticals for quality assessment. Dissolution rate defines how quickly a solid solute dissolves into a solvent, impacting drug bioavailability and chemical reactions. Both rates influence product performance, but rehydration rate emphasizes water absorption kinetics while dissolution rate centers on solute dispersion dynamics.
Key Differences Between Rehydration and Dissolution
Rehydration rate measures how quickly a dried substance absorbs water and returns to its original state, while dissolution rate quantifies the speed at which a solid solute dissolves into a solvent forming a solution. Key differences include rehydration involving physical water uptake without changing the chemical structure, whereas dissolution results in molecular dispersion of the solute. Understanding these rates helps optimize product performance in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical applications.
Factors Influencing Rehydration Rate
Rehydration rate is primarily influenced by particle size, porosity, and the nature of the solute, which determine how quickly water penetrates and interacts with the material. Temperature and agitation intensity also play crucial roles, as higher temperatures and increased stirring enhance water absorption and accelerate rehydration. In contrast, dissolution rate depends more on solubility characteristics and surface area, highlighting the distinct mechanisms governing rehydration and dissolution processes.
Factors Affecting Dissolution Rate
Dissolution rate is influenced by factors such as particle size, surface area, temperature, and stirring speed, all of which enhance the interaction between the solute and solvent. The chemical nature of the substance, including its solubility and crystalline form, also plays a critical role in determining how quickly it dissolves. Understanding these factors can help you optimize formulations for better bioavailability and consistent drug release profiles.
Importance of Rehydration Rate in Food Science
Rehydration rate is crucial in food science because it directly affects the texture, flavor, and overall quality of dehydrated food products. While dissolution rate measures how quickly a substance dissolves in a solvent, rehydration rate reflects the ability of dried foods to absorb water and return to their original state, impacting consumer satisfaction. Your understanding of rehydration rate helps in optimizing food processing techniques for better preservation and sensory attributes.
Significance of Dissolution Rate in Pharmaceuticals
Dissolution rate plays a crucial role in pharmaceuticals as it directly impacts the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of oral medications by controlling the speed at which the active drug ingredient becomes available for absorption. While rehydration rate is important for reconstituting powdered formulations, it is the dissolution rate that determines how quickly and efficiently the drug dissolves in gastrointestinal fluids. Optimizing dissolution rate ensures consistent drug release, enhances patient outcomes, and supports regulatory compliance in drug development.
Measuring Rehydration Rate: Methods and Tools
Measuring rehydration rate involves tracking the time required for a dehydrated substance to absorb water and return to its original state, typically using gravimetric analysis or volumetric methods. Tools such as moisture analyzers, spectrophotometers, and automated titrators provide precise data on water uptake, enabling accurate assessment of product quality and consistency. Your ability to select the appropriate method depends on the material's characteristics and the desired accuracy of the rehydration rate measurement.
Assessing Dissolution Rate: Techniques and Standards
Assessing dissolution rate involves techniques such as UV-Vis spectroscopy, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and basket or paddle apparatus to measure the time it takes for a substance to dissolve completely in a solvent. Standardized methods defined by pharmacopeias like the USP and EP ensure consistent evaluation of dissolution profiles, critical for drug quality and bioavailability. These techniques provide precise dissolution rate data that can be compared against rehydration rate to optimize formulation performance.
Practical Applications of Controlling Rehydration and Dissolution
Controlling rehydration and dissolution rates is crucial in pharmaceuticals to optimize drug bioavailability and therapeutic effects, ensuring medications release active ingredients at desired speeds. In food technology, precise management of these rates improves product texture and flavor reconstitution, enhancing consumer experience. Your ability to tailor rehydration and dissolution directly impacts product quality, stability, and efficacy across diverse industrial applications.
Optimizing Product Performance: Balancing Rehydration and Dissolution
Optimizing product performance requires a precise balance between rehydration rate and dissolution rate to ensure maximum efficacy and consumer satisfaction. A faster rehydration rate improves the reconstitution time of powders in liquids, while an adequate dissolution rate guarantees complete ingredient release for optimal bioavailability. Tailoring these parameters in your formulation enhances functionality and ensures consistent product quality.
Rehydration rate vs dissolution rate Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com