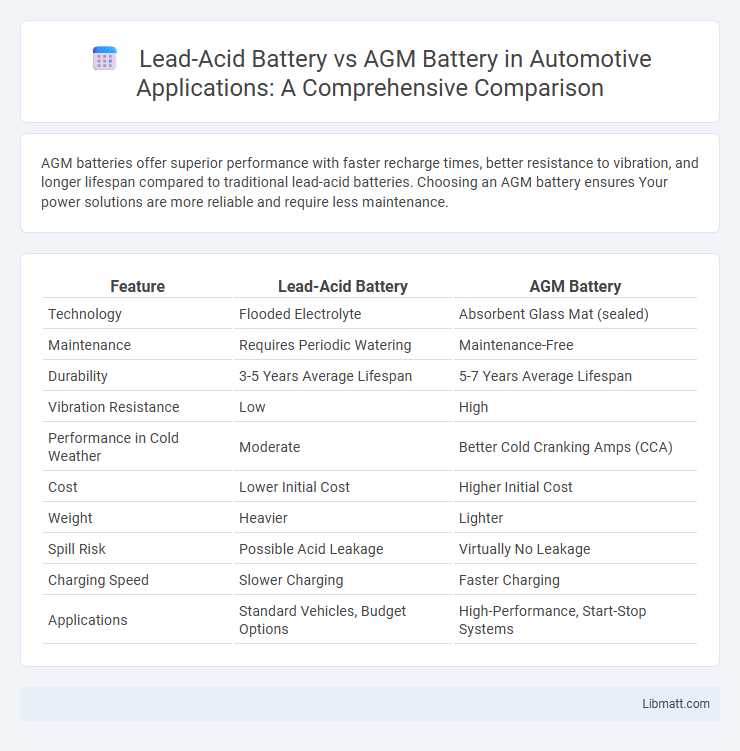
AGM batteries offer superior performance with faster recharge times, better resistance to vibration, and longer lifespan compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. Choosing an AGM battery ensures Your power solutions are more reliable and require less maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lead-Acid Battery | AGM Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Flooded Electrolyte | Absorbent Glass Mat (sealed) |
| Maintenance | Requires Periodic Watering | Maintenance-Free |
| Durability | 3-5 Years Average Lifespan | 5-7 Years Average Lifespan |
| Vibration Resistance | Low | High |
| Performance in Cold Weather | Moderate | Better Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) |
| Cost | Lower Initial Cost | Higher Initial Cost |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Spill Risk | Possible Acid Leakage | Virtually No Leakage |
| Charging Speed | Slower Charging | Faster Charging |
| Applications | Standard Vehicles, Budget Options | High-Performance, Start-Stop Systems |
Overview of Lead-Acid and AGM Batteries
Lead-acid batteries have been widely used for decades, offering reliable energy storage through a liquid electrolyte and lead plates. AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries represent an advanced variation, utilizing fiberglass mats to immobilize the electrolyte, leading to enhanced durability and faster charging. Your choice between lead-acid and AGM batteries impacts factors such as maintenance requirements, lifespan, and performance in deep cycling applications.
Construction and Design Differences
Lead-acid batteries feature a traditional design with liquid electrolyte and lead plates submerged in sulfuric acid, requiring regular maintenance to prevent acid stratification and corrosion. AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries utilize a fiberglass mat to immobilize the electrolyte, allowing for spill-proof, vibration-resistant construction with enhanced durability and faster recharge times. Understanding these construction and design differences can help you select the battery that best fits your power and maintenance needs.
Performance Comparison
Lead-acid batteries offer reliable performance with a lower initial cost but suffer from shorter cycle life and reduced efficiency under deep discharge conditions. AGM batteries provide superior performance through faster recharging, higher resistance to vibration, and longer lifespan, making them ideal for demanding applications and frequent cycling. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize cost-effectiveness or enhanced durability and consistent power delivery.
Charging and Maintenance Requirements
Lead-acid batteries require regular water top-ups and careful charging to prevent sulfation, which can reduce battery lifespan, while AGM batteries are sealed and maintenance-free, allowing for easier charging without electrolyte management. AGM batteries can handle faster charging rates and have lower self-discharge compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, making them more suitable for applications where reliable power and minimal upkeep are essential. Choosing an AGM battery helps you avoid frequent maintenance and ensures consistent performance, especially in demanding or variable charging conditions.
Lifespan and Durability
Lead-acid batteries typically have a lifespan of 3 to 5 years, with moderate durability under standard conditions, making them suitable for basic automotive and stationary applications. AGM batteries offer enhanced durability and longer lifespan, often lasting 4 to 7 years due to their sealed design and superior resistance to vibration and deep discharges. Choosing an AGM battery can improve your system's reliability and reduce maintenance needs compared to conventional lead-acid options.
Cost Analysis
Lead-acid batteries typically have a lower upfront cost compared to AGM batteries, making them a budget-friendly option for basic energy storage needs. AGM batteries, while more expensive initially, offer longer cycle life and better performance, which can reduce replacement frequency and overall cost over time. Your choice depends on balancing initial investment against long-term value and reliability.
Applications and Use Cases
Lead-acid batteries are commonly used in automotive starters, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and backup power systems due to their cost-effectiveness and reliable energy output. AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries excel in high-performance applications such as motorcycles, marine vessels, and off-grid solar systems, where vibration resistance, maintenance-free operation, and faster charging capabilities are essential. Understanding your specific energy demands and environmental conditions will help determine whether a lead-acid or AGM battery is best suited for your application.
Safety Considerations
Lead-acid batteries pose safety risks such as acid leaks and hydrogen gas buildup, which can lead to corrosion and potential explosions if not properly ventilated. AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries enhance safety by sealing the electrolyte, reducing acid leakage, and minimizing gas emissions during charging. Their spill-proof design and resistance to vibration make AGM batteries a safer choice for use in vehicles, solar power systems, and backup energy storage.
Environmental Impact
Lead-acid batteries contain toxic lead and sulfuric acid, posing significant environmental hazards if improperly disposed of, causing soil and water contamination. AGM batteries, a sealed form of lead-acid technology, reduce acid leakage risks and have a longer lifespan, resulting in less frequent replacements and reduced environmental waste. Proper recycling programs are essential for both battery types to minimize lead pollution and ensure the recovery of valuable materials.
Which Battery Type Is Right for You?
Choosing between a lead-acid battery and an AGM battery depends on your specific power needs and usage environment. Lead-acid batteries are cost-effective and suitable for applications where weight and vibration resistance are less critical, while AGM batteries offer better performance, longer lifespan, and maintenance-free operation with improved resistance to shock and temperature extremes. Evaluate your device's power requirements, budget, and maintenance preferences to determine which battery type aligns best with your needs.
Lead-acid battery vs AGM battery Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com