Low-band jammers disrupt communication signals operating at lower frequency ranges, such as VHF and UHF bands, affecting devices like walkie-talkies and some mobile phones. High-band jammers target higher frequency signals used by GPS, Wi-Fi, and advanced cellular networks, making them crucial for interfering with modern wireless technologies.
Table of Comparison
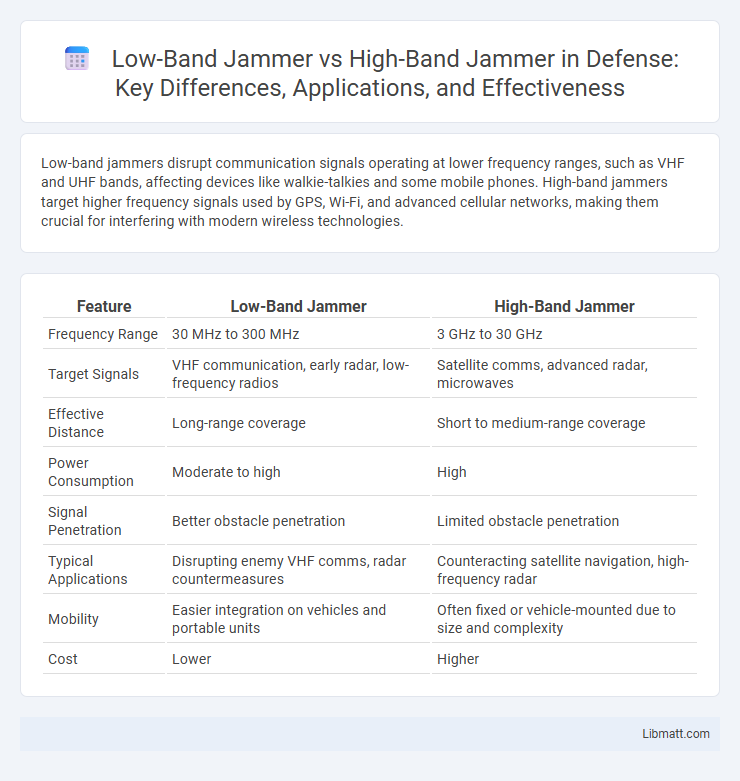
| Feature | Low-Band Jammer | High-Band Jammer |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 30 MHz to 300 MHz | 3 GHz to 30 GHz |
| Target Signals | VHF communication, early radar, low-frequency radios | Satellite comms, advanced radar, microwaves |
| Effective Distance | Long-range coverage | Short to medium-range coverage |
| Power Consumption | Moderate to high | High |
| Signal Penetration | Better obstacle penetration | Limited obstacle penetration |
| Typical Applications | Disrupting enemy VHF comms, radar countermeasures | Counteracting satellite navigation, high-frequency radar |
| Mobility | Easier integration on vehicles and portable units | Often fixed or vehicle-mounted due to size and complexity |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Signal Jammers
Low-band jammers disrupt communication by targeting frequencies typically used for AM radio, VHF, and some cellular services, effectively blocking signals in larger geographical areas. High-band jammers focus on higher-frequency bands like GPS, Wi-Fi, and higher cellular bands, useful for precision interference in localized zones. Your choice between low-band and high-band jammers depends on which communication signals you aim to block and the coverage size required.
Understanding Low-Band Jammers
Low-band jammers operate within frequencies typically ranging from 30 MHz to 300 MHz, effectively disrupting communications like VHF and UHF radio signals. These jammers are ideal for interfering with long-range, low-frequency transmissions used in aviation, maritime, and military communication systems. High-band jammers, in contrast, target higher frequency bands above 1 GHz, focusing on GPS, Wi-Fi, and cellular networks, making low-band jammers essential for disrupting essential, broad coverage communication channels.
