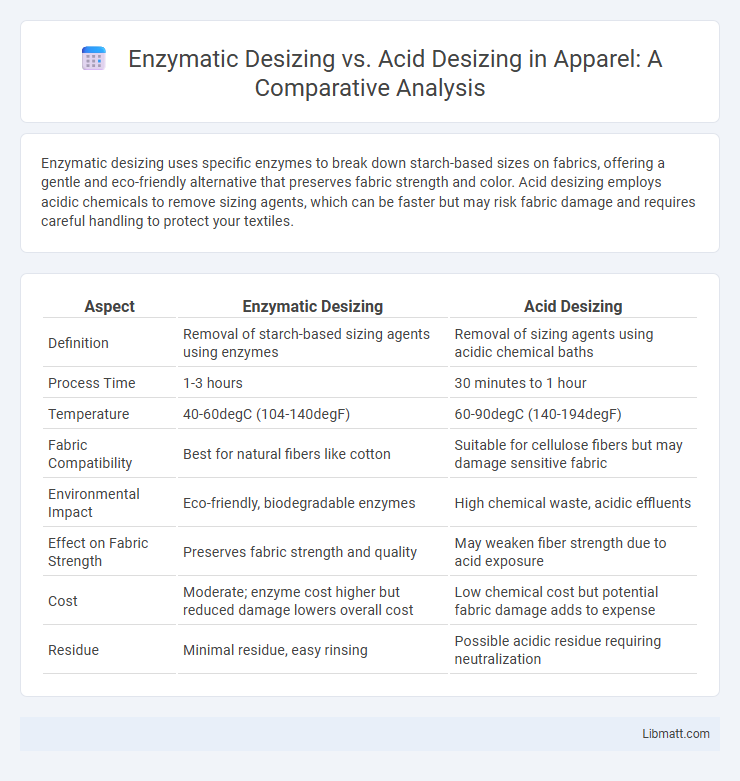
Enzymatic desizing uses specific enzymes to break down starch-based sizes on fabrics, offering a gentle and eco-friendly alternative that preserves fabric strength and color. Acid desizing employs acidic chemicals to remove sizing agents, which can be faster but may risk fabric damage and requires careful handling to protect your textiles.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Enzymatic Desizing | Acid Desizing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removal of starch-based sizing agents using enzymes | Removal of sizing agents using acidic chemical baths |
| Process Time | 1-3 hours | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Temperature | 40-60degC (104-140degF) | 60-90degC (140-194degF) |
| Fabric Compatibility | Best for natural fibers like cotton | Suitable for cellulose fibers but may damage sensitive fabric |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable enzymes | High chemical waste, acidic effluents |
| Effect on Fabric Strength | Preserves fabric strength and quality | May weaken fiber strength due to acid exposure |
| Cost | Moderate; enzyme cost higher but reduced damage lowers overall cost | Low chemical cost but potential fabric damage adds to expense |
| Residue | Minimal residue, easy rinsing | Possible acidic residue requiring neutralization |
Introduction to Desizing in Textile Processing
Desizing in textile processing involves removing starch-based sizing agents applied to yarns to improve weaving efficiency. Enzymatic desizing uses specific enzymes like amylases to break down starch molecules, offering eco-friendly and fabric-safe treatment. Acid desizing employs acidic solutions to hydrolyze starch but can degrade fabric quality and generate hazardous wastewater, making enzymatic methods preferable for sustainable textile manufacturing.
Overview of Enzymatic Desizing
Enzymatic desizing uses amylase enzymes to effectively hydrolyze starch-based sizing agents in textiles, offering a more environmentally friendly and precise alternative to acid desizing. This process operates under milder conditions, minimizing fiber damage while enhancing fabric softness and dye uptake. Compared to acid desizing, enzymatic desizing reduces chemical consumption, wastewater pollution, and energy usage, making it highly suitable for sustainable textile processing.
Overview of Acid Desizing
Acid desizing is a chemical process used to remove starch-based sizing agents from textile fabrics by hydrolyzing the starch molecules under acidic conditions. The method involves treating fabrics with dilute sulfuric or hydrochloric acid solutions at elevated temperatures, which breaks down the starch into soluble sugars that can be washed away. This technique is effective for certain fiber types but requires careful control to prevent fabric damage and ensure environmental safety due to acid disposal concerns.
Mechanism of Action: Enzymatic vs Acid Desizing
Enzymatic desizing utilizes specific enzymes like amylases to selectively hydrolyze starch-based sizing agents on fabric, breaking down complex polysaccharides into soluble sugars that are easily washed away. Acid desizing relies on acidic chemicals, such as sulfuric or hydrochloric acid, to hydrolyze starch through acid-catalyzed cleavage of glycosidic bonds, resulting in starch depolymerization and removal. The enzymatic process is milder and more environmentally friendly, while acid desizing is faster but involves harsher conditions that can damage fibers and generate acidic effluents.
Key Advantages of Enzymatic Desizing
Enzymatic desizing offers superior fabric care by selectively removing starch without damaging fibers, enhancing fabric strength and softness compared to acid desizing. You benefit from a more environmentally friendly process, as enzymatic desizing consumes less water and generates fewer harmful effluents. This method also operates at lower temperatures and pH levels, reducing energy costs and minimizing fabric degradation during textile processing.
Key Advantages of Acid Desizing
Acid desizing offers key advantages such as efficient removal of stubborn sizing agents and compatibility with a wide range of fabric types, including synthetic blends. It operates effectively at lower temperatures, reducing energy consumption and minimizing fabric damage compared to harsh alkaline methods. You benefit from enhanced fabric softness and improved dye uptake, leading to superior textile quality and process consistency.
Comparative Analysis: Efficiency and Effectiveness
Enzymatic desizing offers higher specificity and eco-friendliness by breaking down starch-based sizing agents at moderate temperatures, leading to better fabric integrity and reduced chemical waste. Acid desizing, while faster and effective on various sizing materials, may cause fiber damage and requires neutralization steps to prevent fabric degradation. Overall, enzymatic desizing demonstrates superior efficiency in preserving fabric quality and minimizing environmental impact compared to acid desizing.
Environmental Impact: Enzymatic vs Acid Desizing
Enzymatic desizing significantly reduces environmental impact compared to acid desizing by utilizing biodegradable enzymes that minimize hazardous chemical discharge and lower water pollution. Acid desizing involves strong acids that generate acidic effluents requiring extensive neutralization and treatment, increasing ecological risks and operational costs. Enzymatic processes operate under milder conditions, leading to energy savings and less toxic waste generation, aligning with sustainable textile manufacturing goals.
Cost Implications and Industrial Feasibility
Enzymatic desizing offers cost savings through lower energy consumption, reduced chemical usage, and minimal fabric damage, making it economically attractive for sensitive textiles. Acid desizing, while faster, incurs higher costs due to corrosive chemical handling, wastewater treatment, and potential fiber degradation requiring additional processing. Your choice depends on balancing initial investment and operational expenses with fabric type and production scale for optimal industrial feasibility.
Future Trends and Innovations in Desizing Methods
Enzymatic desizing is gaining traction due to its eco-friendly properties and precise starch removal capabilities, while acid desizing remains valued for its efficiency with synthetic fibers. Emerging innovations focus on enhancing enzyme formulations to improve temperature resistance and reusability, reducing environmental impact and processing costs. Your textile processing operations can benefit from integrating hybrid desizing techniques, combining enzymatic and acid methods for optimized fabric quality and sustainability.
enzymatic desizing vs acid desizing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com