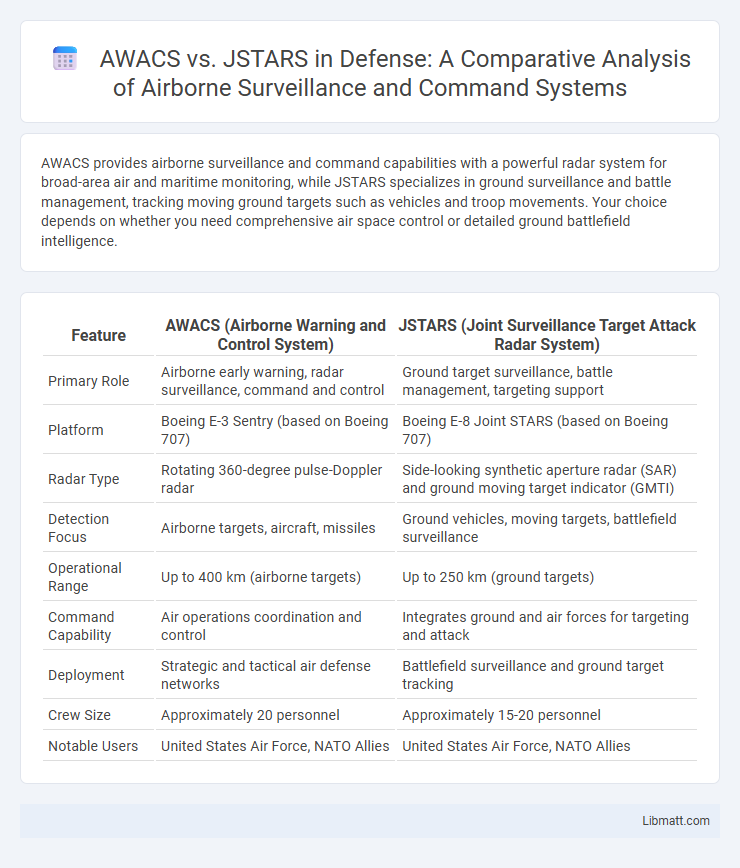
AWACS provides airborne surveillance and command capabilities with a powerful radar system for broad-area air and maritime monitoring, while JSTARS specializes in ground surveillance and battle management, tracking moving ground targets such as vehicles and troop movements. Your choice depends on whether you need comprehensive air space control or detailed ground battlefield intelligence.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System) | JSTARS (Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Airborne early warning, radar surveillance, command and control | Ground target surveillance, battle management, targeting support |
| Platform | Boeing E-3 Sentry (based on Boeing 707) | Boeing E-8 Joint STARS (based on Boeing 707) |
| Radar Type | Rotating 360-degree pulse-Doppler radar | Side-looking synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and ground moving target indicator (GMTI) |
| Detection Focus | Airborne targets, aircraft, missiles | Ground vehicles, moving targets, battlefield surveillance |
| Operational Range | Up to 400 km (airborne targets) | Up to 250 km (ground targets) |
| Command Capability | Air operations coordination and control | Integrates ground and air forces for targeting and attack |
| Deployment | Strategic and tactical air defense networks | Battlefield surveillance and ground target tracking |
| Crew Size | Approximately 20 personnel | Approximately 15-20 personnel |
| Notable Users | United States Air Force, NATO Allies | United States Air Force, NATO Allies |
Introduction to AWACS and JSTARS
AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System) is an advanced radar surveillance platform designed to detect and track airborne threats at long ranges, providing real-time command and control for air operations. JSTARS (Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System) specializes in ground target detection and battlefield management, using synthetic aperture radar to monitor vehicle movements and coordinate tactical responses. Both systems enhance situational awareness and force coordination but focus on different operational domains--AWACS in the airspace and JSTARS on the ground.
Historical Background and Development
AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System) was developed in the late 1950s to provide long-range airborne radar surveillance and command and control capabilities, primarily to detect and track enemy aircraft and missile threats. JSTARS (Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System) emerged in the 1980s with a focus on ground moving target indicator (GMTI) radar technology, enabling real-time tracking of vehicles and battlefield surveillance. Both systems evolved through continuous upgrades to meet changing combat and intelligence requirements, with AWACS emphasizing airspace management and JSTARS focusing on ground target detection and battle management.
