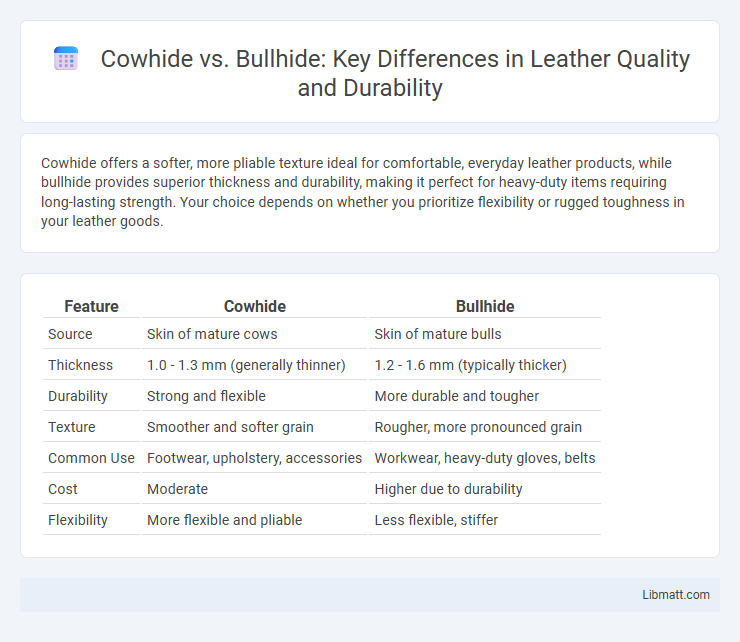
Cowhide offers a softer, more pliable texture ideal for comfortable, everyday leather products, while bullhide provides superior thickness and durability, making it perfect for heavy-duty items requiring long-lasting strength. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize flexibility or rugged toughness in your leather goods.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cowhide | Bullhide |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Skin of mature cows | Skin of mature bulls |
| Thickness | 1.0 - 1.3 mm (generally thinner) | 1.2 - 1.6 mm (typically thicker) |
| Durability | Strong and flexible | More durable and tougher |
| Texture | Smoother and softer grain | Rougher, more pronounced grain |
| Common Use | Footwear, upholstery, accessories | Workwear, heavy-duty gloves, belts |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to durability |
| Flexibility | More flexible and pliable | Less flexible, stiffer |
Introduction to Cowhide and Bullhide
Cowhide and bullhide are two popular types of leather derived from cattle, distinguished primarily by their source animals. Cowhide comes from cows, offering a softer and more flexible texture, while bullhide is obtained from male bovines, known for its exceptional thickness and durability. Choosing between cowhide and bullhide depends on your need for softness or rugged sturdiness in leather products.
Origins and Sourcing Methods
Cowhide originates primarily from domesticated cattle raised for both dairy and beef industries, sourced through sustainable ranching practices that prioritize animal welfare and environmental impact. Bullhide, on the other hand, comes specifically from bulls, often selected from mature male cattle valued for thicker, denser hides with higher durability and strength. Your choice may depend on the sourcing methods tied to animal age and breed, which directly influence the texture and longevity of the leather product.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
Cowhide is thicker and more durable with a uniform grain, ideal for heavy-duty use, while bullhide tends to be tougher and denser with a coarser texture. Cowhide generally offers more flexibility and a smoother finish, making it suitable for fine leather goods. Bullhide's sturdiness and resistance to abrasion make it preferred for rugged applications such as belts and boots.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Bullhide offers superior durability and strength compared to cowhide due to its thicker grain and tighter fiber structure, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications such as protective gear and work gloves. Cowhide, while still strong and durable, tends to be more flexible and softer, which suits general-purpose leather goods but may wear faster under extreme conditions. The higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance of bullhide result in longer-lasting performance in demanding environments.
Texture and Appearance Differences
Cowhide features a softer, more supple texture with a generally smoother surface, making it ideal for garments and accessories that require flexibility and comfort. Bullhide, in contrast, is thicker and stiffer, with a coarser grain pattern that offers enhanced durability and a rugged, natural look. Your choice between these hides depends on whether you prioritize a softer feel or a tougher, more textured appearance.
Common Applications and Uses
Cowhide is widely used for durable products like upholstery, saddles, and jackets due to its balance of toughness and flexibility, making it ideal for everyday wear and heavy-duty items. Bullhide offers greater thickness and stiffness, commonly utilized in tool belts, work gloves, and protective gear where maximum durability and impact resistance are essential. Your choice between cowhide and bullhide should depend on the specific application's need for flexibility versus rugged strength.
Comfort and Flexibility Factors
Cowhide offers greater comfort and flexibility due to its softer texture and thinner composition, making it ideal for everyday use and garments that require ease of movement. Bullhide, being thicker and stiffer, provides more durability and protection but sacrifices some comfort and flexibility. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize softness and pliability or rugged toughness in leather products.
Maintenance and Care Tips
Cowhide leather requires regular conditioning every 3 to 6 months to prevent drying and cracking, while bullhide, known for its toughness, benefits from more frequent conditioning, especially after heavy use. Both materials should be cleaned with a damp cloth and mild soap, avoiding harsh chemicals to maintain their natural texture and durability. Proper storage in a cool, dry place and protecting from prolonged exposure to direct sunlight will extend the life of both cowhide and bullhide products.
Price and Value Considerations
Bullhide typically commands a higher price due to its greater density, durability, and thickness compared to cowhide. While cowhide offers an affordable, versatile option with moderate durability, bullhide provides better long-term value for your investment because it withstands wear and tear more effectively. Your choice should consider how much you prioritize upfront cost versus lasting performance.
Which Hide is Best for Specific Needs?
Cowhide offers durability and flexibility ideal for upholstery and garments, providing a softer texture that molds well to shapes. Bullhide, known for its thicker, tougher grain, excels in heavy-duty applications like motorcycle gear and work gloves, delivering superior abrasion resistance. Choosing between cowhide and bullhide depends on specific needs: cowhide suits comfort and appearance, while bullhide prioritizes ruggedness and protection.
Cowhide vs bullhide Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com