Line-of-sight guidance relies on direct visual or sensor-based tracking between the controller and the target, ensuring precise navigation within the operator's visual range. Beyond line-of-sight guidance enables control of devices or vehicles without direct visibility, using advanced communication systems like GPS and telemetry to extend operational reach.
Table of Comparison
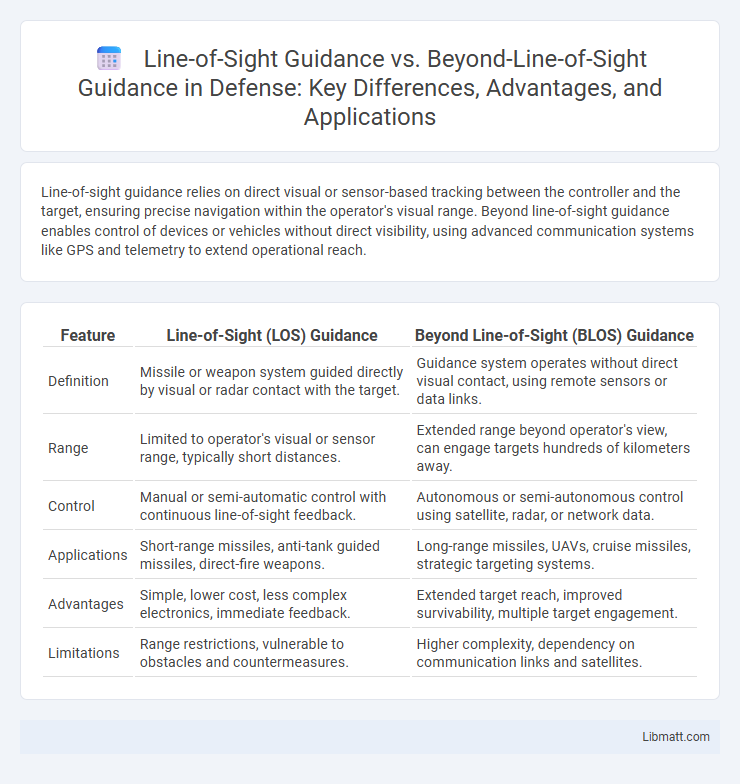
| Feature | Line-of-Sight (LOS) Guidance | Beyond Line-of-Sight (BLOS) Guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Missile or weapon system guided directly by visual or radar contact with the target. | Guidance system operates without direct visual contact, using remote sensors or data links. |
| Range | Limited to operator's visual or sensor range, typically short distances. | Extended range beyond operator's view, can engage targets hundreds of kilometers away. |
| Control | Manual or semi-automatic control with continuous line-of-sight feedback. | Autonomous or semi-autonomous control using satellite, radar, or network data. |
| Applications | Short-range missiles, anti-tank guided missiles, direct-fire weapons. | Long-range missiles, UAVs, cruise missiles, strategic targeting systems. |
| Advantages | Simple, lower cost, less complex electronics, immediate feedback. | Extended target reach, improved survivability, multiple target engagement. |
| Limitations | Range restrictions, vulnerable to obstacles and countermeasures. | Higher complexity, dependency on communication links and satellites. |
Introduction to Guidance Systems
Line-of-sight guidance systems rely on direct visual or sensor contact between the operator and the target, facilitating real-time control and immediate responsiveness during navigation. Beyond line-of-sight guidance extends control capabilities using satellite, radar, or communication networks, enabling operations in obstructed or distant environments beyond direct observation. Understanding these guidance technologies helps you select the appropriate system for mission requirements, balancing immediacy and operational range.
Defining Line-of-Sight (LOS) Guidance
Line-of-Sight (LOS) guidance refers to a navigation system where control commands are based on the direct visual or sensor-based observation of a target or path within the operator's or sensor's immediate line of sight. This method relies on real-time feedback from the immediate environment, enabling precise maneuvering usually in short-range or clear visibility conditions. Your choice of LOS guidance systems impacts responsiveness and accuracy in applications like UAVs, robotics, and maritime navigation.
