Semi-active laser guidance offers precise targeting by homing in on reflected laser signals, making it highly effective in environments with clear line-of-sight, whereas GPS guidance provides all-weather, long-range accuracy using satellite signals for consistent navigation. Your choice depends on mission requirements, with semi-active laser best for dynamic, close-range targeting and GPS guiding for broader, autonomous operations.
Table of Comparison
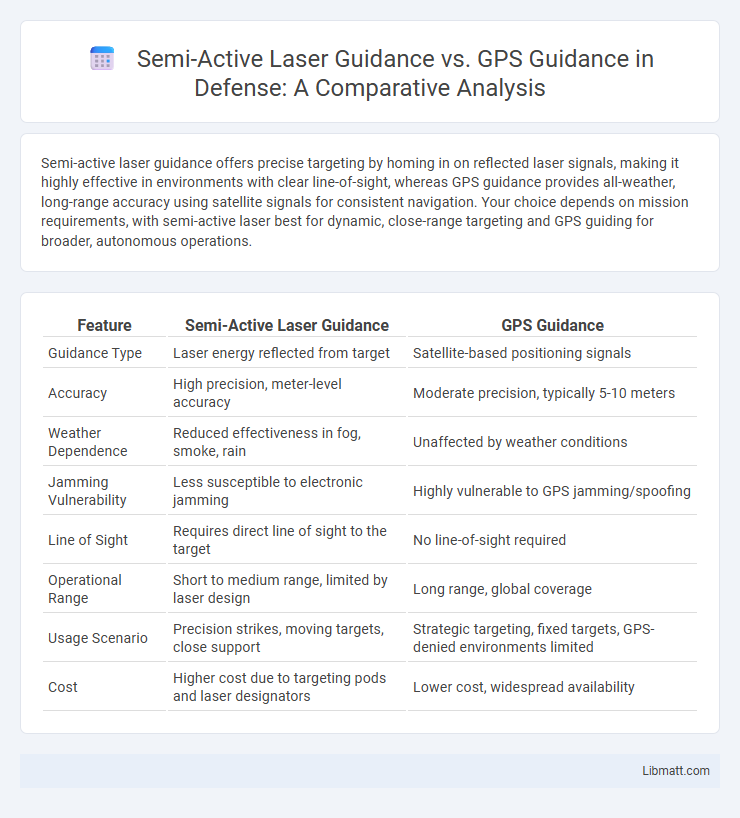
| Feature | Semi-Active Laser Guidance | GPS Guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Guidance Type | Laser energy reflected from target | Satellite-based positioning signals |
| Accuracy | High precision, meter-level accuracy | Moderate precision, typically 5-10 meters |
| Weather Dependence | Reduced effectiveness in fog, smoke, rain | Unaffected by weather conditions |
| Jamming Vulnerability | Less susceptible to electronic jamming | Highly vulnerable to GPS jamming/spoofing |
| Line of Sight | Requires direct line of sight to the target | No line-of-sight required |
| Operational Range | Short to medium range, limited by laser design | Long range, global coverage |
| Usage Scenario | Precision strikes, moving targets, close support | Strategic targeting, fixed targets, GPS-denied environments limited |
| Cost | Higher cost due to targeting pods and laser designators | Lower cost, widespread availability |
Introduction to Precision-Guided Munitions
Semi-active laser guidance relies on a laser designator to illuminate the target, allowing the munition to home in on reflected laser energy with high accuracy, especially in dynamic combat environments. GPS guidance uses satellite signals to deliver pinpoint targeting data, ensuring reliability over long distances and in adverse weather conditions where laser guidance might be obstructed. Your choice between these systems depends on operational needs, such as target visibility, electronic countermeasure resilience, and desired strike precision.
Overview of Semi-Active Laser Guidance
Semi-active laser guidance relies on a laser designator to illuminate the target, allowing the missile or bomb to home in on the reflected laser energy for precise targeting. This method offers high accuracy in dynamic combat environments by enabling real-time target updates and minimizing collateral damage. Your choice between semi-active laser guidance and GPS guidance depends on mission requirements, with laser guidance excelling in rapidly changing or obscured target scenarios.
