Spun cut produces finer, more uniform fiber strands ideal for soft and stretchy fabrics, enhancing Your garment's texture and comfort. Cube cut creates thicker, more distinct fibers that provide greater durability and structure, perfect for robust textile applications.
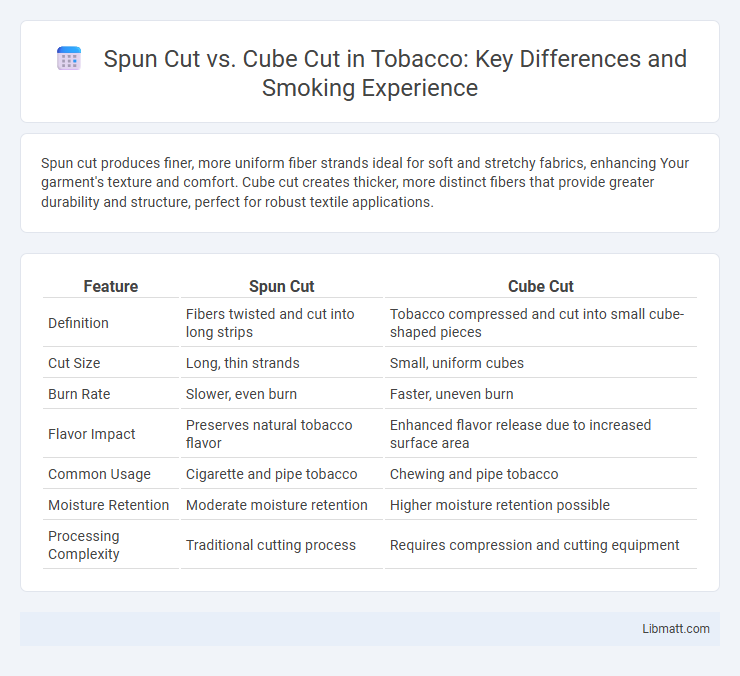
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spun Cut | Cube Cut |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fibers twisted and cut into long strips | Tobacco compressed and cut into small cube-shaped pieces |
| Cut Size | Long, thin strands | Small, uniform cubes |
| Burn Rate | Slower, even burn | Faster, uneven burn |
| Flavor Impact | Preserves natural tobacco flavor | Enhanced flavor release due to increased surface area |
| Common Usage | Cigarette and pipe tobacco | Chewing and pipe tobacco |
| Moisture Retention | Moderate moisture retention | Higher moisture retention possible |
| Processing Complexity | Traditional cutting process | Requires compression and cutting equipment |
Overview of Spun Cut and Cube Cut
Spun cut involves creating fabric loops by spinning yarns tightly, resulting in a textured surface ideal for durability and insulation. Cube cut refers to precise, three-dimensional block-shaped fabric cuts that enhance structural design and reduce material waste. Understanding the differences between spun cut and cube cut helps optimize your textile manufacturing process for specific applications and aesthetic preferences.
Defining Spun Cut
Spun cut defines a manufacturing process where material is rotated at high speeds while a cutting tool shapes it into precise cylindrical or symmetrical forms, often used for metal or plastic components. This technique contrasts with cube cut, which involves cutting material into distinct cube-shaped pieces through straightforward, linear slicing methods. Understanding the differences in cutting approaches helps optimize your production for both dimensional accuracy and surface finish, tailored to specific project needs.
Defining Cube Cut
Cube cut is a precise cutting technique that shapes materials into uniform, cube-like pieces, enhancing even cooking and presentation. Unlike spun cut, which involves slicing in a circular motion, cube cut emphasizes consistent, straight edges and equal dimensions. Your dishes benefit from this method by achieving uniform texture and appearance, perfect for recipes needing exact portion sizes.
Key Differences Between Spun Cut and Cube Cut
Spun cut involves slicing a product into thin, circular discs by rotating it against a blade, commonly used for spiralized vegetables and garnishes, while cube cut produces uniform, small square pieces through precise, linear slicing ideal for dicing ingredients evenly. The spun cut emphasizes continuous rotation and thin, round slices, whereas the cube cut focuses on stable positioning and consistent cubic dimensions tailored for soups, salads, or stir-fries. Each technique impacts texture and presentation, with spun cutting enhancing visual appeal and cube cutting ensuring uniform cooking and portion control.
Advantages of Spun Cut
Spun cut offers enhanced precision by rotating the material during cutting, resulting in smoother edges and reduced burr formation compared to cube cut methods. This technique minimizes material waste and improves surface finish, which is essential for high-quality manufacturing processes. Your production efficiency can significantly increase by adopting spun cut technology, especially when dealing with complex geometries and delicate materials.
Advantages of Cube Cut
Cube cut offers precise, uniform pieces that enhance cooking consistency and presentation quality, making it ideal for professional chefs and home cooks alike. Its even shape allows for faster, more predictable cooking times and better texture retention in dishes compared to spun cut. You gain greater control over portion size and aesthetic appeal, elevating your culinary results.
Applications of Spun Cut
Spun cut is widely used in agricultural and industrial machinery for processing fibrous materials due to its efficient fiber separation and cleaning capabilities. This cutting method enhances material uniformity in textile production and improves quality in paper manufacturing by producing finely shredded fibers. You can rely on spun cut technology to optimize raw material preparation for enhanced downstream processing performance.
Applications of Cube Cut
Cube cut blades excel in precision cutting applications, often used in industries such as woodworking, metalworking, and manufacturing for producing clean, accurate cuts on various materials. Their geometry allows for efficient chip removal and reduced heat buildup, enhancing durability and performance in tasks like fine woodworking, PCB fabrication, and mold making. Your projects benefit from the cube cut's ability to maintain tight tolerances and sharp edges, ensuring superior finish quality and reduced material wastage.
Choosing Between Spun Cut and Cube Cut
Choosing between a spun cut and a cube cut depends on your specific application needs and material properties. Spun cuts, characterized by their smooth, rounded edges, are ideal for reducing stress concentrations and improving fatigue resistance in rotating components. Cube cuts, with their sharper, well-defined edges, offer precise geometric control and are preferred for applications requiring exact dimensional tolerance and ease of assembly.
Conclusion: Which Cut is Best?
Spun cut offers smoother edges and reduced material waste, ideal for intricate shapes and precision work. Cube cut provides faster production speeds and consistent, clean cuts, making it suitable for high-volume manufacturing. Choosing the best cut depends on whether you prioritize fine detail and efficiency (spun cut) or speed and uniformity (cube cut).
Spun cut vs Cube cut Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com