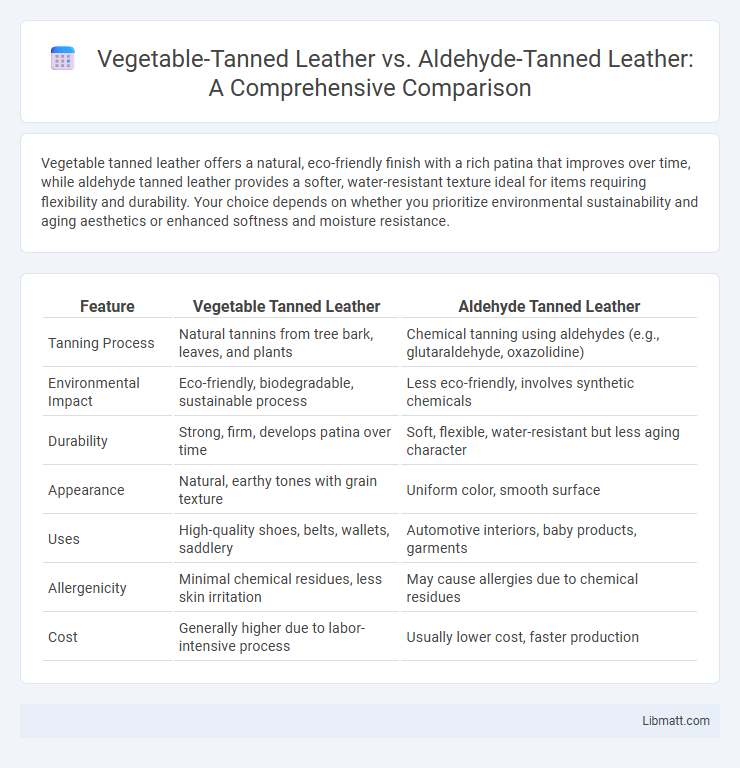
Vegetable tanned leather offers a natural, eco-friendly finish with a rich patina that improves over time, while aldehyde tanned leather provides a softer, water-resistant texture ideal for items requiring flexibility and durability. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize environmental sustainability and aging aesthetics or enhanced softness and moisture resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable Tanned Leather | Aldehyde Tanned Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Tanning Process | Natural tannins from tree bark, leaves, and plants | Chemical tanning using aldehydes (e.g., glutaraldehyde, oxazolidine) |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, sustainable process | Less eco-friendly, involves synthetic chemicals |
| Durability | Strong, firm, develops patina over time | Soft, flexible, water-resistant but less aging character |
| Appearance | Natural, earthy tones with grain texture | Uniform color, smooth surface |
| Uses | High-quality shoes, belts, wallets, saddlery | Automotive interiors, baby products, garments |
| Allergenicity | Minimal chemical residues, less skin irritation | May cause allergies due to chemical residues |
| Cost | Generally higher due to labor-intensive process | Usually lower cost, faster production |
Introduction to Leather Tanning Methods
Vegetable tanned leather relies on natural tannins extracted from tree bark and plants, resulting in a durable, eco-friendly material that develops a rich patina over time. Aldehyde tanned leather uses synthetic aldehyde chemicals, such as glutaraldehyde or oxazolidine, to produce soft, water-resistant leather with improved flexibility and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional chrome tanning. Understanding these tanning methods highlights differences in sustainability, final texture, and leather longevity crucial for footwear, accessories, and upholstery applications.
What is Vegetable Tanned Leather?
Vegetable tanned leather is crafted using natural tannins extracted from tree bark, leaves, and other plant materials, resulting in a durable, biodegradable material that develops a rich patina over time. This eco-friendly tanning process takes several weeks and produces leather known for its firmness, natural fragrance, and ability to mold to the user's shape. Unlike aldehyde tanned leather, which is chemically processed for softness and water resistance, vegetable tanned leather retains its organic characteristics and ages gracefully, making it a preferred choice for high-quality leather goods.
What is Aldehyde Tanned Leather?
Aldehyde tanned leather is treated using aldehyde chemicals, primarily glutaraldehyde or oxazolidine, which provide a soft, water-resistant, and hypoallergenic material suitable for products like baby shoes and automotive upholstery. This tanning process avoids chromium compounds, making aldehyde tanned leather a popular choice for consumers seeking environmentally friendlier and less toxic leather options. Your preference might depend on aldehyde tanned leather's quick tanning time and its ability to maintain flexibility without compromising durability.
Key Differences Between Vegetable and Aldehyde Tanning
Vegetable tanned leather uses natural tannins from tree bark and plants, resulting in a firmer, more environmentally friendly material with rich, earthy tones that develop a patina over time. Aldehyde tanned leather relies on synthetic chemicals such as glutaraldehyde, producing a softer, more flexible leather that is hypoallergenic and often used in automotive and baby products. Key differences include durability, environmental impact, tanning time--with vegetable tanning taking weeks versus aldehyde tanning's rapid process--and the leather's ability to mold and age naturally.
Environmental Impact of Tanning Processes
Vegetable tanned leather uses natural tannins from tree bark, leaves, and fruits, making it biodegradable and less harmful to ecosystems compared to aldehyde tanned leather, which relies on synthetic chemicals that can release pollutants into water sources. The slow processing time in vegetable tanning reduces energy consumption, while aldehyde tanning often requires energy-intensive steps and produces waste that challenges wastewater treatment. Choosing vegetable tanned leather supports sustainable fashion and minimizes the ecological footprint of leather production.
Durability and Aging: How Each Leather Performs
Vegetable tanned leather develops a rich patina over time, enhancing its appearance and durability through natural oxidation and exposure to elements. Aldehyde tanned leather remains softer and more flexible without significant color change but is less resistant to wear and tends to show cracks or peeling with prolonged use. Durability in vegetable tanned leather surpasses aldehyde tanned leather, making it ideal for products requiring long-lasting aging qualities.
Aesthetic Qualities and Coloration
Vegetable tanned leather offers rich, natural hues that deepen and develop a unique patina over time, enhancing its aesthetic appeal with warm, earthy tones. Aldehyde tanned leather typically features a more uniform, lighter coloration with a smooth, supple surface, maintaining consistent appearance and resistance to grime and stains. Your choice depends on whether you prefer the evolving character of vegetable tanned leather or the stable, refined look of aldehyde tanned leather.
Common Uses and Applications
Vegetable tanned leather is commonly used for high-quality leather goods such as belts, wallets, and saddlery due to its durability and natural aging properties. Aldehyde tanned leather, often found in automotive upholstery, gloves, and baby shoes, offers a softer, more flexible feel with enhanced water resistance. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize traditional craftsmanship or modern comfort and ease of maintenance.
Health and Safety Considerations
Vegetable tanned leather uses natural tannins from plant sources, minimizing exposure to harmful chemicals and making it a safer choice for your skin and indoor environments. Aldehyde tanned leather involves synthetic chemicals like glutaraldehyde, which can release irritants or allergens during manufacturing and use, posing potential health risks. Prioritizing vegetable tanned leather supports better indoor air quality and reduces the likelihood of chemical sensitivities.
Which Leather Type Is Right for You?
Vegetable tanned leather offers a natural, durable, and eco-friendly option that develops a rich patina over time, making it ideal for those who appreciate craftsmanship and longevity. Aldehyde tanned leather provides a softer, more water-resistant finish with quicker production times, suitable for users seeking comfort and efficiency in maintenance. Your choice depends on whether you value tradition and durability or prefer softness and ease of care in your leather goods.
Vegetable tanned leather vs aldehyde tanned leather Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com