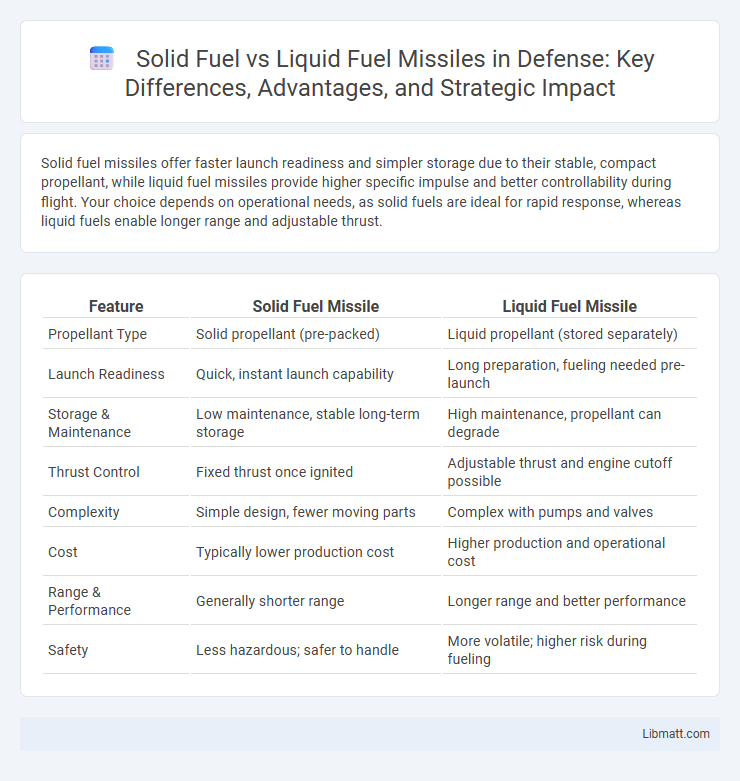
Solid fuel missiles offer faster launch readiness and simpler storage due to their stable, compact propellant, while liquid fuel missiles provide higher specific impulse and better controllability during flight. Your choice depends on operational needs, as solid fuels are ideal for rapid response, whereas liquid fuels enable longer range and adjustable thrust.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solid Fuel Missile | Liquid Fuel Missile |
|---|---|---|
| Propellant Type | Solid propellant (pre-packed) | Liquid propellant (stored separately) |
| Launch Readiness | Quick, instant launch capability | Long preparation, fueling needed pre-launch |
| Storage & Maintenance | Low maintenance, stable long-term storage | High maintenance, propellant can degrade |
| Thrust Control | Fixed thrust once ignited | Adjustable thrust and engine cutoff possible |
| Complexity | Simple design, fewer moving parts | Complex with pumps and valves |
| Cost | Typically lower production cost | Higher production and operational cost |
| Range & Performance | Generally shorter range | Longer range and better performance |
| Safety | Less hazardous; safer to handle | More volatile; higher risk during fueling |
Introduction to Missile Propulsion: Solid vs Liquid Fuels
Solid fuel missiles offer rapid launch capabilities and simpler storage due to their stable chemical composition, making them ideal for quick response scenarios. Liquid fuel missiles provide higher specific impulse and thrust control through adjustable combustion, which benefits precision targeting and extended range. Understanding these propulsion characteristics helps you choose the appropriate missile system based on mission requirements and operational constraints.
Fundamental Differences Between Solid and Liquid Fuel Missiles
Solid fuel missiles use a pre-cast, stable propellant that provides rapid launch readiness and simpler storage, whereas liquid fuel missiles rely on separate liquid oxidizers and fuels that require fueling before launch, resulting in longer preparation times. The solid propellant's uniform composition offers greater structural integrity and safer handling, while liquid fuel systems enable higher specific impulse and throttle control, allowing more precise trajectory adjustments. Your strategic choice between the two depends on priorities such as responsiveness, maintenance complexity, and performance flexibility for mission requirements.
Propellant Composition and Storage Requirements
Solid fuel missiles use a mixture of powdered oxidizers and binders in a hardened matrix, providing high stability and ease of long-term storage without degradation. Liquid fuel missiles rely on separate tanks of reactive liquid oxidizers and fuels, demanding complex plumbing and cryogenic or pressurized containment systems to maintain performance and prevent evaporation. Solid propellants offer simpler storage and quicker launch readiness, while liquid fuels require rigorous maintenance to manage volatility and ensure operational safety.
Launch Readiness and Response Times
Solid fuel missiles offer superior launch readiness due to their pre-packed propellant, enabling rapid response times with minimal preparation. Liquid fuel missiles require fueling before launch, which extends preparation time and limits immediate deployment capabilities. Your choice between solid and liquid fuel missiles directly impacts strategic flexibility and mission timing during critical operations.
Thrust Control and Mission Flexibility
Solid fuel missiles offer rapid thrust generation with limited in-flight thrust control, restricting mission flexibility due to fixed burn rates; liquid fuel missiles provide precise thrust modulation throughout flight, enabling variable trajectories and extended mission profiles. Thrust control in liquid fuel systems allows for throttling, multiple engine starts, and shutdowns, enhancing maneuverability and adaptability to dynamic mission requirements. Solid fuel's simpler design favors quick launch readiness but compromises adjustable thrust, impacting operational versatility compared to the dynamically controllable liquid propulsion systems.
Safety, Handling, and Logistics Considerations
Solid fuel missiles offer superior safety due to their stable, inert propellant, reducing the risk of accidental ignition during storage and handling. Liquid fuel missiles require complex logistics because their propellants are often toxic, highly volatile, and need specialized fueling procedures, increasing maintenance demands and operational risks. Your choice impacts deployment readiness, as solid fuels allow quicker launches with minimal preparation, while liquid fuels require more time and infrastructure for fueling and maintenance.
Cost Efficiency in Production and Maintenance
Solid fuel missiles generally offer superior cost efficiency in production and maintenance due to simpler manufacturing processes and longer shelf-life that reduces storage expenses. Liquid fuel missiles require more complex handling and fueling infrastructure, increasing operational costs and maintenance demands. Your defense budget benefits from solid fuel's lower recurring costs and quicker deployment readiness.
Reliability and Performance in Combat Scenarios
Solid fuel missiles offer greater reliability due to their simple design and stable fuel composition, enabling rapid launch readiness and consistent performance under diverse combat conditions. Liquid fuel missiles, while capable of higher thrust and longer range, require complex fueling procedures that reduce immediate availability and increase maintenance challenges in high-stress scenarios. Your choice between solid and liquid fuel missile systems directly impacts operational efficiency, response time, and mission success in dynamic battlefield environments.
Strategic Applications and Deployment Choices
Solid fuel missiles offer rapid launch capabilities and simpler storage requirements, making them ideal for mobile and quick-response strategic deployments. Liquid fuel missiles provide higher specific impulse and longer burn times, which enable greater range and payload capacity suitable for fixed-site strategic deterrence. Deployment choices hinge on operational flexibility, with solid fuel favored for battlefield readiness and liquid fuel preferred for intercontinental ballistic missile systems requiring extended flight duration.
Future Trends in Missile Propulsion Technology
Future trends in missile propulsion technology prioritize enhancements in solid fuel and liquid fuel systems to maximize range, speed, and reliability. Solid fuel missiles continue evolving with advanced composite propellants offering improved energy density and storage stability, making them ideal for rapid deployment and mobile platforms. Liquid fuel propulsion progresses toward cleaner, storable bipropellants and hybrid systems, providing higher thrust control and enabling precise targeting for next-generation, long-range missile applications.
solid fuel vs liquid fuel missile Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com