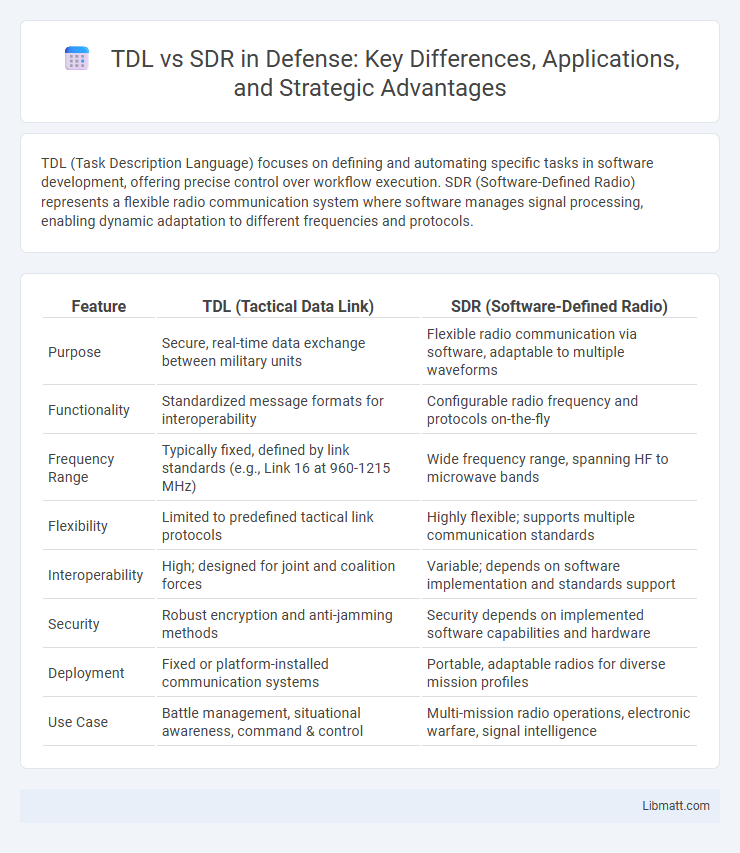
TDL (Task Description Language) focuses on defining and automating specific tasks in software development, offering precise control over workflow execution. SDR (Software-Defined Radio) represents a flexible radio communication system where software manages signal processing, enabling dynamic adaptation to different frequencies and protocols.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | TDL (Tactical Data Link) | SDR (Software-Defined Radio) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Secure, real-time data exchange between military units | Flexible radio communication via software, adaptable to multiple waveforms |
| Functionality | Standardized message formats for interoperability | Configurable radio frequency and protocols on-the-fly |
| Frequency Range | Typically fixed, defined by link standards (e.g., Link 16 at 960-1215 MHz) | Wide frequency range, spanning HF to microwave bands |
| Flexibility | Limited to predefined tactical link protocols | Highly flexible; supports multiple communication standards |
| Interoperability | High; designed for joint and coalition forces | Variable; depends on software implementation and standards support |
| Security | Robust encryption and anti-jamming methods | Security depends on implemented software capabilities and hardware |
| Deployment | Fixed or platform-installed communication systems | Portable, adaptable radios for diverse mission profiles |
| Use Case | Battle management, situational awareness, command & control | Multi-mission radio operations, electronic warfare, signal intelligence |
Introduction to TDL and SDR
TDL (Transmission Distance Limit) and SDR (Software-Defined Radio) represent two distinct concepts in telecommunications. TDL refers to the maximum distance a signal can travel in a communication system without significant degradation, impacting network design and performance optimization. SDR is a flexible radio communication technology where components traditionally implemented in hardware are instead executed by software, enabling adaptability across multiple protocols and frequencies for your communication needs.
What is TDL?
TDL (Time Division Loop) is a communication protocol that organizes data transmission in a sequential time-slot manner, optimizing bandwidth and reducing interference in network systems. TDL enhances signal clarity by allocating fixed time intervals for each data channel, ensuring efficient and synchronized communication. Your network performance benefits from TDL's structured approach, which supports high-speed data transfers and reliable connectivity in complex environments.
What is SDR?
SDR, or Special Drawing Rights, is an international reserve asset created by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to supplement member countries' official reserves. It is not a currency but represents a claim to freely usable currencies of IMF members, enhancing global liquidity. You can view SDR as a supplementary foreign exchange reserve that supports balance of payments stability among nations.
Key Differences Between TDL and SDR
TDL (Tunable Delay Line) adjusts signal timing by introducing precise delays, enhancing synchronization in communication systems, while SDR (Software Defined Radio) uses software to process radio signals, offering flexible modulation and demodulation. TDL primarily optimizes hardware timing for improved signal integrity, whereas SDR provides versatile, programmable radio functionality without changing hardware. Your choice depends on whether fixed, fine-tuned signal delay or adaptable, software-controlled radio processing best suits your application needs.
Advantages of TDL
TDL offers significant advantages over SDR by providing enhanced spectral efficiency and better handling of multipath propagation, which improves overall signal reliability and quality. Its time-division approach allows for multiple users to share the same frequency band without interference, leading to higher network capacity and reduced latency. TDL systems also consume less power compared to SDR, making them ideal for energy-sensitive applications and long-term deployments.
Benefits of SDR
Sales Development Representatives (SDRs) enable targeted lead qualification by engaging prospects early in the sales funnel, increasing conversion rates and reducing sales cycle length. SDRs specialize in personalized outreach and relationship building, which enhances customer experience and improves pipeline quality. Their focused role allows Account Executives to concentrate on closing deals, driving higher revenue efficiency and better overall sales performance.
Use Cases for TDL
Tactical Data Links (TDL) are primarily used in military communications to enable real-time data exchange between command and control centers, aircraft, ships, and ground forces, enhancing situational awareness and coordinated responses. TDL supports complex operations such as missile tracking, target designation, and joint force interoperability, making it essential for modern defense strategies. Its secure, high-speed data transmission capabilities facilitate effective command and control in dynamic combat environments.
Use Cases for SDR
Software-Defined Radio (SDR) offers unparalleled flexibility by enabling users to program and reconfigure radio functions digitally, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid adaptation to varying signal environments. You can implement SDR in diverse use cases such as cognitive radio, spectrum monitoring, military communications, and wireless protocol development, where dynamic spectrum access and multi-band operation are essential. Practical deployment includes real-time signal analysis, remote sensing, and IoT device interoperability, leveraging software to optimize performance across multiple communication standards.
TDL vs SDR: Which to Choose?
When deciding between Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) and Software-Defined Radio (SDR), consider that TDM offers reliable, fixed-channel communication suitable for legacy systems, while SDR provides flexible, programmable signal processing ideal for modern, adaptive applications. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize stability and simplicity or versatility and the ability to update features via software. SDR's capability to support multiple protocols on a single device makes it the preferred option for evolving wireless communication needs.
Future Trends in TDL and SDR
Future trends in Time Delay Line (TDL) technology emphasize increased integration with digital signal processing to enhance precision and reduce latency in wireless communications. Software Defined Radio (SDR) continues to evolve with advancements in machine learning algorithms, enabling adaptive, real-time spectrum management and improved signal recognition. Your ability to implement these innovations will drive more flexible, efficient, and intelligent radio systems in next-generation networks.
TDL vs SDR Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com