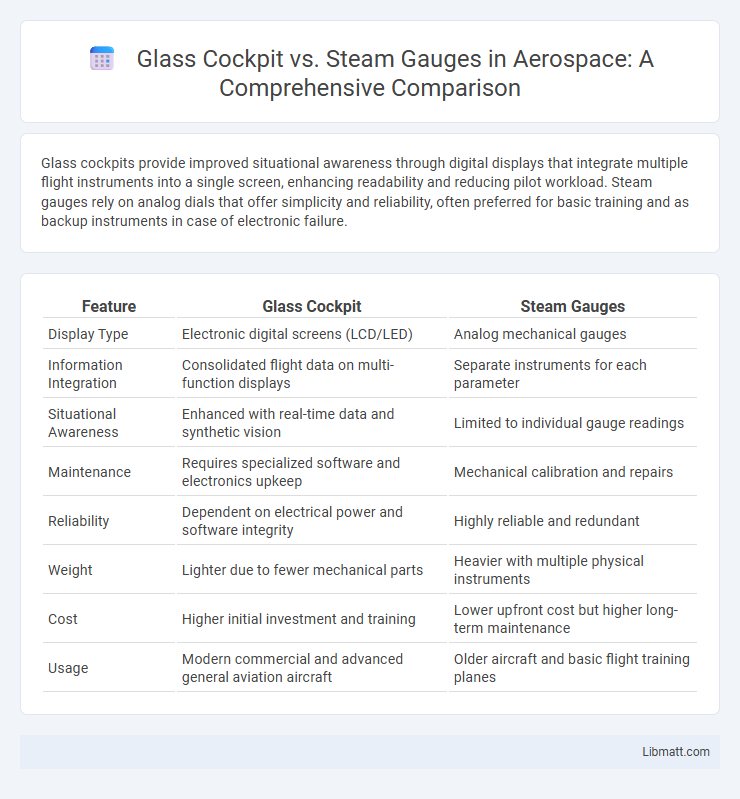
Glass cockpits provide improved situational awareness through digital displays that integrate multiple flight instruments into a single screen, enhancing readability and reducing pilot workload. Steam gauges rely on analog dials that offer simplicity and reliability, often preferred for basic training and as backup instruments in case of electronic failure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Cockpit | Steam Gauges |
|---|---|---|
| Display Type | Electronic digital screens (LCD/LED) | Analog mechanical gauges |
| Information Integration | Consolidated flight data on multi-function displays | Separate instruments for each parameter |
| Situational Awareness | Enhanced with real-time data and synthetic vision | Limited to individual gauge readings |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized software and electronics upkeep | Mechanical calibration and repairs |
| Reliability | Dependent on electrical power and software integrity | Highly reliable and redundant |
| Weight | Lighter due to fewer mechanical parts | Heavier with multiple physical instruments |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and training | Lower upfront cost but higher long-term maintenance |
| Usage | Modern commercial and advanced general aviation aircraft | Older aircraft and basic flight training planes |
Introduction to Aircraft Cockpit Systems
Glass cockpits utilize digital displays and integrated avionics systems, providing pilots with enhanced situational awareness, customizable instrument layouts, and real-time data updates. In contrast, steam gauges rely on analog dials and mechanical instruments that display individual flight parameters without data integration. Modern aircraft increasingly favor glass cockpit technology due to improved reliability, reduced pilot workload, and advanced navigation capabilities.
Defining Glass Cockpits
Glass cockpits feature digital flight instrument displays using LCD or LED screens that integrate multiple flight data sources into a single, customizable interface. These systems provide real-time avionics information, enhanced situational awareness, and reduced pilot workload compared to traditional steam gauges, which rely on individual analog dials for each instrument. Advanced glass cockpits support functions such as GPS navigation, weather radar, and traffic alerts, contributing to more efficient and safer flight operations.
Understanding Steam Gauges
Steam gauges provide pilots with mechanical, analog readouts of critical flight data such as airspeed, altitude, and attitude, relying on pressure and vacuum systems. These instruments are prized for their simplicity, reliability, and ease of interpretation, especially in older or smaller aircraft where advanced technology may be unavailable. Understanding steam gauges is essential for pilots transitioning from traditional cockpits or flying in aircraft without glass cockpit systems, ensuring full situational awareness through tactile and visual cues.
Key Differences Between Glass Cockpits and Steam Gauges
Glass cockpits utilize advanced digital displays that integrate multiple flight parameters into a single screen, enhancing situational awareness and reducing pilot workload, while steam gauges rely on individual analog instruments for each flight function, which can increase scan complexity. Glass cockpits offer real-time data updates, customizable layouts, and often include GPS and autopilot integration, whereas steam gauges provide fundamental flight information with mechanical reliability and simplicity. The transition to glass cockpits allows for improved navigation accuracy, easier system diagnostics, and streamlined pilot training compared to traditional steam gauge configurations.
Advantages of Glass Cockpits
Glass cockpits offer enhanced situational awareness through integrated digital displays that consolidate flight data, reducing pilot workload and improving decision-making accuracy. Advanced features like real-time navigation, weather updates, and system diagnostics provide safer and more efficient flight management compared to traditional steam gauges. Your ability to monitor multiple parameters simultaneously with customizable layouts ensures quicker response times and increased operational safety.
Benefits of Traditional Steam Gauges
Traditional steam gauges offer proven reliability and simplicity, ensuring pilots can quickly interpret critical flight data without the complexities of digital systems. These analog instruments operate independently of electrical power, providing consistent functionality even during system failures, which enhances overall flight safety. Your familiarity with steam gauges can improve response time in emergency situations due to their clear, direct readings.
Transition Challenges for Pilots
Pilots transitioning from steam gauges to glass cockpits face challenges in adapting to digital interfaces that display integrated navigational, engine, and flight data. This transition requires mastering new systems, including multifunction displays and autopilot controls, demanding enhanced situational awareness and technical proficiency. Training must emphasize interpreting synthetic vision and managing touchscreen inputs to ensure safety and operational efficiency in modern glass cockpit environments.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
Glass cockpits offer enhanced reliability through integrated diagnostics and fewer moving parts, reducing maintenance frequency compared to traditional steam gauges. Steam gauges, while simpler and easier to repair with basic tools, often require regular calibration and manual inspections to ensure accuracy. Modern glass displays also support remote software updates, improving long-term maintenance efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Cost Implications for Operators
Glass cockpits generally involve higher initial costs due to advanced avionics and touchscreen displays, but they can reduce long-term maintenance expenses and increase operational efficiency. Steam gauges, being mechanical and simpler, have lower upfront costs but often incur higher maintenance and repair expenses over time. Your choice between the two should consider both the short-term budget and the potential savings on reliability and pilot workload in the long run.
Future Trends in Aircraft Cockpit Technology
Glass cockpits are rapidly replacing traditional steam gauges due to enhanced situational awareness, integration capabilities, and reduced pilot workload. Future trends in aircraft cockpit technology emphasize advanced touchscreen interfaces, augmented reality overlays, and artificial intelligence-driven decision support systems to improve safety and efficiency. Your investment in glass cockpit upgrades prepares your aircraft for seamless adaptation to these emerging technologies.
Glass cockpit vs Steam gauges Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com