Tiltrotor aircraft combine the vertical lift capability of helicopters with the speed and range of fixed-wing planes, allowing you to transition seamlessly between hovering and fast forward flight. Coaxial rotors, featuring two counter-rotating blades stacked on a single axis, provide enhanced stability and lift efficiency, especially in hover, without the need for a tail rotor.
Table of Comparison
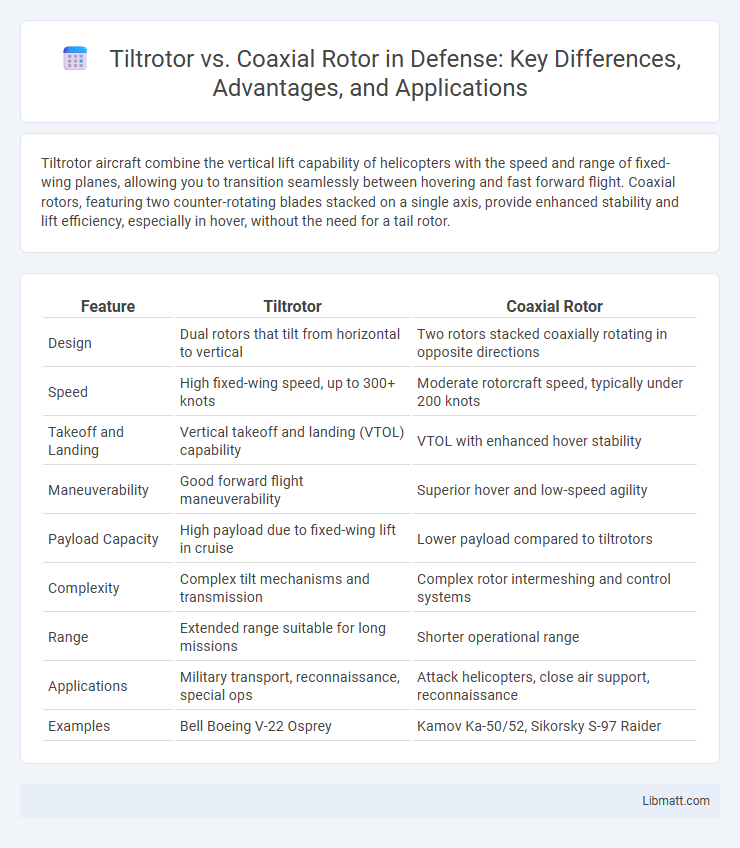
| Feature | Tiltrotor | Coaxial Rotor |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Dual rotors that tilt from horizontal to vertical | Two rotors stacked coaxially rotating in opposite directions |
| Speed | High fixed-wing speed, up to 300+ knots | Moderate rotorcraft speed, typically under 200 knots |
| Takeoff and Landing | Vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) capability | VTOL with enhanced hover stability |
| Maneuverability | Good forward flight maneuverability | Superior hover and low-speed agility |
| Payload Capacity | High payload due to fixed-wing lift in cruise | Lower payload compared to tiltrotors |
| Complexity | Complex tilt mechanisms and transmission | Complex rotor intermeshing and control systems |
| Range | Extended range suitable for long missions | Shorter operational range |
| Applications | Military transport, reconnaissance, special ops | Attack helicopters, close air support, reconnaissance |
| Examples | Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey | Kamov Ka-50/52, Sikorsky S-97 Raider |
Introduction to Tiltrotor and Coaxial Rotor Technologies
Tiltrotor technology combines the vertical lift capability of a helicopter with the speed and range of a fixed-wing aircraft by using rotors that tilt between vertical and horizontal positions. Coaxial rotor systems feature two counter-rotating rotors mounted on the same axis, eliminating the need for a tail rotor and improving lift efficiency and maneuverability. Both technologies enhance vertical flight performance but cater to different operational requirements and aerodynamic principles.
Design Overview: Tiltrotor vs Coaxial Rotor
Tiltrotor aircraft combine the vertical lift capability of helicopters with the speed and range of fixed-wing airplanes by rotating their large rotors from a vertical to a horizontal position during flight, enabling efficient transition between hovering and forward flight. Coaxial rotor systems utilize two counter-rotating rotors mounted on the same axis, which eliminates the need for a tail rotor and improves maneuverability, lift efficiency, and compactness in helicopter design. The tiltrotor design offers high-speed cross-country performance and versatility, whereas the coaxial rotor emphasizes enhanced lift capacity and stability in confined or urban environments.
