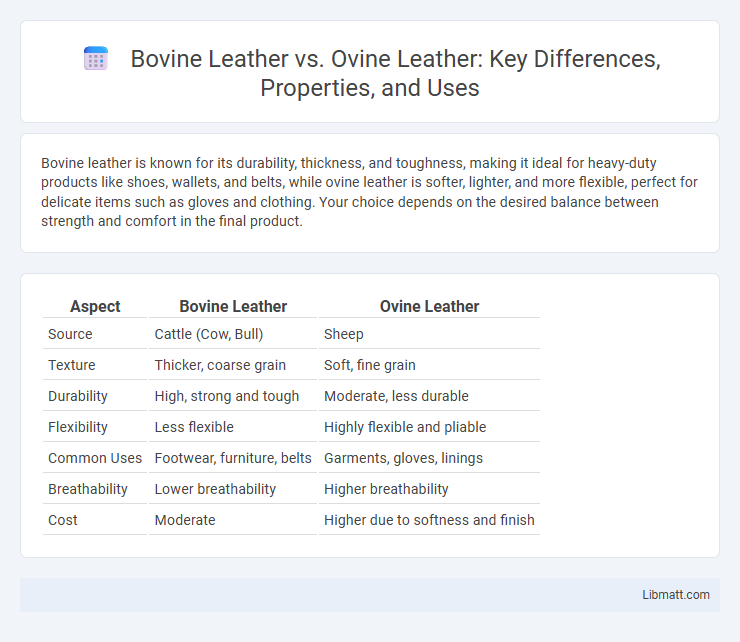
Bovine leather is known for its durability, thickness, and toughness, making it ideal for heavy-duty products like shoes, wallets, and belts, while ovine leather is softer, lighter, and more flexible, perfect for delicate items such as gloves and clothing. Your choice depends on the desired balance between strength and comfort in the final product.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bovine Leather | Ovine Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Cattle (Cow, Bull) | Sheep |
| Texture | Thicker, coarse grain | Soft, fine grain |
| Durability | High, strong and tough | Moderate, less durable |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | Highly flexible and pliable |
| Common Uses | Footwear, furniture, belts | Garments, gloves, linings |
| Breathability | Lower breathability | Higher breathability |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to softness and finish |
Introduction to Bovine and Ovine Leather
Bovine leather, derived from cattle hides, is known for its durability, thickness, and coarse texture, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications like footwear and upholstery. Ovine leather, sourced from sheep, offers a finer grain, softer feel, and greater flexibility, often preferred for garments and delicate accessories. Your choice between bovine and ovine leather depends on the desired balance between toughness and suppleness for the intended product.
Origin and Sourcing of Bovine vs Ovine Leather
Bovine leather originates from cattle, primarily sourced from cows raised globally for beef and dairy production, ensuring large-scale availability and consistent quality. Ovine leather comes from sheep, typically obtained from animals raised in regions with significant sheep farming, such as New Zealand and Australia, offering softer and thinner hides compared to bovine leather. Your choice between these leathers depends on the desired texture and durability, with bovine leather known for toughness and ovine leather valued for its lightweight and flexibility.
Physical Characteristics: Texture and Appearance
Bovine leather exhibits a coarse grain with pronounced natural markings and a thicker texture, making it highly durable and suitable for heavy-duty applications. Ovine leather, derived from sheep, is significantly softer and more supple, featuring a fine, smooth texture with a matte finish that enhances comfort and flexibility. The visual appearance of bovine leather tends to be rugged and robust, whereas ovine leather provides a more refined, delicate look ideal for luxury garments and accessories.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Bovine leather offers superior durability and strength compared to ovine leather due to its thicker grain structure and denser fiber composition, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications like footwear and upholstery. Ovine leather, derived from sheep, is softer and more supple but less resistant to wear and tear, often better suited for lighter products such as garments and accessories. When choosing leather for long-lasting use, understanding the robust nature of bovine leather will help protect your investment.
Comfort and Flexibility Factors
Bovine leather offers greater durability and thickness, which can limit flexibility but provides robust support for heavy-duty applications. Ovine leather, derived from sheep, is renowned for its superior softness and enhanced flexibility, making it more comfortable for garments and accessories requiring fine movement. The inherent grain structure and thinner profile of ovine leather contribute significantly to its lightweight feel and adaptability to body contours.
Typical Uses and Applications
Bovine leather is widely used in the production of heavy-duty goods such as shoes, belts, furniture upholstery, and automotive interiors due to its durability and thickness. Ovine leather, derived from sheep, is preferred for lightweight items like gloves, garments, and high-end fashion accessories because of its softness and flexibility. Your choice between the two leathers should depend on the durability requirements and texture preferences of your specific application.
Cost and Market Value Differences
Bovine leather typically commands a higher market value than ovine leather due to its greater durability and widespread use in premium products such as luxury shoes and high-end furniture. Ovine leather, sourced from sheep, tends to be more affordable and preferred for lightweight, flexible items like gloves and garments, influencing its lower price point. Market demand for bovine leather remains robust globally, especially in automotive and upholstery industries, which drives its cost above that of ovine leather.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Bovine leather requires regular cleaning with a damp cloth and conditioning every 3 to 6 months to prevent drying and cracking due to its thicker grain structure. Ovine leather, being softer and thinner, demands more frequent conditioning, typically every 1 to 3 months, to maintain its suppleness and avoid deterioration from moisture exposure. Both types benefit from avoiding prolonged direct sunlight and excessive water contact to extend their durability and appearance.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
Bovine leather production often has a higher environmental impact due to larger resource consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to ovine leather, which generally requires less water and land. Ethical concerns also vary, with bovine leather linked to intensive cattle farming practices, while ovine leather typically comes from sheep farms that may offer more sustainable grazing methods. Your choice between bovine and ovine leather can influence the sustainability and ethical footprint of leather goods, making it important to consider the sourcing and farming practices behind each material.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Bovine and Ovine Leather
Bovine leather offers higher durability and thickness, making it ideal for heavy-use products like footwear and furniture, while ovine leather provides softness and flexibility, perfect for garments and delicate accessories. Your choice depends on the end-use requirements, with bovine leather suited for long-lasting, rugged applications and ovine leather favored for comfort and elegance. Understanding these differences ensures you select the best leather type to match your product's performance and aesthetic needs.
Bovine leather vs ovine leather Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com