Flat grain refers to rice kernels that remain full and plump after harvesting, indicating better quality and higher yield, while shrunken grain appears smaller and distorted due to incomplete grain filling or environmental stress. Understanding the difference helps you select rice varieties that ensure optimal cooking quality and nutritional value.
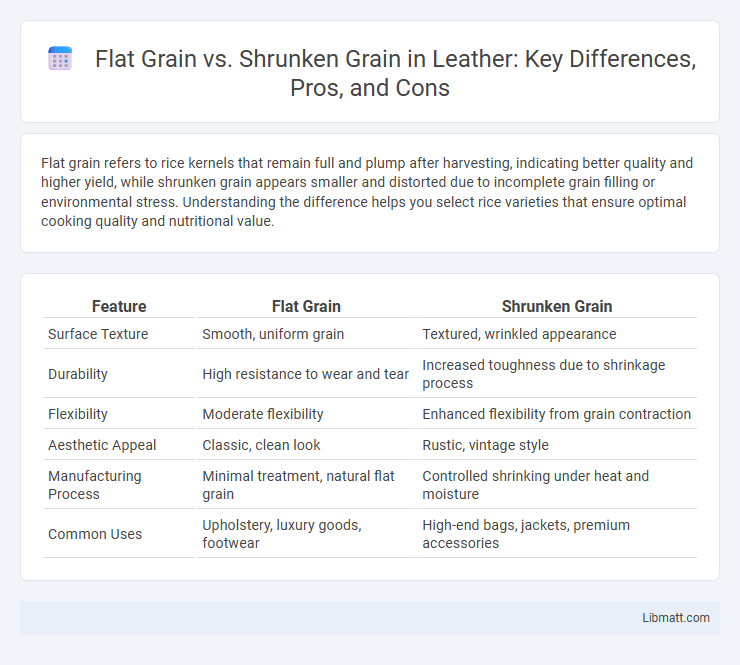
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flat Grain | Shrunken Grain |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Texture | Smooth, uniform grain | Textured, wrinkled appearance |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear | Increased toughness due to shrinkage process |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Enhanced flexibility from grain contraction |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Classic, clean look | Rustic, vintage style |
| Manufacturing Process | Minimal treatment, natural flat grain | Controlled shrinking under heat and moisture |
| Common Uses | Upholstery, luxury goods, footwear | High-end bags, jackets, premium accessories |
Understanding Flat Grain and Shrunken Grain
Flat grain refers to rice kernels that are uniform in shape and size, exhibiting a smooth, flattened appearance. Shrunken grain, by contrast, is characterized by kernels that are smaller, wrinkled, and denser due to incomplete development or exposure to environmental stress. Understanding these distinctions helps you assess grain quality, as flat grains typically indicate higher milling efficiency and better cooking properties compared to shrunken grains.
Key Differences Between Flat Grain and Shrunken Grain
Flat grain rice features elongated, slender kernels with a smooth, uniform surface, whereas shrunken grain rice has shorter, thicker kernels that appear wrinkled or collapsed due to reduced starch content. The starch composition differs significantly; flat grain typically contains higher amylose levels contributing to a firmer texture, while shrunken grain is lower in starch, resulting in a denser, chewier consistency. These variations influence cooking properties, with flat grain rice absorbing water evenly and maintaining shape, contrasting the uneven water absorption and quicker cooking time of shrunken grains.
Causes of Flat Grain in Cereals
Flat grain in cereals primarily results from environmental stress factors such as drought, extreme temperatures, and nutrient deficiencies during the grain-filling period, which disrupts normal starch accumulation and kernel development. Genetic predisposition and hormonal imbalances also contribute to the formation of flat grains by affecting cell division and elongation in the endosperm. Flat grains show reduced hectoliter weight and lower milling quality compared to well-filled grains, impacting overall crop yield and market value.
Factors Leading to Shrunken Grain Formation
Environmental stressors such as high temperatures and drought during the grain-filling stage significantly contribute to shrunken grain formation in crops. Nutrient deficiencies, particularly in nitrogen and potassium, exacerbate this condition by impairing grain development and reducing starch accumulation. Managing irrigation and soil fertility effectively helps minimize the occurrence of shrunken grains, thereby improving overall crop yield and quality.
Impact on Yield and Quality
Flat grains generally offer higher yield potential due to their larger kernel size and uniform shape, which facilitates better packing density during storage and processing. Shrunken grains often result from environmental stress or genetic factors, leading to reduced kernel weight and lower overall yield. Your crop quality can be affected by shrunken grains, as they may have altered milling properties and lower nutritional content compared to flat grains.
Effects on Milling and Processing Efficiency
Flat grains generally offer higher milling yields due to their uniform size and shape, which facilitates efficient kernel removal and reduces breakage during processing. Shrunken grains, however, often result in lower milling efficiency as their irregular shape causes uneven milling and increased starch damage. Optimizing your grain selection to prioritize flat kernels can enhance processing throughput and improve flour quality.
Nutritional Implications of Flat vs. Shrunken Grain
Flat grain varieties typically exhibit lower starch content and higher protein levels compared to shrunken grains, impacting their overall nutritional profile. Shrunken grains often contain a concentrated amount of nutrients such as essential amino acids and vitamins due to reduced endosperm size. Understanding these differences can help optimize Your dietary choices for protein intake and energy density.
Identification and Assessment Methods
Flat grain is typically identified by its smooth, even surface and uniform size, while shrunken grain appears smaller with a wrinkled or collapsed appearance due to incomplete kernel development. Assessment methods include visual inspection, grain sieving, and using image analysis technology to measure size and shape variations accurately. Your ability to distinguish between these grains impacts quality control in milling and processing industries.
Best Practices to Minimize Grain Defects
To minimize grain defects such as flat and shrunken grains, maintain optimal moisture levels during the growing and harvesting stages, ensuring proper irrigation and drying techniques. Implement precise nutrient management, particularly focusing on nitrogen and potassium, to promote uniform grain development. Regular field monitoring and adopting resistant crop varieties also reduce the risk of defects, enhancing overall grain quality.
Future Trends in Grain Quality Improvement
Future trends in grain quality improvement emphasize genetic engineering techniques to enhance resistance in flat grain varieties against pests and environmental stresses. Advances in precision breeding aim to reduce shrunken grain occurrences by optimizing starch synthesis pathways for improved kernel plumpness and nutritional content. Integrating genomic selection with AI-driven phenotyping accelerates the development of cultivars exhibiting superior yield and grain uniformity.
Flat grain vs shrunken grain Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com