Cold launch involves deploying a rocket from a submarine or underwater platform without an ignition until after it exits the water, minimizing the risk of damage to the vehicle and launch platform. Hot launch ignites the rocket engine while still on the launch pad or platform, providing immediate thrust but requiring more robust infrastructure to withstand the intense heat and pressure.
Table of Comparison
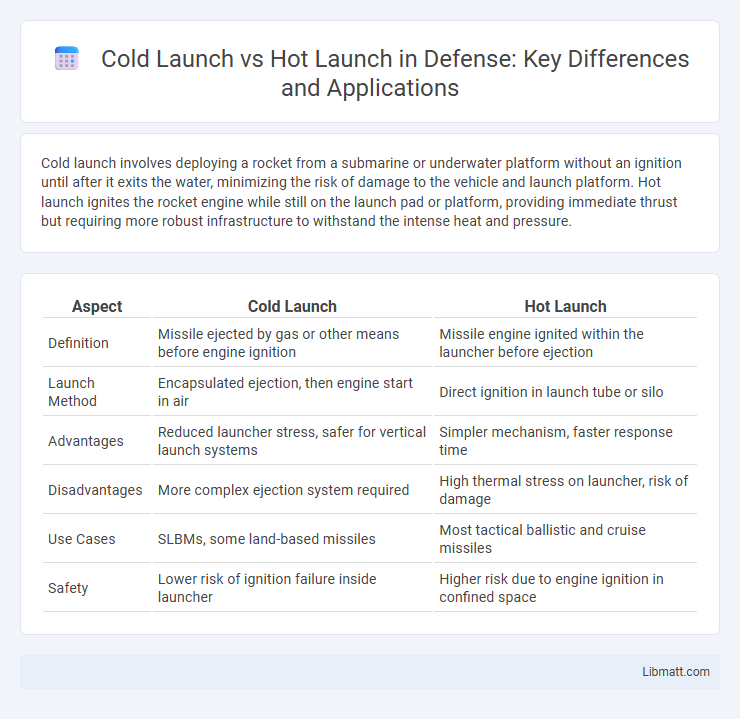
| Aspect | Cold Launch | Hot Launch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Missile ejected by gas or other means before engine ignition | Missile engine ignited within the launcher before ejection |
| Launch Method | Encapsulated ejection, then engine start in air | Direct ignition in launch tube or silo |
| Advantages | Reduced launcher stress, safer for vertical launch systems | Simpler mechanism, faster response time |
| Disadvantages | More complex ejection system required | High thermal stress on launcher, risk of damage |
| Use Cases | SLBMs, some land-based missiles | Most tactical ballistic and cruise missiles |
| Safety | Lower risk of ignition failure inside launcher | Higher risk due to engine ignition in confined space |
Understanding Cold Launch and Hot Launch
Cold launch and hot launch are two distinct rocket deployment methods, with cold launch involving the ejection of a missile or rocket from a launch tube using compressed gas before ignition, minimizing heat and launch platform stress. Hot launch ignites the rocket engine while still in the tube, providing immediate thrust but requiring robust structural support to handle intense heat and pressure. Understanding these methods enhances your knowledge of aerospace engineering and launch system design.
Key Differences Between Cold and Hot Launch
Cold launch involves ejecting a missile or spacecraft before igniting its engine, minimizing damage to the launch platform and allowing safer launches from confined spaces. In contrast, hot launch ignites the engine while the vehicle remains on the platform, providing immediate thrust but requiring more robust infrastructure to withstand heat and exhaust. Your choice between cold and hot launch methods depends on mission requirements, platform limitations, and safety considerations.
Advantages of Cold Launch Strategies
Cold launch strategies reduce initial system stress by gradually bringing components online, enhancing overall reliability and longevity. This approach minimizes the risk of thermal shock and mechanical failure, leading to lower maintenance costs and fewer unscheduled downtimes. Cold launches also allow for thorough diagnostics and calibration before full operation, improving performance accuracy and safety in mission-critical applications.
Advantages of Hot Launch Tactics
Hot launch tactics offer faster deployment by igniting the rocket engine while still on the launch pad, enabling immediate liftoff and reducing total mission time. This method enhances reliability through continuous engine operation, minimizing potential issues associated with engine ignition in mid-air during a cold launch. Your mission benefits from increased control and efficiency, improving success rates for orbital insertions.
Challenges in Cold Launch Implementation
Cold launch implementation faces significant challenges including the complexity of initiating rocket ignition outside the launch tube, requiring precise timing and robust ignition systems to ensure successful engine start in mid-air. Thermal and mechanical stresses during ejection impose stringent design constraints on both the launch vehicle and missile, demanding advanced materials and engineering solutions. Furthermore, achieving stable flight trajectory immediately after ejection is critical, as any deviation can compromise mission success or payload delivery accuracy.
Risks Associated With Hot Launches
Hot launches carry increased risks of catastrophic failure due to ignition occurring while the rocket is still on the launch pad, which can result in explosions and severe damage to infrastructure. The immediate activation of engines subjects the vehicle to intense thermal and mechanical stresses before clearance, raising the likelihood of malfunction. You must carefully evaluate these hazards when planning a hot launch to ensure safety and mission success.
When to Choose a Cold Launch Approach
Choose a cold launch approach when your product requires extensive initial user onboarding or education, ensuring users fully understand its value before widespread release. This method suits complex software updates, major feature introductions, or markets where competition demands a polished first impression. Your team benefits from controlled feedback and minimized risk by rolling out gradually without public exposure.
When a Hot Launch is Most Effective
A hot launch is most effective when rapid deployment and immediate operational capability are crucial, such as in missile defense systems or time-sensitive satellite insertions. This method allows the rocket to ignite its engines while still on the launch pad or shortly after liftoff, minimizing the risk of engine failure during critical ignition phases. Hot launches are preferred in scenarios demanding quick response and high reliability under urgent conditions.
Case Studies: Cold vs Hot Launch Successes
Cold launch strategies demonstrated success in the aerospace sector with SpaceX's Falcon 9, showcasing smooth initial ignition without extensive pre-launch engine firing. Hot launch proved effective in missile systems, such as the Russian S-400, where immediate full-thrust engine ignition ensured rapid response and reliability. These case studies highlight cold launch's advantage in reducing thermal stress versus hot launch's strength in rapid deployment scenarios.
Cold Launch vs Hot Launch: Which Suits Your Product?
Cold launch involves releasing a product without major promotion, allowing organic growth and user feedback to shape its development, while hot launch uses extensive marketing and media blitz to create immediate buzz and high visibility. Your choice depends on factors like budget, target audience, and product readiness; cold launch suits products needing refinement and gradual adoption, whereas hot launch fits highly polished offerings seeking rapid market penetration. Evaluating your product lifecycle and user engagement goals helps determine the optimal launch strategy for maximizing impact and long-term success.
cold launch vs hot launch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com