Fundamentals of GPS Guidance Technology
GPS guidance technology operates by using a constellation of satellites that transmit precise signals to a receiver on the guided munition, enabling accurate real-time position and velocity calculation. This system relies on trilateration, where the receiver analyzes the time delays from multiple satellite signals to determine its exact location on Earth. Unlike semi-active laser guidance, which depends on reflected laser energy from a target, GPS guidance functions independently of weather conditions and line-of-sight visibility, offering reliable targeting in diverse environments.
Accuracy Comparison: Laser vs GPS Guidance
Semi-active laser guidance offers superior accuracy compared to GPS guidance by homing in on reflected laser signals with precision often within a few meters. GPS guidance, while reliable for broad targeting, can experience errors caused by signal jamming, atmospheric conditions, or satellite availability, leading to reduced accuracy that typically ranges from 5 to 15 meters. For missions requiring pinpoint targeting and minimal deviation, your choice of semi-active laser guidance ensures enhanced precision over GPS-based systems.
Operational Range and Limitations
Semi-active laser guidance operates effectively within a limited operational range, typically up to 10 kilometers, relying on continuous laser illumination from an external source, which restricts its use in adverse weather and requires line-of-sight visibility. GPS guidance offers a substantially broader operational range, often exceeding 100 kilometers, providing all-weather, day-and-night targeting capabilities without the need for external illumination. However, GPS systems can be susceptible to jamming, signal loss, and reduced accuracy in urban or heavily forested environments.
Environmental and Weather Considerations
Semi-active laser guidance relies on laser designators to illuminate targets, making it highly effective in clear weather but susceptible to reduced accuracy during fog, rain, or dust conditions that scatter or absorb laser signals. GPS guidance offers consistent targeting performance regardless of weather, as satellite signals penetrate clouds and precipitation; however, it can be vulnerable to jamming and signal obstruction in dense urban or mountainous environments. Choosing between these systems depends on the operational environment, with semi-active laser guidance favored in line-of-sight, clear conditions, and GPS guidance preferred for all-weather, beyond-visual-range engagements.
Cost Analysis: Development and Deployment
Semi-active laser guidance systems generally incur higher development costs due to the need for sophisticated laser designators and targeting mechanisms, while GPS guidance benefits from widespread availability and lower hardware expenses. Deployment costs for semi-active laser guidance include continuous tracking and maintenance of laser designators on the field, which can increase operational complexity and expenses compared to GPS systems that require minimal active management once coordinates are programmed. Your choice between these guidance methods should consider both initial investment and ongoing operational costs, as GPS solutions typically offer more cost-effective scalability and reduced logistical burdens.
Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures
Semi-active laser guidance systems are vulnerable to atmospheric conditions such as fog, smoke, or dust, which can obstruct the laser designation, while GPS guidance is susceptible to jamming, spoofing, and signal loss due to satellite dependency. Countermeasures for semi-active laser guidance include deploying multiple laser designators, employing advanced filtering technologies, and maintaining line-of-sight clearance to enhance targeting reliability. For GPS guidance, implementing anti-jamming technology, encrypted signals, and integrating inertial navigation systems provide robust protection against electronic interference and signal deception, ensuring your targeting accuracy is maintained.
Use Cases and Mission Suitability
Semi-active laser guidance excels in dynamic, short-range scenarios requiring high precision, such as close air support and urban combat, where targets are laser-designated by ground forces or aircraft. GPS guidance offers reliable, all-weather accuracy for long-range, strategic strikes and navigation in environments where laser designation is impractical or unavailable. Your choice depends on mission parameters, with laser guidance preferred for pinpoint targeting and GPS for broader operational flexibility.
Future Trends in Munition Guidance Systems
Semi-active laser guidance offers high precision by homing in on reflected laser signals, making it effective in dynamic target environments, while GPS guidance provides reliable all-weather, long-range targeting with global coverage. Future trends indicate integration of semi-active laser and GPS guidance systems to enhance accuracy, flexibility, and resilience against electronic warfare threats. Your munition systems will increasingly utilize hybrid guidance technologies, combining real-time targeting updates and autonomous navigation to improve mission success rates.
semi-active laser guidance vs GPS guidance Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com