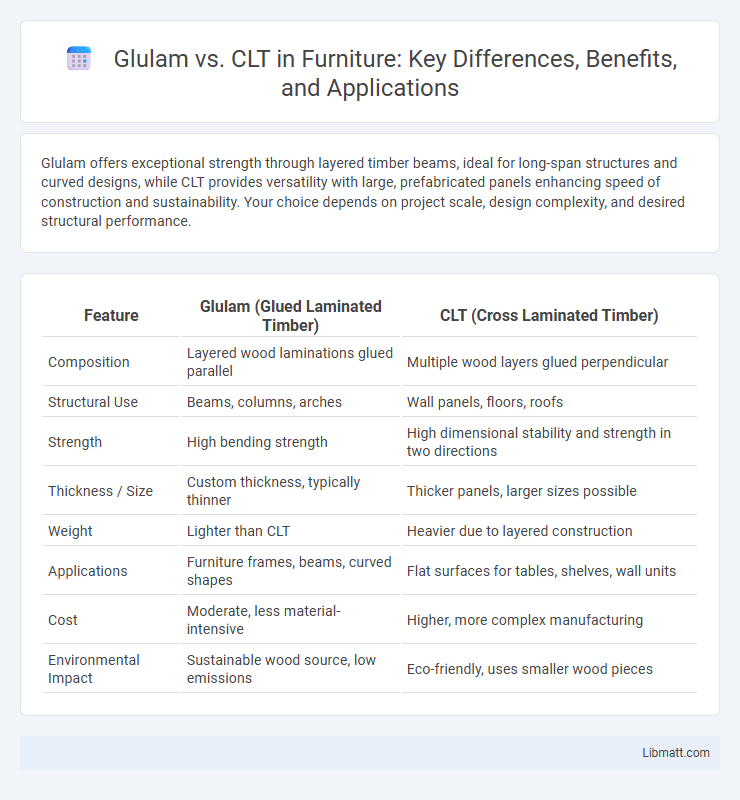
Glulam offers exceptional strength through layered timber beams, ideal for long-span structures and curved designs, while CLT provides versatility with large, prefabricated panels enhancing speed of construction and sustainability. Your choice depends on project scale, design complexity, and desired structural performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glulam (Glued Laminated Timber) | CLT (Cross Laminated Timber) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Layered wood laminations glued parallel | Multiple wood layers glued perpendicular |
| Structural Use | Beams, columns, arches | Wall panels, floors, roofs |
| Strength | High bending strength | High dimensional stability and strength in two directions |
| Thickness / Size | Custom thickness, typically thinner | Thicker panels, larger sizes possible |
| Weight | Lighter than CLT | Heavier due to layered construction |
| Applications | Furniture frames, beams, curved shapes | Flat surfaces for tables, shelves, wall units |
| Cost | Moderate, less material-intensive | Higher, more complex manufacturing |
| Environmental Impact | Sustainable wood source, low emissions | Eco-friendly, uses smaller wood pieces |
Introduction to Glulam and CLT
Glulam, short for glued laminated timber, is an engineered wood product made by bonding layers of lumber with durable adhesives, offering high strength and design flexibility for beams and columns. Cross-laminated timber (CLT) consists of multiple layers of solid-sawn lumber stacked crosswise and glued, providing exceptional structural stability and load-bearing capacity in large-scale construction. Your choice between Glulam and CLT depends on project requirements, including span length, rigidity, and architectural design preferences.
Material Composition and Manufacturing
Glulam consists of multiple layers of dimensioned lumber bonded with durable, moisture-resistant adhesives, offering high strength along the grain. Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) is made from stacked layers of solid-sawn lumber boards arranged perpendicular to each other and bonded with structural adhesives, enhancing dimensional stability and load distribution. Your choice between Glulam and CLT should consider the specific material composition and manufacturing processes that influence structural performance and application suitability.
Structural Strength and Performance
Glulam beams offer exceptional structural strength with high flexural capacity, making them ideal for long-span applications and heavy load-bearing structures. Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) provides superior dimensional stability and rigidity due to its cross-layered construction, which distributes loads evenly and resists lateral forces effectively. Choosing between Glulam and CLT depends on your project's specific performance requirements, such as span length, load conditions, and desired flexibility in design.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glulam (glued laminated timber) and CLT (cross-laminated timber) both contribute to sustainable construction by using renewable wood resources and promoting carbon sequestration. Glulam typically uses smaller wood sections bonded into strong, versatile beams, reducing wood waste and supporting sustainable forest management. CLT panels, composed of stacked and glued layers, offer high strength and thermal efficiency, enabling longer spans and less material consumption, which lowers embodied energy and environmental impact in building projects.
Cost Considerations
Glulam typically incurs higher upfront costs due to its labor-intensive manufacturing process but offers long-term savings through its strength and durability. CLT often provides more cost-effective solutions for large-scale projects with quicker installation times and reduced waste. Evaluating Your project size and budget constraints will help determine the most economical choice between Glulam and CLT.
Design Flexibility and Applications
Glulam offers exceptional design flexibility due to its ability to be manufactured in curved and customized shapes, making it ideal for architectural elements like arches and beams in complex structures. CLT provides robust dimensional stability and consistency, enabling rapid assembly in large-scale projects such as multi-story buildings and commercial facilities. Both materials support sustainable construction but are selected based on structural requirements and design complexity.
Installation and Construction Process
Glulam offers faster installation due to its lightweight panels and straightforward connection methods, making it ideal for projects with tight schedules. CLT requires precise on-site assembly and specialized equipment to manage large, prefabricated panels, which can extend construction timelines but enhances structural stability. Both materials support efficient construction, but project complexity and design specifications determine the choice between Glulam's modular ease and CLT's robust panel integration.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Glulam offers superior fire resistance with its predictable charring rate and inherent structural integrity during fire exposure, allowing it to maintain load-bearing capacity longer than many alternatives. Cross-laminated timber (CLT) provides enhanced fire safety through its thick, layered construction that chars on the surface while protecting inner layers, slowing structural degradation. Both materials meet rigorous fire safety standards, but design specifications and protective treatments play critical roles in optimizing their performance in building fire scenarios.
Durability and Maintenance
Glulam offers exceptional durability with its strong, laminated layers resistant to warping and cracking, making it ideal for long-lasting structural applications. CLT features high stability due to its cross-laminated design, providing excellent resistance to moisture and fire, requiring minimal maintenance over time. Your choice between Glulam and CLT should consider the specific environmental conditions and maintenance capabilities to ensure the longevity of your timber structure.
Choosing Between Glulam and CLT
Choosing between Glulam and CLT depends on project scale and structural requirements; Glulam offers superior strength for long spans and curved designs, while CLT excels in prefabrication and quick assembly for large panelized walls and floors. Environmental impact is a key factor, as both use sustainably sourced wood but CLT often results in lower embodied energy due to factory precision and panel optimization. Cost considerations vary with Glulam typically higher for intricate designs, whereas CLT provides cost efficiency in modular construction and reduced onsite labor.
Glulam vs CLT Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com