Overview of Beyond Line-of-Sight (BLOS) Guidance
Beyond Line-of-Sight (BLOS) guidance enables control of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or missiles beyond the operator's direct visual range, using satellite communication, radio links, or autonomous navigation systems. This technology expands operational reach, allowing real-time data exchange and precise targeting in complex environments where direct line-of-sight is obstructed. BLOS systems integrate GPS, inertial navigation, and secure communication protocols to maintain control, enhancing mission flexibility and effectiveness compared to traditional Line-of-Sight (LOS) guidance.
Key Differences Between LOS and BLOS
Line-of-sight (LOS) guidance requires direct visual or sensor contact between the controller and the target, limiting operational range to the transmitter's visible horizon, typically a few kilometers. Beyond line-of-sight (BLOS) guidance leverages satellite links, UAV relays, or autonomous systems to control vehicles or missiles at extended distances, well beyond visual or radar range. Your choice between LOS and BLOS impacts mission flexibility, communication latency, and the effectiveness of long-range engagements.
Advantages of Line-of-Sight Guidance
Line-of-sight guidance offers real-time control and precise targeting by maintaining direct visual or sensor contact with the target, reducing latency and improving accuracy in dynamic environments. This method enhances situational awareness and simplifies navigation since the operator or system receives immediate feedback without relying on intermediaries or communication relays. Furthermore, line-of-sight systems are less susceptible to electronic jamming or signal loss compared to beyond line-of-sight guidance, ensuring more reliable mission performance in contested or complex operational theaters.
Benefits of Beyond Line-of-Sight Guidance
Beyond line-of-sight (BLOS) guidance enables control of vehicles or drones beyond the operator's visual range, significantly extending mission capabilities. It enhances operational flexibility, allowing for remote or automated navigation in complex or hazardous environments, which increases safety and efficiency. You benefit from improved situational awareness and the ability to engage targets or complete tasks in inaccessible or obstructed areas.
Technological Requirements for LOS and BLOS
Line-of-sight (LOS) guidance systems rely on direct visual or radio-wave transmissions between the controller and the vehicle, requiring clear, unobstructed paths and relatively short distances, typically supported by infrared or radio frequency technologies. Beyond line-of-sight (BLOS) guidance demands advanced communication infrastructure such as satellite links, high-frequency radios, or cellular networks to maintain control over long ranges or obstructed environments. BLOS systems often integrate GPS, inertial navigation systems, and secure data links to ensure continuous guidance beyond the operator's visual and radio horizon.
Use Cases in Military and Civilian Applications
Line-of-sight (LOS) guidance is essential for short-range military targeting systems such as anti-tank missiles and direct fire weapons, where visibility and accurate positioning are critical. Beyond line-of-sight (BLOS) guidance enables long-range operations, including drone navigation, satellite communications, and missile strike capabilities, by using satellite links, GPS, or relay drones to operate beyond visual or radar range. Your ability to choose between LOS and BLOS guidance depends on mission requirements, such as engagement distance, environmental conditions, and the need for real-time data transmission.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Line-of-sight guidance systems face challenges such as limited range and vulnerability to obstacles that block direct visibility, restricting operational flexibility. Beyond line-of-sight guidance overcomes distance and visibility barriers but encounters limitations like signal latency, reliance on complex communication networks, and susceptibility to electronic interference. Your choice between these approaches must consider the trade-offs between direct control precision and extended operational reach amid environmental and technological constraints.
Future Trends in Guidance System Technology
Future trends in guidance system technology emphasize enhancing autonomy and precision through integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms in both line-of-sight (LOS) and beyond line-of-sight (BLOS) guidance systems. The development of advanced sensor fusion techniques and secure satellite communication networks aims to improve real-time target tracking and obstacle avoidance, particularly in BLOS scenarios where direct visual confirmation is unavailable. Emerging technologies such as quantum navigation and 5G-enabled data links promise to revolutionize guidance accuracy and responsiveness, expanding operational capabilities in complex environments.
line-of-sight guidance vs beyond line-of-sight guidance Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com