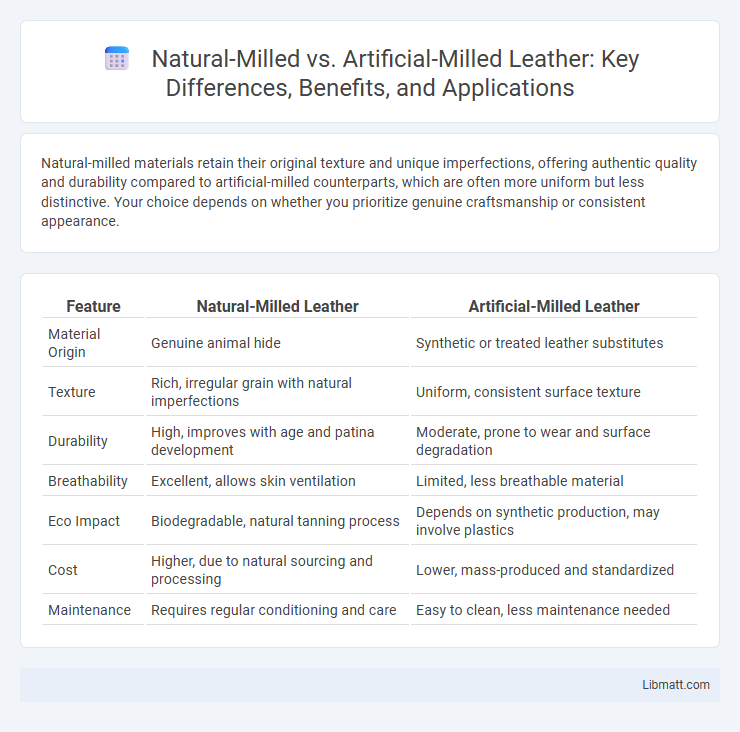
Natural-milled materials retain their original texture and unique imperfections, offering authentic quality and durability compared to artificial-milled counterparts, which are often more uniform but less distinctive. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize genuine craftsmanship or consistent appearance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Natural-Milled Leather | Artificial-Milled Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Genuine animal hide | Synthetic or treated leather substitutes |
| Texture | Rich, irregular grain with natural imperfections | Uniform, consistent surface texture |
| Durability | High, improves with age and patina development | Moderate, prone to wear and surface degradation |
| Breathability | Excellent, allows skin ventilation | Limited, less breathable material |
| Eco Impact | Biodegradable, natural tanning process | Depends on synthetic production, may involve plastics |
| Cost | Higher, due to natural sourcing and processing | Lower, mass-produced and standardized |
| Maintenance | Requires regular conditioning and care | Easy to clean, less maintenance needed |
Introduction to Milled Materials
Natural-milled materials originate from raw resources processed through traditional mechanical grinding methods, preserving most of their innate properties and mineral content. Artificial-milled materials are synthetically produced or enhanced through controlled industrial milling processes to achieve specific particle sizes and uniformity tailored for various applications. Both milling types significantly impact material texture, quality, and performance in industries such as pharmaceuticals, ceramics, and construction.
Defining Natural-Milled and Artificial-Milled
Natural-milled materials are processed using traditional methods that preserve the original texture and qualities by removing only the outermost layer without chemical alteration. Artificial-milled materials undergo mechanical and chemical treatments to achieve a uniform and refined finish, often enhancing durability and appearance. Understanding the difference between natural-milled and artificial-milled helps you select materials that best suit your needs for authenticity and performance.
Raw Material Sources
Natural-milled products are derived primarily from raw materials sourced directly from nature, such as whole grains, seeds, and minerals, ensuring minimal processing and preservation of innate nutrients. Artificial-milled items typically utilize synthetic or heavily processed raw materials, including chemically treated grains and refined substrates, which may compromise the original nutritional profile. The distinction in raw material sources significantly impacts the quality, purity, and health benefits of the final milled product.
Key Processing Methods
Natural-milled rice undergoes traditional processing methods such as sun drying, winnowing, and hand paddy threshing, preserving its bran layer and nutrients. Artificial-milled rice is processed using mechanized systems like rice hullers and polishers that remove the husk and bran layer, resulting in a smoother, longer shelf-life grain but reduced fiber content. Advanced machines enable uniform milling, enhancing appearance and cooking properties while minimizing grain breakage.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Natural-milled rice retains its bran layer, preserving higher levels of fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, which contributes to a denser texture and richer nutritional profile. Artificial-milled rice typically undergoes extensive polishing, removing significant amounts of nutrients and resulting in a smoother, less fibrous grain with altered starch composition. The chemical properties of natural-milled rice include higher lipid content and essential minerals, whereas artificial-milled rice exhibits reduced lipid levels and an increased glycemic index due to starch modification.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Natural-milled processes typically have a lower environmental impact due to minimal chemical use and reduced energy consumption, supporting better sustainability practices. Artificial-milled production often relies on synthetic chemicals and higher energy inputs, contributing to greater carbon emissions and resource depletion. Choosing natural milling aligns with eco-friendly agriculture and promotes long-term soil health and biodiversity preservation.
Performance in Industrial Applications
Natural-milled materials retain unique microstructures and impurities that can enhance wear resistance and thermal stability in industrial applications, making them ideal for tooling and heavy machinery components. Artificial-milled products offer consistent particle size distribution and purity, improving process repeatability and performance in precision manufacturing such as semiconductor or pharmaceutical industries. Selecting between natural and artificial milling depends on application-specific performance metrics, including durability, thermal resistance, and process consistency.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Natural-milled materials typically involve slower, more labor-intensive processes, leading to higher initial costs compared to artificial-milled options produced through automated systems. Your choice between natural-milled and artificial-milled products impacts long-term economic factors such as durability, maintenance expenses, and resale value. Artificial-milled materials often offer cost efficiency and consistency, but natural-milled alternatives can provide unique qualities that may justify the premium price in specialized markets.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Natural-milled products dominate the market due to growing consumer demand for eco-friendly and minimally processed goods, reflecting a significant shift towards sustainability. Artificial-milled items still maintain a strong presence, favored for their uniform texture and longer shelf life, appealing to convenience-oriented buyers. Understanding these trends helps you make informed choices that align with your values and product expectations.
Future Outlook and Innovations
Natural-milled materials are expected to benefit from advancements in eco-friendly processing technologies that reduce energy consumption and enhance purity levels. Artificial-milled products will increasingly integrate AI-driven precision milling to achieve consistent particle size distribution and improved mechanical properties. Innovations in hybrid milling techniques combining natural and artificial methods are projected to create materials with superior performance and sustainability profiles.
Natural-milled vs artificial-milled Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com