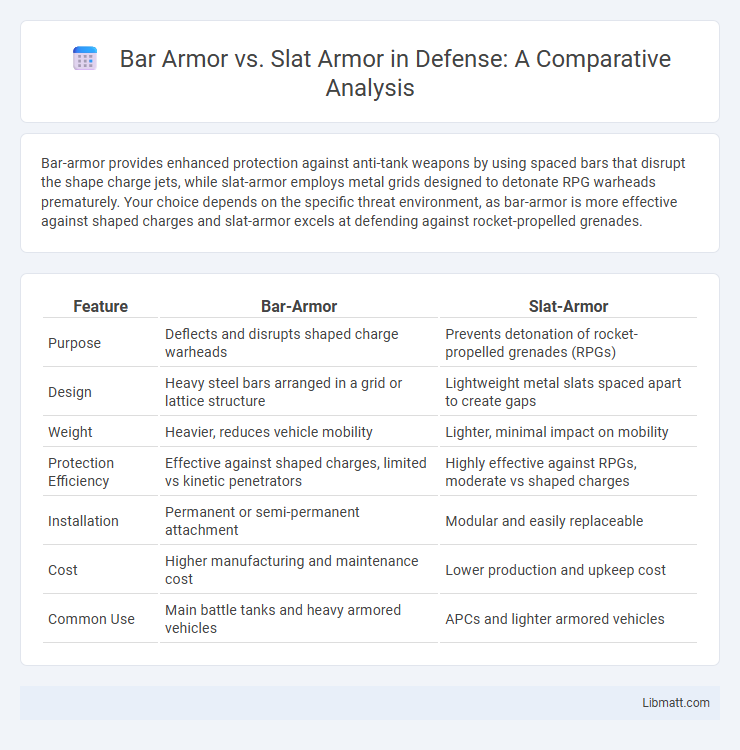
Bar-armor provides enhanced protection against anti-tank weapons by using spaced bars that disrupt the shape charge jets, while slat-armor employs metal grids designed to detonate RPG warheads prematurely. Your choice depends on the specific threat environment, as bar-armor is more effective against shaped charges and slat-armor excels at defending against rocket-propelled grenades.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bar-Armor | Slat-Armor |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Deflects and disrupts shaped charge warheads | Prevents detonation of rocket-propelled grenades (RPGs) |
| Design | Heavy steel bars arranged in a grid or lattice structure | Lightweight metal slats spaced apart to create gaps |
| Weight | Heavier, reduces vehicle mobility | Lighter, minimal impact on mobility |
| Protection Efficiency | Effective against shaped charges, limited vs kinetic penetrators | Highly effective against RPGs, moderate vs shaped charges |
| Installation | Permanent or semi-permanent attachment | Modular and easily replaceable |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing and maintenance cost | Lower production and upkeep cost |
| Common Use | Main battle tanks and heavy armored vehicles | APCs and lighter armored vehicles |
Introduction to Bar Armor and Slat Armor
Bar armor and slat armor are specialized vehicle protection systems designed to defend against explosive threats, such as rocket-propelled grenades (RPGs). Bar armor consists of rigid metal bars arranged to prevent the warhead from making contact with the vehicle, effectively disrupting its detonation mechanism. In contrast, slat armor uses a grid or cage-like structure to absorb and deflect the impact of attack, providing a lightweight yet effective barrier for military and armored vehicles.
Historical Development of Bar and Slat Armor
Bar armor originated during World War II as a cost-effective solution to counter shaped-charge warheads on tanks, while slat armor evolved later to provide enhanced protection against rocket-propelled grenades (RPGs) with its grid-like framework. The historical development of bar armor emphasized simplicity and ease of attachment, whereas slat armor's design improved debris dispersion and increased the likelihood of premature warhead detonation. Your choice between bar and slat armor should consider the balance between weight, protection level, and specific threat environments based on their historical performance.
Design Principles: Bar-Armor vs Slat-Armor
Bar-armor features vertical or horizontal steel bars spaced to disrupt the trajectory of RPGs and shaped charges, minimizing warhead detonation effectiveness. Slat-armor employs a grid-like framework of metal slats designed to deform or prematurely detonate incoming projectiles, reducing armor penetration. Your choice between the two should consider the specific threat environment and the balance between weight, cost, and protective coverage.
Materials Used in Bar and Slat Armor
Bar armor commonly utilizes high-strength steel bars or reinforced aluminum alloys to provide robust protection against ballistic threats and projectiles. Slat armor typically consists of spaced steel or composite metal slats arranged around the vehicle, designed to deflect or disrupt shaped-charge warheads effectively. Your choice between bar armor and slat armor should consider the materials' weight, durability, and specific threat resistance for optimal vehicle defense.
Protection Capabilities Against Modern Threats
Bar-armor provides effective protection against RPGs by disrupting shaped charges, while slat-armor offers enhanced defense against a broader range of modern threats, including rocket-propelled grenades and anti-tank weapons, by preventing proper detonation at a distance. Slat-armor's grid structure reduces the risk of penetration by absorbing and deflecting explosive forces more efficiently than solid bar-armor. Your vehicle's survival in high-threat environments is significantly improved with slat-armor due to its superior multi-threat protective capabilities.
Weight and Mobility Considerations
Bar-armor offers lighter protection compared to slat-armor, resulting in better vehicle mobility and reduced fuel consumption. Slat-armor, while heavier due to its reinforced steel grid design, provides superior defense against RPGs but can significantly impact speed and maneuverability. The choice between bar-armor and slat-armor depends on balancing weight constraints with the tactical need for enhanced blast protection.
Cost and Maintenance Factors
Bar armor typically offers a more cost-effective solution due to its simpler design and easier repair requirements, making it ideal for budget-conscious military or armored vehicle operators. In contrast, slat armor involves higher initial expenses and more specialized maintenance because of its intricate mesh-like structure designed to deflect rocket-propelled grenades. Your choice between bar armor and slat armor should consider both upfront investment and long-term upkeep to ensure operational readiness without overwhelming maintenance resources.
Real-World Applications in Military Vehicles
Bar armor provides effective protection against rocket-propelled grenades (RPGs) by detonating warheads before impact, commonly used on older Soviet and Russian armored vehicles like the BMP-2 and T-72 tanks. Slat armor features a grid-like structure that disables shaped charges by disrupting their fusing mechanisms, widely adopted on U.S. military vehicles such as the Humvee and Stryker to enhance survivability in urban combat zones. Both armor types offer lightweight solutions to improve vehicle defense without significantly compromising mobility or operational performance.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Armor Type
Bar armor offers enhanced deflection against shaped charge warheads and minimizes penetration by creating gaps for jet disruption, but it is less effective against kinetic energy penetrators and can add significant weight to vehicles. Slat armor excels at preventing RPGs and rocket-propelled grenades from detonating by deforming warheads before impact, providing lighter overall protection with easier integration on vehicles, though it may be less effective against newer tandem-charge munitions. Selecting between bar and slat armor depends on the specific threat environment, vehicle weight constraints, and operational mobility requirements.
Future Trends in Vehicle Armor Technology
Bar-armor and slat-armor represent evolving solutions in vehicle armor technology designed to counteract RPGs and shaped charges effectively. Future trends emphasize integrating lightweight composite materials with enhanced modular designs to improve mobility without sacrificing protection. Advancements in sensor technology and adaptive armor systems are expected to synergize with physical armor types like bar and slat-armor, enabling real-time threat detection and dynamic defense responses.
bar-armor vs slat-armor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com