Aerodynamic Efficiency Comparison
Tiltrotor aircraft achieve higher aerodynamic efficiency by combining vertical takeoff capabilities with fixed-wing cruise performance, enabling faster speeds and longer ranges due to reduced drag in forward flight. Coaxial rotors offer enhanced lift and stability through counter-rotating blades but typically face increased aerodynamic interference, resulting in higher drag and lower cruise efficiency. Your choice depends on prioritizing speed and efficiency in forward flight (tiltrotor) or superior hover performance with compact design (coaxial rotor).
Speed and Performance Capabilities
Tiltrotor aircraft achieve higher speeds and longer ranges by combining vertical takeoff capabilities with efficient fixed-wing flight, reaching speeds around 250-300 knots. Coaxial rotor helicopters excel in maneuverability and stability with their counter-rotating rotors, but generally have lower maximum speeds, typically under 200 knots due to rotor blade aerodynamics. Performance limitations of coaxial rotors include increased mechanical complexity and aerodynamic drag at high speeds compared to tiltrotor designs optimized for fast cruise.
Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL) Capabilities
Tiltrotor aircraft combine the vertical lift benefits of helicopters with the speed and range of fixed-wing planes, enabling efficient Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL) by tilting rotors from vertical to horizontal positions. Coaxial rotor systems provide powerful lift and enhanced stability through two counter-rotating rotors stacked on a single mast, facilitating smooth VTOL operations even in confined areas. Your choice between tiltrotor and coaxial rotor platforms depends on mission needs for speed, hover efficiency, and operational flexibility in diverse VTOL scenarios.
Maneuverability and Stability Differences
Tiltrotor aircraft provide superior maneuverability by combining vertical takeoff and landing capabilities with fixed-wing flight efficiency, enabling rapid transitions between hover and forward flight modes. Coaxial rotor systems offer enhanced stability through counter-rotating rotors that cancel out torque effects, improving hover precision and reducing pilot workload in turbulent conditions. While tiltrotors excel in speed and range, coaxial rotor helicopters maintain better low-speed control and hover stability, making each design suited for distinct operational requirements.
Payload and Range Considerations
Tiltrotor aircraft offer superior range and payload capacity compared to coaxial rotor designs due to their fixed-wing flight capabilities, allowing faster speeds and longer distances. Coaxial rotors provide enhanced maneuverability and vertical lift efficiency but typically have limited payload and shorter range because of increased aerodynamic drag and mechanical complexity. When planning Your mission, selecting a tiltrotor maximizes distance and cargo capacity, while coaxial rotors excel in agility and vertical operations.
Maintenance and Operational Costs
Tiltrotor aircraft typically incur higher maintenance and operational costs due to complex mechanical systems like rotating nacelles and variable pitch propellers requiring frequent inspections and specialized parts. Coaxial rotor helicopters benefit from simpler transmission systems and fewer moving components, leading to lower maintenance demands and reduced downtime. Operational costs for tiltrotors also increase because of higher fuel consumption and limited availability of qualified maintenance personnel compared to the more conventional and widely supported coaxial rotor platforms.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Tiltrotor aircraft excel in long-range military transport and search-and-rescue missions due to their vertical takeoff combined with fixed-wing flight efficiency, primarily used by defense and emergency response sectors. Coaxial rotor helicopters dominate in urban air mobility and offshore oil platform logistics, benefiting industries requiring compact, high-lift capabilities and enhanced maneuverability in confined spaces. Your choice between tiltrotor and coaxial rotor depends on operational range, payload needs, and environmental constraints specific to aviation and aerospace markets.
Future Prospects of Tiltrotor and Coaxial Rotor Aircraft
Tiltrotor aircraft offer exceptional speed and range advantages by combining vertical takeoff capabilities with efficient forward flight, making them ideal for rapid military and commercial transport applications. Coaxial rotor designs deliver superior maneuverability and compactness, enabling enhanced performance in urban air mobility and unmanned aerial vehicle markets. Your choice between these technologies will depend on mission requirements, with ongoing advancements promising expanded operational roles and improved energy efficiency for both rotorcraft types.
tiltrotor vs coaxial rotor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com