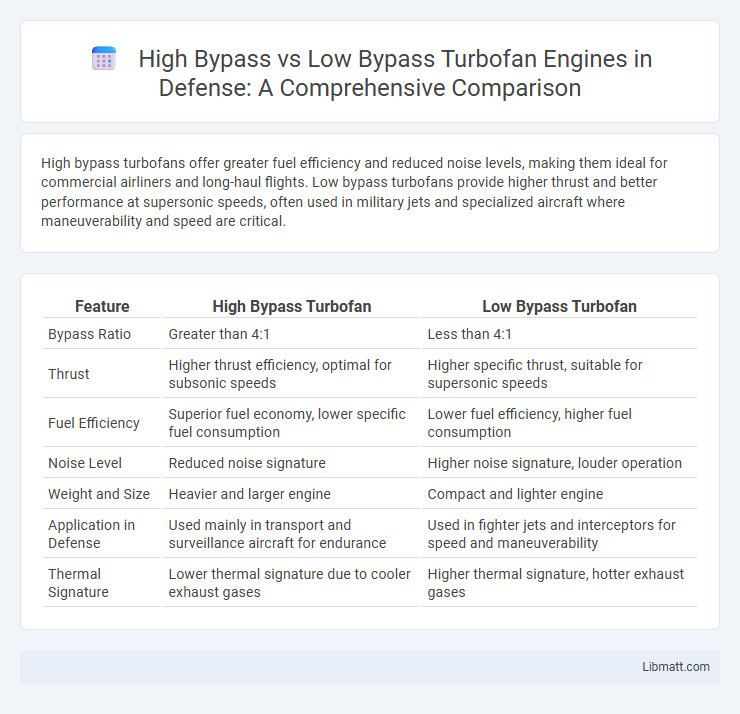
High bypass turbofans offer greater fuel efficiency and reduced noise levels, making them ideal for commercial airliners and long-haul flights. Low bypass turbofans provide higher thrust and better performance at supersonic speeds, often used in military jets and specialized aircraft where maneuverability and speed are critical.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High Bypass Turbofan | Low Bypass Turbofan |
|---|---|---|
| Bypass Ratio | Greater than 4:1 | Less than 4:1 |
| Thrust | Higher thrust efficiency, optimal for subsonic speeds | Higher specific thrust, suitable for supersonic speeds |
| Fuel Efficiency | Superior fuel economy, lower specific fuel consumption | Lower fuel efficiency, higher fuel consumption |
| Noise Level | Reduced noise signature | Higher noise signature, louder operation |
| Weight and Size | Heavier and larger engine | Compact and lighter engine |
| Application in Defense | Used mainly in transport and surveillance aircraft for endurance | Used in fighter jets and interceptors for speed and maneuverability |
| Thermal Signature | Lower thermal signature due to cooler exhaust gases | Higher thermal signature, hotter exhaust gases |
Introduction to Turbofan Engines
Turbofan engines, widely used in commercial and military aviation, differ primarily by their bypass ratio, which influences efficiency and noise levels. High bypass turbofan engines feature a larger fan that directs more air around the core, optimizing fuel efficiency and reducing noise during flight, making them ideal for commercial airliners. In contrast, low bypass turbofan engines generate greater thrust with a smaller fan and higher exhaust velocity, favoring military jets that require speed and maneuverability over fuel economy.
Defining Bypass Ratio
Bypass ratio defines the amount of air that bypasses the engine core compared to the air passing through it, significantly influencing turbofan performance. High bypass turbofans feature bypass ratios typically above 4:1, improving fuel efficiency and reducing noise by accelerating a larger volume of air at lower speed. Low bypass turbofans, with bypass ratios below 2:1, offer higher thrust-to-weight ratios suited for supersonic or military applications but consume more fuel and generate greater noise levels.
Overview of High Bypass Turbofans
High bypass turbofan engines feature a large fan that directs a significant amount of air around the engine core, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and reduced noise levels compared to low bypass turbofans. These engines typically have bypass ratios greater than 5:1, which enhances thrust and makes them ideal for commercial airliners and long-haul flights. High bypass turbofans excel in delivering high thrust with lower fuel consumption, contributing to environmentally friendly operations and cost savings in aviation.
Overview of Low Bypass Turbofans
Low bypass turbofans feature a smaller bypass ratio, typically below 2:1, resulting in higher exhaust velocity and better performance at supersonic speeds. These engines are commonly used in military aircraft due to their enhanced thrust and maneuverability capabilities. Understanding the trade-offs in fuel efficiency and noise levels helps optimize your aircraft choice based on mission requirements.
Thrust Generation Differences
High bypass turbofan engines generate thrust primarily through a large volume of air accelerated by the fan, resulting in greater efficiency and quieter operation, ideal for commercial airliners. Low bypass turbofan engines produce thrust by accelerating a smaller mass of air at higher velocity, resulting in higher specific thrust and better performance at supersonic speeds, commonly used in fighter jets. Your choice depends on whether fuel efficiency and noise reduction or speed and agility are prioritized.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison
High bypass turbofan engines achieve superior fuel efficiency by directing a larger volume of air around the engine core, resulting in greater thrust with less fuel consumption, commonly used in commercial airliners for long-haul flights. Low bypass turbofans generate higher thrust with a smaller air bypass ratio, leading to increased fuel burn but enhanced performance suitable for military jets and supersonic speeds. The fuel efficiency advantage of high bypass turbofans can range from 15% to 30% better compared to low bypass models, especially during cruise conditions at subsonic speeds.
Noise and Environmental Impact
High bypass turbofan engines generate significantly lower noise levels due to their larger fan diameter and slower exhaust velocities, making them more suitable for noise-sensitive environments. These engines also exhibit greater fuel efficiency and reduced carbon emissions compared to low bypass turbofans, contributing to a smaller environmental footprint. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize your choice for quieter, eco-friendly aviation technology.
Applications in Civil and Military Aviation
High bypass turbofan engines are predominantly used in civil aviation for commercial airliners due to their fuel efficiency, lower noise levels, and ability to produce high thrust at subsonic speeds. In contrast, low bypass turbofan engines are favored in military aviation for fighter jets and supersonic aircraft where higher thrust-to-weight ratios and faster acceleration are critical. Your choice between high and low bypass turbofans depends on mission requirements, balancing efficiency for long-haul flights against performance for combat and high-speed maneuvering.
Maintenance and Operating Costs
High bypass turbofan engines offer lower operating costs due to improved fuel efficiency and reduced wear on engine components, leading to longer maintenance intervals. Low bypass turbofans tend to have higher maintenance requirements and operating expenses because of their increased fuel consumption and more frequent component replacements. Your choice between them should consider the balance between upfront costs and long-term efficiency gains.
Future Trends in Turbofan Technology
Future trends in turbofan technology emphasize increasing bypass ratios to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, with high bypass turbofans becoming the industry standard for commercial aviation. Innovations such as geared turbofan designs and advanced composite materials improve performance and lower operational costs by reducing weight and optimizing airflow. Low bypass turbofans, primarily used in military applications, are evolving with adaptive cycle engines that offer variable bypass ratios to balance fuel efficiency and thrust for multi-mission versatility.
High bypass turbofan vs Low bypass turbofan Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com