Off-peak energy rates are typically lower due to reduced demand during non-busy hours, helping you save on electricity costs by shifting usage to these times. On-peak energy is charged at higher rates during periods of high demand, reflecting the increased strain on the power grid and resource costs.
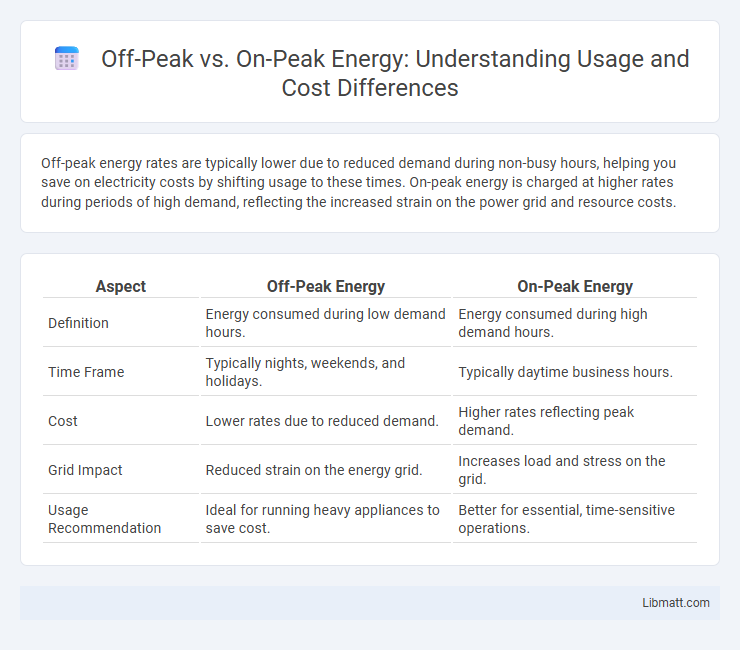
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Off-Peak Energy | On-Peak Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Energy consumed during low demand hours. | Energy consumed during high demand hours. |
| Time Frame | Typically nights, weekends, and holidays. | Typically daytime business hours. |
| Cost | Lower rates due to reduced demand. | Higher rates reflecting peak demand. |
| Grid Impact | Reduced strain on the energy grid. | Increases load and stress on the grid. |
| Usage Recommendation | Ideal for running heavy appliances to save cost. | Better for essential, time-sensitive operations. |
Understanding Off-Peak and On-Peak Energy
Off-peak energy refers to electricity consumed during times of low demand, usually at night or weekends, while on-peak energy is used during high-demand periods such as daytime weekdays. Utilities often charge lower rates for off-peak hours to encourage consumers to shift usage and balance grid load efficiently. Understanding these energy periods helps you optimize your electricity costs by adjusting consumption to off-peak times.
How Energy Consumption Patterns Influence Cost
Energy consumption patterns significantly influence cost through off-peak and on-peak pricing structures, where electricity rates are higher during peak demand hours and lower during off-peak times. Shifting Your energy usage to off-peak periods can reduce electricity bills by taking advantage of lower rates when the grid is less strained. Understanding these patterns helps optimize energy costs and supports grid stability by balancing demand more effectively.
Peak Hours: Identifying High-Demand Times
Peak hours refer to specific periods during the day when electricity demand reaches its highest levels, typically between 4 PM and 9 PM on weekdays. During these high-demand times, energy consumption spikes due to increased residential, commercial, and industrial activities, leading to higher electricity rates. Utility companies use peak hour identification to manage grid stability and implement time-of-use pricing to encourage energy conservation.
Off-Peak Benefits: Cost Savings and Efficiency
Off-peak energy usage typically offers significant cost savings as electricity rates are lower during periods of reduced demand, allowing you to reduce your utility bills effectively. Utilizing off-peak hours enhances energy efficiency by balancing grid load, which minimizes strain on power plants and reduces the need for additional infrastructure. Leveraging off-peak benefits supports sustainable energy consumption and promotes financial savings for both residential and commercial users.
On-Peak Challenges: Higher Rates and Grid Stress
On-peak energy periods typically incur higher electricity rates due to increased demand, leading to elevated costs for consumers and businesses. The concentration of energy usage during on-peak hours puts significant stress on the electrical grid, raising the risk of outages and reducing grid reliability. Utilities often implement demand charges and time-of-use pricing during these peak times to manage load and encourage energy conservation.
Impact on Residential and Commercial Users
Off-peak energy rates offer residential and commercial users lower electricity costs by encouraging consumption during hours of reduced demand, typically at night or weekends. On-peak energy rates are higher due to increased demand during daytime hours, affecting businesses with heavy daytime operations more significantly. Managing energy use around these pricing structures helps users optimize expenses and reduce strain on power grids.
Smart Meters and Time-of-Use Pricing
Smart meters enable precise tracking of energy consumption during Off-Peak and On-Peak hours, supporting Time-of-Use pricing models that encourage cost savings. By shifting your energy usage to Off-Peak periods, you can reduce electricity bills and optimize efficiency. Utility companies rely on smart meter data to adjust rates dynamically, promoting grid stability and sustainable energy consumption.
Reducing Carbon Footprint with Off-Peak Usage
Using off-peak energy significantly reduces your carbon footprint by tapping into electricity during times of lower demand when renewable sources like wind and solar are more abundant. On-peak energy usage often relies on fossil fuel power plants to meet high demand, leading to higher greenhouse gas emissions. Shifting your energy consumption to off-peak hours supports cleaner power grids and promotes sustainable environmental practices.
Strategies to Shift Energy Use to Off-Peak Periods
Shifting your energy use to off-peak periods can significantly reduce electricity costs by taking advantage of lower rates during those times. Implement strategies such as scheduling high-energy appliances like dishwashers and washing machines to run during off-peak hours, utilizing programmable thermostats to adjust heating and cooling when demand is lower, and charging electric vehicles overnight. Incorporating smart home devices and energy management systems helps optimize consumption patterns, ensuring maximum savings and efficiency.
Future Trends in Energy Management and Peak Pricing
Future trends in energy management emphasize advanced demand response technologies and smart grid integration to optimize off-peak and on-peak energy consumption. Dynamic peak pricing models leverage real-time data and AI to incentivize shifting Your usage to off-peak hours, reducing costs and grid strain. Renewable energy expansion and energy storage systems will further enhance flexibility and efficiency in managing peak demand periods.
Off-Peak vs On-Peak Energy Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com