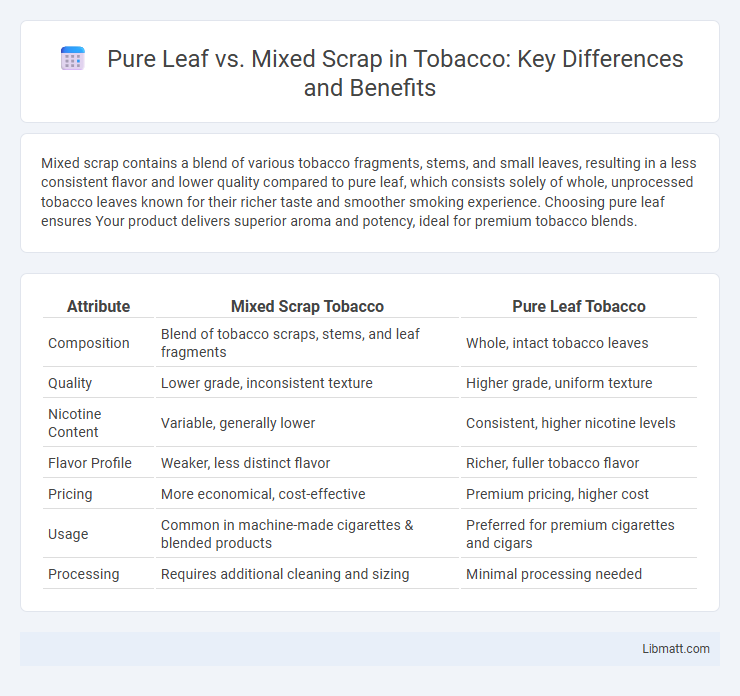
Mixed scrap contains a blend of various tobacco fragments, stems, and small leaves, resulting in a less consistent flavor and lower quality compared to pure leaf, which consists solely of whole, unprocessed tobacco leaves known for their richer taste and smoother smoking experience. Choosing pure leaf ensures Your product delivers superior aroma and potency, ideal for premium tobacco blends.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Mixed Scrap Tobacco | Pure Leaf Tobacco |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Blend of tobacco scraps, stems, and leaf fragments | Whole, intact tobacco leaves |
| Quality | Lower grade, inconsistent texture | Higher grade, uniform texture |
| Nicotine Content | Variable, generally lower | Consistent, higher nicotine levels |
| Flavor Profile | Weaker, less distinct flavor | Richer, fuller tobacco flavor |
| Pricing | More economical, cost-effective | Premium pricing, higher cost |
| Usage | Common in machine-made cigarettes & blended products | Preferred for premium cigarettes and cigars |
| Processing | Requires additional cleaning and sizing | Minimal processing needed |
Introduction to Mixed Scrap and Pure Leaf
Mixed scrap consists of a heterogeneous combination of metal pieces, often containing various alloys and impurities, making it less uniform than pure leaf. Pure leaf refers to thin, flat sheets of metal, typically gold or silver, known for their high purity and consistent quality used in decoration or manufacturing. The key distinction lies in the composition and application, where pure leaf is prized for its aesthetic and material integrity, while mixed scrap is primarily valued for recycling and metal recovery.
Defining Mixed Scrap: Composition and Characteristics
Mixed scrap consists of a combination of various recyclable materials including mixed metals, plastics, paper, and electronics, whereas pure leaf refers specifically to uniform, uncontaminated recyclable paper leaves. The composition of mixed scrap varies widely and often requires extensive sorting and processing to separate valuable materials, while pure leaf maintains consistent quality and ease of recycling due to its homogeneity. Characteristics of mixed scrap include higher contamination levels, more diverse material types, and increased challenges in recycling efficiency compared to the clean, single-material nature of pure leaf.
What is Pure Leaf? Key Features
Pure Leaf refers to high-quality tobacco leaves that are free from stems, dust, and mixed plant materials commonly found in mixed scrap. Key features of Pure Leaf include uniformity in leaf size, color, and texture, ensuring consistent flavor and combustion in tobacco products. You can expect Pure Leaf to enhance product quality by providing a cleaner, smoother smoking experience compared to mixed scrap.
Sources of Mixed Scrap and Pure Leaf
Mixed scrap primarily originates from manufacturing offcuts, post-industrial waste, and production residues, while pure leaf scrap comes exclusively from tobacco leaves that do not meet quality standards for direct use. Sources of mixed scrap include factory trimmings and rejected processed materials, whereas pure leaf scrap is sourced from unprocessed, lower-grade or damaged tobacco leaves. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize your use of raw materials based on quality requirements and processing needs.
Processing Differences: Mixed Scrap vs Pure Leaf
Mixed scrap requires extensive sorting and cleaning processes to separate various materials and contaminants, while pure leaf undergoes minimal processing due to its uniform composition. The inconsistent quality of mixed scrap demands advanced techniques such as shredding and chemical treatment to achieve material purity, in contrast to pure leaf, which can proceed directly to compression or packaging stages. Consequently, processing mixed scrap is more time-consuming and costly compared to the streamlined handling of pure leaf.
Quality and Purity Comparison
Pure leaf scrap offers superior quality and higher purity compared to mixed scrap, as it contains fewer contaminants and non-ferrous materials. Mixed scrap may include various metals and impurities, reducing its overall value and complicating recycling processes. To ensure optimal material recovery and maximum resale value, you should prioritize sourcing pure leaf scrap whenever possible.
Market Value and Demand Trends
Mixed scrap typically commands a lower market value compared to pure leaf due to impurities and inconsistent composition, affecting its quality perception. Demand trends show a rising preference for pure leaf in industries such as tobacco and tea manufacturing, driven by the need for higher product purity and standardized flavor profiles. To maximize your returns, targeting markets that prioritize quality and purity in raw materials is essential.
Environmental Impact Analysis
Mixed scrap generates higher environmental pollution due to contamination and lower recycling efficiency compared to pure leaf scrap, which offers a more sustainable recycling process with minimal waste and reduced energy consumption. Pure leaf scrap enables better resource recovery and decreases greenhouse gas emissions by ensuring higher purity in metal recycling streams. Lifecycle assessments indicate that prioritizing pure leaf scrap significantly lowers landfill usage and mitigates toxic runoff risks in comparison to mixed scrap disposal.
Application Suitability: Mixed Scrap vs Pure Leaf
Mixed scrap is ideal for applications requiring lower quality metal inputs, such as construction materials and automotive parts, due to its heterogeneous composition and variable purity levels. Pure leaf scrap, characterized by its high purity and uniformity, is well-suited for specialized manufacturing processes like aerospace components and electronic devices, where material consistency is critical. Selecting between mixed scrap and pure leaf depends on application-specific quality requirements, cost considerations, and downstream processing capabilities.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Choosing the right material depends on your project's specific requirements and budget constraints. Mixed scrap offers cost-effective versatility with varying quality, while pure leaf provides consistent, high-grade material ideal for precision applications. Evaluating your priorities for quality, performance, and cost will help determine whether mixed scrap or pure leaf best suits your needs.
Mixed scrap vs pure leaf Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com