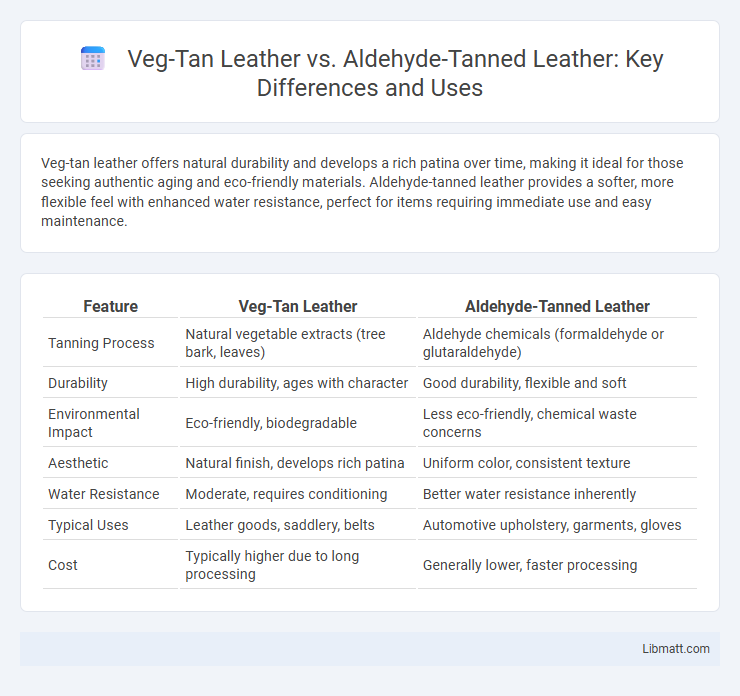
Veg-tan leather offers natural durability and develops a rich patina over time, making it ideal for those seeking authentic aging and eco-friendly materials. Aldehyde-tanned leather provides a softer, more flexible feel with enhanced water resistance, perfect for items requiring immediate use and easy maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Veg-Tan Leather | Aldehyde-Tanned Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Tanning Process | Natural vegetable extracts (tree bark, leaves) | Aldehyde chemicals (formaldehyde or glutaraldehyde) |
| Durability | High durability, ages with character | Good durability, flexible and soft |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Less eco-friendly, chemical waste concerns |
| Aesthetic | Natural finish, develops rich patina | Uniform color, consistent texture |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, requires conditioning | Better water resistance inherently |
| Typical Uses | Leather goods, saddlery, belts | Automotive upholstery, garments, gloves |
| Cost | Typically higher due to long processing | Generally lower, faster processing |
Introduction to Leather Tanning Methods
Vegetable-tanned leather uses natural tannins from tree bark, leaves, and fruits, creating a durable and eco-friendly material often favored for craftsmanship and longevity. Aldehyde-tanned leather employs synthetic aldehyde compounds, such as glutaraldehyde, producing a softer, more water-resistant finish commonly used in automotive and garment industries. Both methods transform raw hides into versatile leather but differ significantly in chemical processing, environmental impact, and end-use properties.
What Is Veg-Tan Leather?
Veg-tan leather is crafted using natural tannins extracted from tree bark, leaves, and other plant materials, offering a durable and eco-friendly option known for developing a rich patina over time. Unlike aldehyde-tanned leather, which uses synthetic chemicals for quicker processing, veg-tan leather undergoes a slower, more traditional tanning process that enhances its strength and natural characteristics. Your choice of veg-tan leather ensures a product with unique aging properties, making it ideal for high-quality artisanal goods.
What Is Aldehyde-Tanned Leather?
Aldehyde-tanned leather is processed using aldehyde tanning agents, such as glutaraldehyde or oxazolidine, which create a flexible, water-resistant material often used in automotive and garment industries. This type of leather offers a softer feel and better wet strength compared to traditional vegetable-tanned leather, which relies on natural tannins from tree bark and plants. Understanding the difference between veg-tan leather and aldehyde-tanned leather helps you choose the right type of leather based on durability, texture, and environmental impact.
Tanning Processes Compared
Vegetable-tanned leather undergoes a natural tanning process using tannins extracted from tree bark and plant materials, which results in a firm, durable, and eco-friendly product that develops a rich patina over time. Aldehyde-tanned leather uses synthetic aldehydes, such as glutaraldehyde or oxazolidine, to create a softer, more pliable leather often preferred for automotive and garment applications due to its resistance to heat and water. The fundamental difference lies in the organic, slow-curing process of vegetable tanning versus the chemically-driven, faster curing method of aldehyde tanning, affecting the leather's texture, environmental impact, and end-use performance.
Environmental Impact: Veg-Tan vs Aldehyde-Tanned
Vegetable-tanned leather uses natural tannins from tree bark and plant extracts, resulting in a biodegradable product with minimal chemical pollutants, making it environmentally preferable. Aldehyde-tanned leather relies on synthetic aldehydes, which involve hazardous chemicals and generate toxic waste that can harm ecosystems. The eco-friendliness of vegetable tanning stems from its renewable resources and lower impact on water and soil quality compared to aldehyde-tanning processes.
Durability and Aging Characteristics
Veg-tan leather exhibits excellent durability with a firm yet flexible texture that improves in character over time, developing a rich patina and softening with use. Aldehyde-tanned leather offers superior water resistance and color retention but tends to be less breathable and may show less pronounced aging characteristics compared to vegetable-tanned leather. Over time, veg-tan leather becomes more durable and aesthetically appealing, while aldehyde-tanned leather maintains its initial appearance with minimal change.
Aesthetic Differences and Coloring
Veg-tan leather showcases a rich, natural patina that deepens in color over time due to its organic tanning process, offering warm earth tones and visible grain patterns. Aldehyde-tanned leather allows for more consistent and vibrant color finishes, as the tanning agents fix dyes more uniformly, resulting in a smoother surface and brighter hues. While veg-tan leather develops unique variations from exposure and use, aldehyde-tanned leather maintains a more stable, uniform appearance with less pronounced aging effects.
Common Uses and Applications
Veg-tan leather is commonly used in high-quality leather goods such as wallets, belts, saddles, and artisanal crafts due to its durability and ability to develop a rich patina over time. Aldehyde-tanned leather, often referred to as wet-white leather, is popular in automotive upholstery, gloves, and fashion accessories because of its softness, lightweight nature, and water-resistant properties. Both types serve distinct market needs, with veg-tan favored for traditional, long-lasting products and aldehyde-tanned chosen for products requiring pliability and quick production.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Veg-tan leather requires minimal maintenance, benefiting from natural oils and occasional conditioning to prevent drying and cracking, making it ideal for items exposed to regular wear. Aldehyde-tanned leather, often softer and more water-resistant, demands less frequent conditioning but should be kept away from excessive moisture and heat to maintain its flexibility and prevent surface damage. Both types benefit from gentle cleaning with a damp cloth and avoiding harsh chemicals to preserve their quality and longevity.
Choosing the Right Leather for Your Needs
Veg-tan leather offers natural durability and develops a rich patina over time, ideal for products requiring longevity and an organic aesthetic. Aldehyde-tanned leather provides a softer, more flexible texture with resistance to water and stains, making it suitable for garments and accessories with frequent use. Selecting the right leather depends on desired durability, appearance, and maintenance preferences tailored to specific applications.
Veg-tan leather vs aldehyde-tanned leather Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com