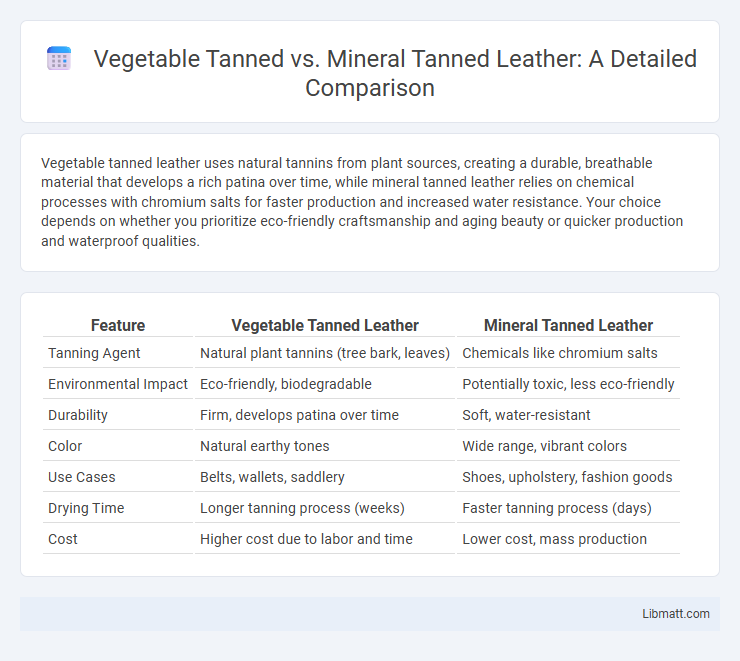
Vegetable tanned leather uses natural tannins from plant sources, creating a durable, breathable material that develops a rich patina over time, while mineral tanned leather relies on chemical processes with chromium salts for faster production and increased water resistance. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize eco-friendly craftsmanship and aging beauty or quicker production and waterproof qualities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable Tanned Leather | Mineral Tanned Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Tanning Agent | Natural plant tannins (tree bark, leaves) | Chemicals like chromium salts |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Potentially toxic, less eco-friendly |
| Durability | Firm, develops patina over time | Soft, water-resistant |
| Color | Natural earthy tones | Wide range, vibrant colors |
| Use Cases | Belts, wallets, saddlery | Shoes, upholstery, fashion goods |
| Drying Time | Longer tanning process (weeks) | Faster tanning process (days) |
| Cost | Higher cost due to labor and time | Lower cost, mass production |
Introduction to Leather Tanning
Vegetable-tanned leather uses natural tannins from tree bark and plants, resulting in durable, eco-friendly leather with a distinct aroma and rich patina over time. Mineral tanning, often employing chromium salts, produces softer, more water-resistant leather with faster processing times but poses environmental challenges due to chemical waste. Understanding the differences in tanning methods is crucial for choosing leather based on durability, environmental impact, and intended use.
What is Vegetable Tanned Leather?
Vegetable tanned leather is a natural leather tanning method that uses tannins and polyphenols extracted from plant materials such as tree bark, leaves, and fruits. This eco-friendly process takes weeks to complete, resulting in durable, stiff leather that develops a rich patina over time. Compared to mineral tanned leather, vegetable tanned leather is more breathable, biodegradable, and preferred for high-quality leather goods like belts, wallets, and saddles.
What is Mineral Tanned Leather?
Mineral tanned leather, also known as chrome-tanned leather, is produced using chromium salts, primarily chromium sulfate, during the tanning process. This method results in leather that is more flexible, water-resistant, and faster to produce compared to vegetable tanned leather. Mineral tanned leather is widely used in footwear, upholstery, and fashion accessories due to its durability and softer feel.
Tanning Processes: Key Differences
Vegetable tanning uses natural tannins from tree bark and plants, creating a slow, eco-friendly process that enhances leather durability and develops a rich patina over time. Mineral tanning, primarily chrome tanning, involves chromium salts, producing leather faster with higher water resistance and uniform color but less environmental sustainability. These fundamental differences in chemical composition and processing impact leather quality, longevity, and ecological footprint.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Vegetable tanned leather involves natural tannins from plant sources like tree bark, resulting in a more biodegradable and less chemically intensive process compared to mineral tanned leather, which primarily uses chromium salts. The chromium-based tanning process generates hazardous waste and can contaminate soil and water, posing significant environmental and health risks. Vegetable tanning, though slower, offers a more sustainable option with reduced pollution and easier waste management, making it preferable for environmentally conscious production.
Durability and Longevity
Vegetable tanned leather is known for its exceptional durability and ability to develop a rich patina over time, enhancing longevity with proper care. Mineral tanned leather, often chrome-tanned, offers greater immediate flexibility and water resistance but may wear out faster under heavy use. Choosing between the two depends on the desired balance between natural aging and robust, long-lasting performance.
Aesthetic and Aging Qualities
Vegetable tanned leather develops a rich patina over time, enhancing its natural texture and color for a unique, classic aesthetic. Mineral tanned leather retains a more consistent appearance, offering greater resistance to water and stains but less visual change as it ages. Your choice depends on whether you prefer evolving character or stable, durable beauty.
Common Uses and Applications
Vegetable tanned leather is prized for its durability and natural finish, making it ideal for crafting high-quality belts, wallets, saddles, and shoes that benefit from a firm yet flexible texture. Mineral tanned leather, often chrome-tanned, offers enhanced softness and water resistance, commonly used in fashion accessories, upholstery, and automotive interiors where pliability and quick production are essential. Both tanning methods influence the leather's suitability for specific applications, with vegetable tanning preferred in artisanal and traditional leather goods, while mineral tanning dominates mass-produced and water-resistant products.
Cost and Availability
Vegetable-tanned leather typically costs more due to its lengthy, eco-friendly tanning process and is often available in limited quantities from specialized artisans. Mineral-tanned leather, particularly chrome-tanned, is less expensive and widely accessible because of its faster, industrial tanning methods. Your choice depends on budget constraints and the availability of desired leather types in your region.
Choosing the Right Leather for Your Needs
Vegetable tanned leather offers durability and develops a rich patina over time, making it ideal for artisanal goods and eco-friendly products, while mineral tanned leather provides water resistance and a softer feel, suited for fashion accessories and upholstery. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize natural aging and environmental sustainability or quick processing and enhanced flexibility. Understanding the distinct tanning methods helps you select leather that aligns perfectly with your project's functional and aesthetic requirements.
Vegetable tanned vs mineral tanned Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com