Swapping body and container elements in web design alters the structural layout, impacting how content is visually organized and styled. You can enhance user experience by strategically placing key content within the container, allowing the body element to serve as a flexible background or wrapper.
Table of Comparison
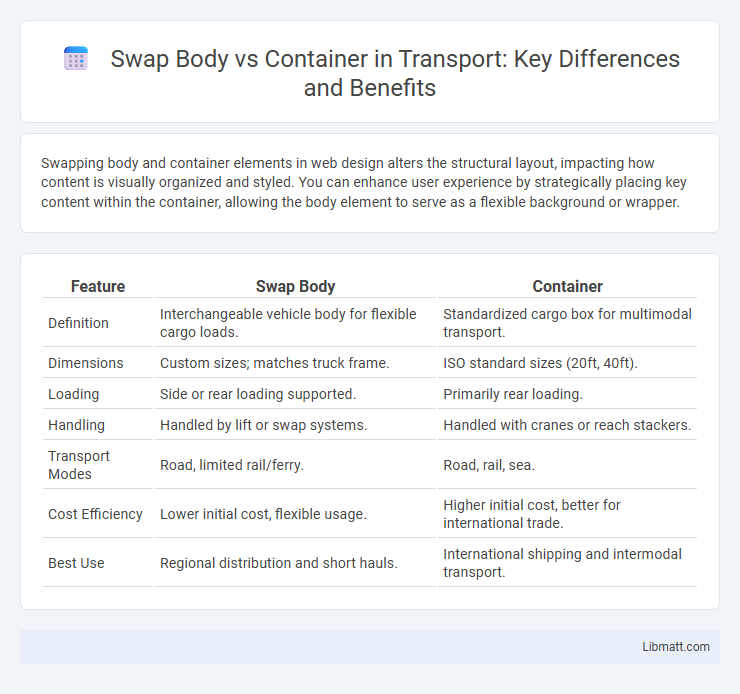
| Feature | Swap Body | Container |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interchangeable vehicle body for flexible cargo loads. | Standardized cargo box for multimodal transport. |
| Dimensions | Custom sizes; matches truck frame. | ISO standard sizes (20ft, 40ft). |
| Loading | Side or rear loading supported. | Primarily rear loading. |
| Handling | Handled by lift or swap systems. | Handled with cranes or reach stackers. |
| Transport Modes | Road, limited rail/ferry. | Road, rail, sea. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial cost, flexible usage. | Higher initial cost, better for international trade. |
| Best Use | Regional distribution and short hauls. | International shipping and intermodal transport. |
Introduction to Swap Body and Container
Swap bodies are specialized freight units designed for easy loading and unloading by trucks without the need for cranes, enhancing flexibility in European intermodal transport. Containers, standardized globally under ISO regulations, facilitate seamless shipping across sea, rail, and road with strong structural integrity and uniform dimensions. Understanding the differences in handling, compatibility, and usage can help optimize Your logistics strategy based on transport modes and infrastructure availability.
Key Differences Between Swap Body and Container
Swap bodies are primarily designed for road transport with optimized dimensions for easy loading and unloading, whereas containers follow standardized sizes for multimodal transport, including sea freight. Swap bodies often feature adjustable legs for quick exchange on trucks without cranes, while containers require heavy equipment for lifting and stacking. The structural design of swap bodies emphasizes lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency, contrasted with containers built to withstand harsh maritime conditions.
Design and Construction Features
Swap bodies feature lightweight steel frames with bolted corner castings and detachable bodies designed for road and rail intermodal transport, offering optimized payload capacity and easier handling. Containers are built with robust welded steel panels and standardized dimensions, ensuring durability and compatibility across global shipping networks. Your choice depends on transport mode flexibility and the need for specialized loading and unloading equipment.
Compatibility with Transport Modes
Swap bodies offer greater compatibility with European road transport due to their standard road vehicle designs, allowing seamless loading and unloading during intermodal transfers. Containers are highly compatible with maritime and rail transport, adhering to international ISO standards that facilitate global shipping and terminal handling. Your choice between swap bodies and containers should align with the primary transport modes and logistical requirements involved in your supply chain.
Loading and Unloading Efficiency
Swap bodies offer higher loading and unloading efficiency due to their ability to be detached from the chassis and stored or loaded separately, minimizing vehicle downtime. Containers require cranes or specialized equipment for loading and unloading, which can slow operations and limit flexibility in locations without such infrastructure. Optimizing your logistics with swap bodies can streamline turnaround times and improve overall supply chain productivity.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Swap bodies generally offer lower initial investment costs compared to containers due to lighter construction and modular design, enhancing fuel efficiency during transport. Containers provide broader compatibility with global shipping standards, potentially reducing handling fees and increasing asset utilization in intermodal logistics. Evaluating ROI depends on operational needs, with swap bodies favoring regional transport cost savings while containers deliver better long-term value in international freight due to standardized stacking and secure cargo protection.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Swap bodies and containers must comply with international regulatory standards such as ISO 668 and CSC (Convention for Safe Containers) to ensure safety and compatibility in intermodal transport. Swap bodies, primarily used in European road and rail transport, conform to specific regional standards like EN 284, whereas containers follow globally recognized regulations facilitating worldwide shipping. Compliance with these standards guarantees structural integrity, secure handling, and legal operation across different transportation modes and jurisdictions.
Applications in Logistics and Supply Chain
Swap bodies offer enhanced flexibility in logistics and supply chain operations by enabling quick transfers between trucks, trailers, and warehouses without unloading goods, significantly reducing downtime. Containers are ideal for long-distance and intermodal transport due to their standardized sizes and robust construction, facilitating seamless handling across ships, trains, and trucks. Your choice between swap bodies and containers depends on whether your priority is rapid local distribution or efficient global transport integration.
Advantages of Swap Bodies Over Containers
Swap bodies offer greater weight efficiency compared to containers, allowing for higher payload capacity while complying with road regulations, which is crucial for optimizing transportation costs. Their adjustable design provides superior flexibility for loading and unloading, reducing turnaround times and enhancing supply chain efficiency. You benefit from improved compatibility with European road and rail networks, making swap bodies ideal for intermodal logistics in regions with strict size and weight constraints.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Choosing between a swap body and a container depends on your business's specific logistical needs. Swap bodies offer greater flexibility for quick loading and unloading in European road transport, while containers provide superior protection and standardized options for multimodal shipping. Evaluating factors like transit routes, cargo type, and handling infrastructure will help you determine the most efficient and cost-effective solution for your operations.
swap body vs container Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com