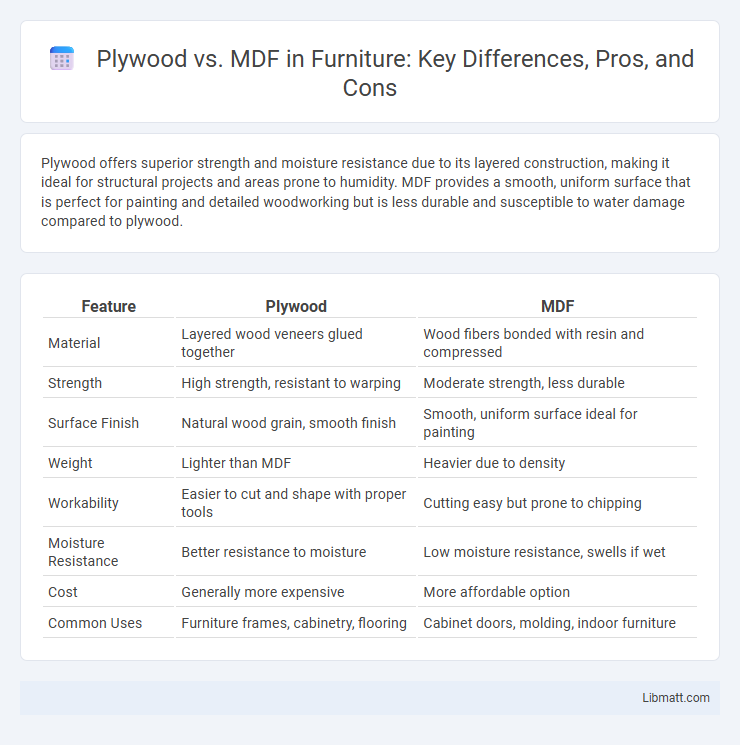
Plywood offers superior strength and moisture resistance due to its layered construction, making it ideal for structural projects and areas prone to humidity. MDF provides a smooth, uniform surface that is perfect for painting and detailed woodworking but is less durable and susceptible to water damage compared to plywood.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plywood | MDF |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Layered wood veneers glued together | Wood fibers bonded with resin and compressed |
| Strength | High strength, resistant to warping | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Surface Finish | Natural wood grain, smooth finish | Smooth, uniform surface ideal for painting |
| Weight | Lighter than MDF | Heavier due to density |
| Workability | Easier to cut and shape with proper tools | Cutting easy but prone to chipping |
| Moisture Resistance | Better resistance to moisture | Low moisture resistance, swells if wet |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More affordable option |
| Common Uses | Furniture frames, cabinetry, flooring | Cabinet doors, molding, indoor furniture |
Introduction to Plywood and MDF
Plywood is a versatile engineered wood product made from thin layers of wood veneer glued together with adjacent layers having their wood grain rotated up to 90 degrees, enhancing strength and durability. MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) is composed of wood fibers combined with resin and compressed under high pressure to create a smooth, uniform panel ideal for detailed painting and machining. Both materials serve specific purposes in furniture making, cabinetry, and construction, with plywood favored for structural applications and MDF preferred for fine finishes.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Plywood consists of multiple layers of thin wood veneers glued together with alternating grain directions, providing enhanced strength and resistance to warping. MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) is made from wood fibers combined with resin and compressed under high pressure and heat, resulting in a smooth, uniform surface ideal for detailed machining. The manufacturing process of plywood involves peeling logs into veneers, while MDF production relies on breaking down wood fibers and binding them into dense panels.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Plywood offers superior strength and durability compared to MDF due to its layered construction of thin wood veneers glued crosswise, which enhances resistance to bending and warping. MDF, composed of wood fibers and resin, is denser and smoother but lacks plywood's structural integrity, making it more susceptible to damage from moisture and heavy loads. For applications requiring load-bearing capacity and long-term durability, plywood is the preferred material over MDF.
Moisture Resistance and Suitability
Plywood offers superior moisture resistance compared to MDF due to its cross-laminated layers of wood veneer, making it ideal for areas exposed to humidity or water. MDF, composed of fine wood fibers bonded with resin, absorbs moisture more easily and can swell or warp when wet, limiting its use to dry indoor environments. Your choice between plywood and MDF should consider the specific moisture conditions of your project to ensure durability and performance.
Workability and Ease of Use
Plywood offers superior workability due to its layered construction, allowing easier cutting, shaping, and fastening without splintering. MDF has a smooth, consistent surface ideal for detailed machining and painting but is more prone to sanding dust and requires pre-drilling to prevent splitting. Both materials suit different applications, with plywood favored for structural projects and MDF suited for fine finishes and intricate designs.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Plywood generally costs more than MDF due to its higher durability and structural strength, making it ideal for projects requiring load-bearing capabilities. MDF offers a more affordable option with a smooth surface perfect for painting, but it lacks moisture resistance and may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications. Budget-conscious consumers often choose MDF for interior furniture and decorative elements, while plywood is preferred for construction and cabinetry demanding longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Plywood is often considered more environmentally sustainable than MDF due to its use of thin wood veneers bonded with adhesive, which allows for efficient use of timber and can incorporate smaller, fast-growing tree species. MDF production involves a high energy process of breaking down wood fibers and uses formaldehyde-based resins, contributing to greater environmental concerns, including volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Choosing plywood with certified sustainable wood sources like FSC can further reduce ecological impact compared to MDF, which generally lacks similar certification options.
Best Uses for Plywood
Plywood excels in applications requiring strength and durability, such as furniture construction, cabinetry, and flooring due to its layered veneer structure. Its resistance to warping and moisture makes it ideal for outdoor projects, boat building, and structural uses in walls and roofs. When You need reliable support and stability, plywood outperforms MDF in situations exposed to heavy loads or fluctuating humidity.
Ideal Applications for MDF
MDF is ideal for indoor projects requiring smooth, uniform surfaces such as cabinetry, furniture, and decorative molding due to its fine texture and ease of painting. Unlike plywood, MDF excels in applications where precision cutting and detailed shaping are essential, making it perfect for cabinetry doors, shelves, and intricate woodwork. Your choice of MDF ensures a cost-effective material that resists warping and splintering in controlled environments.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Plywood and MDF
Plywood offers superior strength, moisture resistance, and durability, making it ideal for structural applications and environments prone to humidity. MDF provides a smooth, uniform surface that is excellent for detailed painting and indoor furniture due to its fine texture and affordability. Selecting between plywood and MDF depends on specific project requirements such as load-bearing needs, exposure to moisture, and finish quality.
plywood vs MDF Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com