Features of High-Band Jammers
High-band jammers operate at higher frequencies, typically between 2 GHz and 18 GHz, enabling them to disrupt signals from devices like Wi-Fi routers, GPS, and cellular networks effectively. They feature advanced modulation capabilities and wider bandwidth coverage, allowing for precise targeting of multiple high-frequency communication signals simultaneously. Your security setup benefits from high-band jammers' ability to counter sophisticated wireless threats with stronger signal interference and enhanced detection resistance.
Frequency Spectrum Differences
Low-band jammers operate within the 30 MHz to 300 MHz frequency range, targeting communication systems such as VHF and UHF radios, while high-band jammers cover higher frequencies from 1 GHz to 6 GHz, disrupting cellular, Wi-Fi, and GPS signals. The frequency spectrum differences directly impact the range and application, with low-band jammers providing broader coverage and penetrating obstacles better, whereas high-band jammers offer more precise interference on modern digital communication channels. Understanding these spectral differences allows you to select the appropriate jammer based on the specific frequency bands you need to control or block.
Typical Applications: Low-Band vs High-Band
Low-band jammers are typically used in applications targeting broader, longer-range signals such as AM/FM radio, VHF communication, and low-frequency radar systems, often employed in perimeter security and anti-surveillance operations. High-band jammers focus on disrupting higher-frequency signals like cellular networks (4G, 5G), Wi-Fi, GPS, and satellite communications, making them ideal for protecting sensitive locations from data interception and unauthorized drone activity. Both types of jammers serve distinct roles in electronic warfare and signal denial, optimized by frequency range for specific operational environments.
Performance Comparison
Low-band jammers emit signals in lower frequency ranges (30 MHz to 300 MHz), effectively disrupting long-range communication and radar systems but often with less precision. High-band jammers operate in higher frequencies (above 1 GHz), offering targeted interference against modern, high-frequency devices such as satellite links and advanced communication systems, typically delivering more focused and efficient disruption. Your choice depends on the desired operational range and the specific communication technologies you aim to counter, as high-band jammers excel in precision while low-band jammers cover broader areas.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Type
Low-band jammers effectively disrupt communications over longer distances and penetrate obstacles like buildings and terrain, making them ideal for broad area coverage, but they often consume more power and have limited effectiveness against high-frequency signals. High-band jammers excel at targeting specific frequencies used in modern wireless devices such as smartphones and Wi-Fi, offering precision and reduced interference outside the targeted band, yet their range is typically shorter and obstacles can significantly reduce their effectiveness. Choosing between low-band and high-band jammers depends on the operational environment and the frequency spectrum of the signals intended to be blocked.
Key Considerations for Selection
Low-band jammers operate primarily in frequencies below 1 GHz, effectively disrupting communications such as AM/FM radio, VHF/UHF radios, and some cellular signals, while high-band jammers target frequencies above 1 GHz, impacting Wi-Fi, GPS, and advanced mobile networks like LTE and 5G. Key considerations for selection include the operational environment, required jamming range, frequency spectrum of the target devices, and legal regulations concerning electromagnetic interference. Power output and antenna type also influence the jammer's effectiveness, with low-band jammers generally requiring larger antennas and higher power for broad coverage, compared to the more localized and frequency-specific high-band jammers.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Low-band jammers often fall under stricter legal scrutiny due to their interference with emergency communication frequencies regulated by agencies like the FCC in the United States. High-band jammers may face regulations related to specific frequency ranges governed by international and national bodies such as the ITU and Ofcom. Understanding these legal frameworks ensures your use complies with regulations designed to prevent unauthorized signal disruption.
Future Trends in Jamming Technology
Low-band jammers, operating in frequencies below 1 GHz, target long-range communication signals like GSM and AM radio, while high-band jammers focus on frequencies above 6 GHz, disrupting satellite and advanced radar systems. Future trends in jamming technology emphasize adaptive frequency hopping and AI-driven signal detection, enhancing the effectiveness of both low-band and high-band jammers against evolving communication protocols. Your electronic defense strategy must integrate these advancements to counter sophisticated threats across diverse frequency spectrums.
low-band jammer vs high-band jammer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com