Drone delivery offers rapid, aerial transportation ideal for small packages and hard-to-reach locations, while autonomous vehicle delivery excels in handling larger payloads over longer distances with established road infrastructure. You can optimize your logistics by choosing drone delivery for speed and flexibility or autonomous vehicles for capacity and range.
Table of Comparison
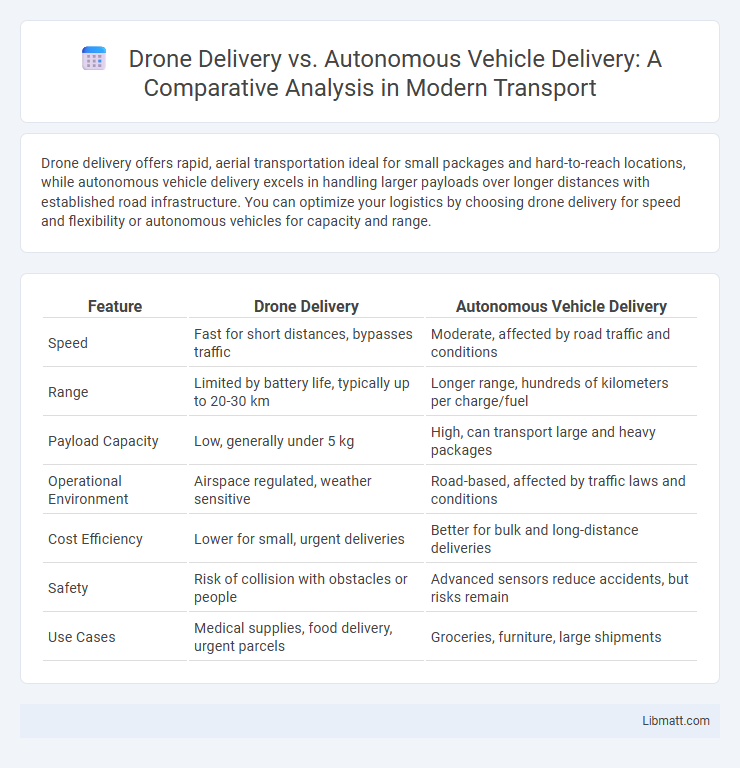
| Feature | Drone Delivery | Autonomous Vehicle Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast for short distances, bypasses traffic | Moderate, affected by road traffic and conditions |
| Range | Limited by battery life, typically up to 20-30 km | Longer range, hundreds of kilometers per charge/fuel |
| Payload Capacity | Low, generally under 5 kg | High, can transport large and heavy packages |
| Operational Environment | Airspace regulated, weather sensitive | Road-based, affected by traffic laws and conditions |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower for small, urgent deliveries | Better for bulk and long-distance deliveries |
| Safety | Risk of collision with obstacles or people | Advanced sensors reduce accidents, but risks remain |
| Use Cases | Medical supplies, food delivery, urgent parcels | Groceries, furniture, large shipments |
Introduction to Autonomous Delivery Technologies
Autonomous delivery technologies encompass drone delivery and autonomous vehicle delivery, both revolutionizing last-mile logistics with distinct advantages. Drone delivery offers rapid, airborne transportation ideal for lightweight parcels and hard-to-reach locations, leveraging GPS navigation and real-time obstacle detection. Autonomous vehicle delivery utilizes self-driving cars or vans to transport larger payloads on conventional roads, supported by advanced sensors, AI, and mapping software for efficient, contactless delivery.
How Drone Delivery Works
Drone delivery operates through remotely piloted or autonomous aerial vehicles that navigate pre-programmed flight paths using GPS and advanced sensors for obstacle avoidance. These drones are equipped to carry small to medium-sized packages, ensuring rapid and efficient delivery by bypassing ground traffic congestion. Your parcels are typically loaded into secure compartments within the drone, which then follows optimized routes to reach your destination safely.
Autonomous Vehicle Delivery Explained
Autonomous vehicle delivery uses self-driving cars equipped with advanced sensors and AI to navigate streets and transport goods efficiently. These vehicles optimize last-mile delivery by reducing human error and operating continuously, enhancing speed and reliability. Compared to drone delivery, autonomous vehicles handle larger payloads and perform well in diverse weather conditions and urban environments.
Speed & Efficiency Comparison
Drone delivery achieves faster transit times by bypassing road traffic and using direct aerial routes, reducing delivery speed by up to 50% compared to ground vehicles. Autonomous vehicles benefit from higher payload capacity and longer operational ranges, optimizing efficiency for bulk or heavier shipments over extended distances. While drones excel in rapid, small-package delivery within urban areas, autonomous vehicles provide consistent speed and efficiency for large-scale, diverse delivery demands.
Range & Accessibility Differences
Drone delivery offers limited range typically up to 15-20 miles due to battery life constraints, making it ideal for quick, short-distance shipments in urban and suburban areas. Autonomous vehicle delivery extends range significantly, capable of covering 100 miles or more on a single charge or fuel tank, providing broader accessibility in diverse terrains and longer routes. When choosing the best option for your delivery needs, consider drone delivery for fast, last-mile drops and autonomous vehicles for extensive, bulk transportation.
Payload Capacity Constraints
Drone delivery faces significant payload capacity constraints, typically limited to small packages weighing under 5 kilograms, which restricts its applicability for larger or heavier items. Autonomous vehicle delivery offers a substantially higher payload capacity, supporting bulkier and heavier goods with payloads ranging from hundreds to thousands of kilograms. These capacity differences critically influence the choice of delivery technology based on package size, weight, and delivery route requirements.
Regulatory & Legal Challenges
Drone delivery faces strict regulatory challenges including airspace restrictions, privacy concerns, and compliance with FAA Part 107 rules, limiting operational altitude and flight zones. Autonomous vehicle delivery must navigate complex traffic laws, vehicle certification standards, and liability issues in accidents, requiring coordination with state and federal transportation authorities. Both technologies require ongoing legal frameworks to address safety, data security, and public acceptance for widespread deployment.
Environmental Impact Analysis
Drone delivery significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to traditional autonomous vehicle delivery by utilizing electric power and requiring less energy per mile traveled. Your choice of drone delivery can minimize urban congestion and lower noise pollution due to quieter flight paths and smaller energy footprints. Data from multiple environmental studies indicate drones emit up to 70% less greenhouse gases than ground vehicles, making them a more sustainable option for last-mile logistics.
Safety & Security Considerations
Drone delivery offers enhanced safety by minimizing human interaction and reducing traffic congestion risks, yet it faces challenges like airspace regulation compliance and vulnerability to hacking. Autonomous vehicle delivery benefits from established road infrastructure and advanced obstacle detection systems, but it must address cybersecurity threats and complex urban pedestrian environments. Your choice should weigh these safety and security factors relative to the delivery environment and regulatory landscape.
Future Outlook: Integrating Drones and Autonomous Vehicles
The future outlook for delivery services combines the strengths of drone delivery and autonomous vehicle delivery to maximize efficiency and reach. Drones offer rapid, aerial transport for lightweight packages in urban and hard-to-access areas, while autonomous vehicles provide robust ground solutions for larger loads and longer distances. Your logistics strategy can benefit from integrating both technologies to create a seamless, scalable delivery network that adapts to diverse customer needs and evolving infrastructure.
drone delivery vs autonomous vehicle delivery Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com