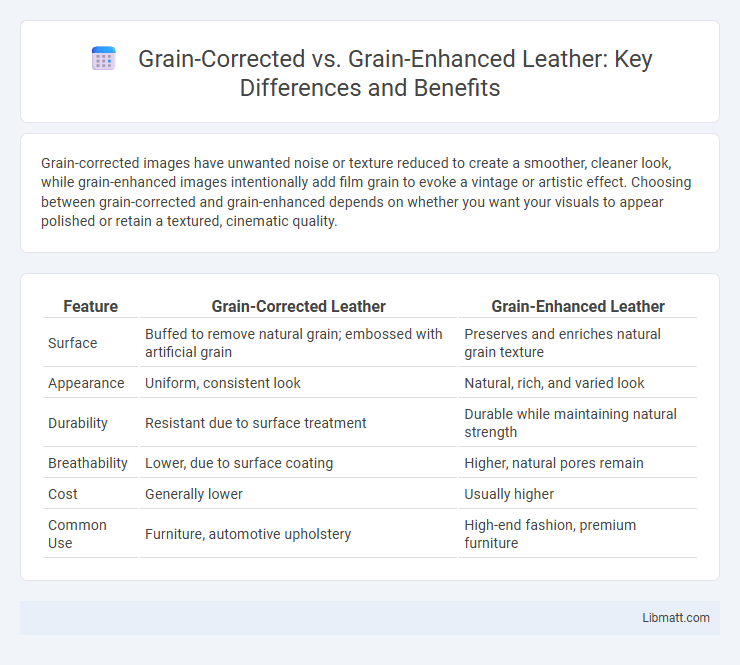
Grain-corrected images have unwanted noise or texture reduced to create a smoother, cleaner look, while grain-enhanced images intentionally add film grain to evoke a vintage or artistic effect. Choosing between grain-corrected and grain-enhanced depends on whether you want your visuals to appear polished or retain a textured, cinematic quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Grain-Corrected Leather | Grain-Enhanced Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Surface | Buffed to remove natural grain; embossed with artificial grain | Preserves and enriches natural grain texture |
| Appearance | Uniform, consistent look | Natural, rich, and varied look |
| Durability | Resistant due to surface treatment | Durable while maintaining natural strength |
| Breathability | Lower, due to surface coating | Higher, natural pores remain |
| Cost | Generally lower | Usually higher |
| Common Use | Furniture, automotive upholstery | High-end fashion, premium furniture |
Understanding Grain-Corrected and Grain-Enhanced Leather
Grain-corrected leather undergoes surface treatments such as embossing, coating, and sanding to mask imperfections, resulting in a more uniform appearance but potentially less natural texture. Grain-enhanced leather retains the original grain surface, showcasing the hide's natural markings and textures while often being treated to improve durability and aesthetic appeal. Understanding the distinctions helps consumers select leather products based on desired authenticity, durability, and visual finish.
Key Differences: Grain-Corrected vs Grain-Enhanced
Grain-corrected techniques reduce noise and improve image clarity by minimizing the appearance of film grain, often preserving fine details for a cleaner visual output. Grain-enhanced processes add or amplify grain to achieve a desired aesthetic, typically enhancing texture and depth for artistic or stylistic effects. The key difference lies in grain-corrected focusing on refinement and noise reduction, whereas grain-enhanced emphasizes augmenting grain to enhance mood and visual interest.
Production Process Comparison
Grain-corrected production involves advanced imaging techniques to identify and remove defective grains, resulting in higher purity and quality through selective processing. Grain-enhanced production focuses on augmenting grain characteristics by applying treatments such as coatings or enzymes to improve nutritional content and functional properties during processing. Both methods incorporate precise control measures but differ in objectives: grain-corrected aims to eliminate imperfections, whereas grain-enhanced targets grain modification for enhanced performance.
Texture and Visual Appearance
Grain-corrected images improve texture by smoothing out noise and irregularities, resulting in a cleaner and more polished visual appearance. Grain-enhanced images preserve or add film grain, enhancing the tactile feel and depth of the texture while maintaining an organic, authentic look. Your choice between the two depends on whether you prioritize clarity and refinement or a nostalgic, textured aesthetic.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Grain-corrected materials exhibit improved durability by eliminating microstructural defects, resulting in enhanced wear resistance under mechanical stress. Grain-enhanced materials, with refined grain sizes, increase hardness and reduce crack propagation, further boosting wear resistance in abrasive environments. Optimizing grain structure directly influences the lifespan and performance of components subjected to high friction and impact.
Common Uses and Applications
Grain-corrected materials are commonly used in construction and manufacturing industries to improve structural integrity by reducing grain boundary defects that can cause weaknesses. Grain-enhanced materials find extensive applications in aerospace and automotive sectors where increased grain size contributes to better mechanical properties such as higher tensile strength and fatigue resistance. Both treatments optimize material performance for specific applications, with grain correction focusing on durability and grain enhancement targeting strength and toughness.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Grain-corrected surfaces demand regular maintenance to preserve their smooth finish, often involving gentle cleaning agents and protective coatings to prevent damage. Grain-enhanced materials require less frequent maintenance, as their textured surfaces naturally conceal minor scratches and wear, reducing the need for constant care. Understanding your environment and usage helps determine whether grain-corrected or grain-enhanced options better fit your maintenance capabilities and expectations.
Cost Factors and Value
Grain-corrected materials typically incur higher processing costs due to the precision techniques required to reduce grain boundary defects, which enhances mechanical properties and durability. In contrast, grain-enhanced materials often involve cost-effective methods such as controlled grain growth to improve strength and toughness, offering a balanced value proposition for large-scale applications. Evaluating the cost-to-performance ratio, grain-corrected options provide superior long-term value in high-stress environments, while grain-enhanced materials serve as economical solutions for moderate performance requirements.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Grain-corrected techniques optimize resource use by reducing waste and minimizing energy consumption, significantly lowering the environmental footprint in agriculture. Grain-enhanced methods, while potentially increasing yield, often demand higher inputs such as water and fertilizers, which can contribute to soil degradation and increased greenhouse gas emissions. Prioritizing grain-corrected practices aligns with sustainable farming goals by promoting efficient nutrient cycles and preserving ecological balance.
How to Choose Between Grain-Corrected and Grain-Enhanced
Grain-corrected wood has been treated to remove natural imperfections, resulting in a smoother and more consistent surface ideal for projects requiring uniform aesthetics. Grain-enhanced wood highlights and deepens the natural grain patterns, adding texture and character to your finished piece for a more rustic or artistic appeal. Your choice between grain-corrected and grain-enhanced depends on whether you prioritize a flawless, refined look or a distinctive, textured appearance in your woodworking project.
Grain-corrected vs grain-enhanced Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com