Core Missions and Operational Roles
AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System) primarily provides airborne surveillance, command, control, and communications to manage airspace and track airborne threats. JSTARS (Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System) specializes in ground surveillance, targeting, and battle management by using advanced radar to detect and track moving ground vehicles and coordinate strikes. Both systems support integrated battlefield awareness but focus respectively on air domain dominance and ground force coordination.
Key Technologies and Systems
AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System) utilizes advanced radar technology such as the AN/APY-1 or AN/APY-2, offering long-range airborne surveillance and targeting capabilities, integrated with a robust command and control system for real-time battlefield management. JSTARS (Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System) features the AN/APY-7 radar designed for ground moving target indication, enabling precise detection and tracking of vehicles and personnel on the battlefield. Both platforms employ sophisticated communication systems for data sharing, but AWACS is primarily optimized for airspace control while JSTARS focuses on ground surveillance and targeting intelligence.
Aircraft Platforms and Specifications
AWACS aircraft, such as the Boeing E-3 Sentry, feature a large rotating radar dome mounted above the fuselage, enabling 360-degree surveillance with powerful radar capable of detecting aircraft and missile threats at long ranges. JSTARS platforms, like the Boeing E-8 Joint STARS, utilize a fixed, side-looking radar beneath the fuselage designed for ground target surveillance, tracking moving vehicles and coordinating ground troops effectively. Your mission requirements will determine the ideal choice, with AWACS excelling in airspace control and JSTARS providing superior battlefield ground target tracking capabilities.
Surveillance and Reconnaissance Capabilities
AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System) offers comprehensive airborne surveillance with advanced radar that detects and tracks enemy aircraft over vast airspace, enabling air battle management and command control. JSTARS (Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System) specializes in ground surveillance by using synthetic aperture radar to identify and track moving ground targets, providing critical battlefield reconnaissance and targeting information. Your decision between AWACS and JSTARS depends on whether you prioritize extensive aerial detection or detailed ground surveillance for operational intelligence.
Communication and Data Link Systems
AWACS employs advanced communication and data link systems that provide real-time airborne surveillance and battle management, enabling seamless coordination with fighter jets, ground forces, and naval assets. JSTARS specializes in ground surveillance with robust data links that integrate radar tracking of ground movements and relay precise targeting information to command centers and strike units. Your choice between the two depends on the operational focus: AWACS excels in airspace control and mid-air connectivity, while JSTARS optimizes ground force integration through its specialized communication networks.
Contribution to Modern Warfare
AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System) enhances modern warfare by providing real-time airborne surveillance, command, and control, enabling rapid detection and tracking of enemy aircraft and missiles. JSTARS (Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System) contributes by delivering ground movement and battlefield intelligence, tracking enemy vehicles and troop deployments to support precision strikes. Your operational awareness improves significantly with AWACS' aerial domain dominance complemented by JSTARS' ground battlefield monitoring.
Comparative Strengths and Limitations
AWACS provides superior airborne early warning and command control with advanced radar capable of tracking multiple airborne targets at long ranges, enhancing situational awareness for air superiority missions. JSTARS specializes in ground surveillance and battle management, using radar to detect, track, and classify moving ground targets, supporting land force operations and targeting. While AWACS excels in aerial threat detection and airspace control, JSTARS offers critical ground force intelligence but with less emphasis on air threats.
Future Trends and Program Upgrades
AWACS platforms are evolving with enhanced radar capabilities and integration of multi-domain sensors to improve airborne command and control, while JSTARS programs emphasize advancements in ground surveillance and data fusion for faster, more accurate targeting. Future upgrades include incorporating artificial intelligence and secure communication links to enhance real-time battlefield awareness and interoperability. Your operational advantage will increase as these systems adopt network-centric warfare technologies to support joint and coalition forces more effectively.
AWACS vs JSTARS Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com