Beech trees have smooth, gray bark and dense, sturdy wood ideal for furniture and flooring, while birch trees feature distinctive white, peeling bark and lighter, more flexible wood often used in plywood and paper products. Your choice between beech and birch depends on whether you prioritize durability and hardness or a lighter material with decorative bark.
Table of Comparison
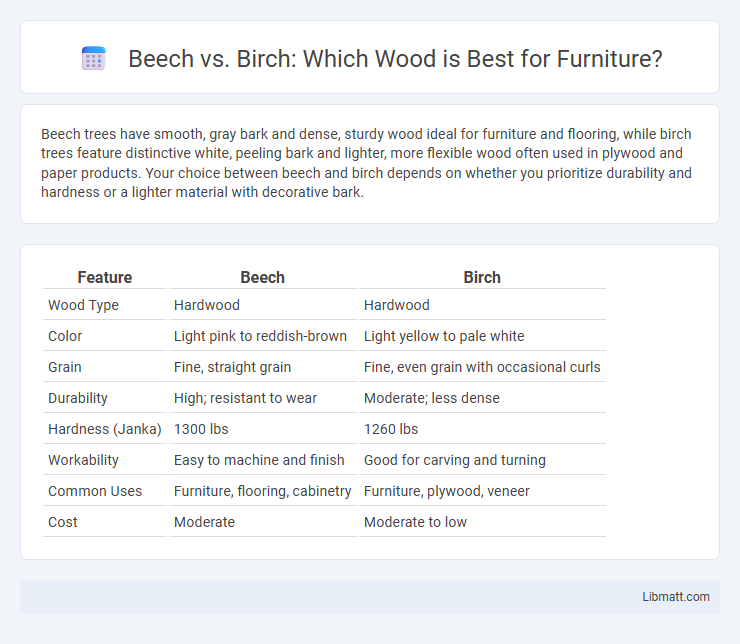
| Feature | Beech | Birch |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Hardwood |
| Color | Light pink to reddish-brown | Light yellow to pale white |
| Grain | Fine, straight grain | Fine, even grain with occasional curls |
| Durability | High; resistant to wear | Moderate; less dense |
| Hardness (Janka) | 1300 lbs | 1260 lbs |
| Workability | Easy to machine and finish | Good for carving and turning |
| Common Uses | Furniture, flooring, cabinetry | Furniture, plywood, veneer |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate to low |
Overview: Beech and Birch at a Glance
Beech trees (genus Fagus) feature smooth, gray bark and dense, hardwood prized for furniture and flooring, commonly found in temperate Europe and North America. Birch trees (genus Betula) display distinctive white or silver bark that peels in thin layers, with lighter wood often used in plywood and paper production, thriving in cooler climates across the Northern Hemisphere. Both species play crucial ecological roles, supporting diverse wildlife habitats and contributing to forest biodiversity.
Botanical Classification and Distribution
Beech (Fagus) and birch (Betula) belong to different botanical families, with beech classified under Fagaceae and birch under Betulaceae, highlighting their distinct evolutionary paths. Beech species predominantly thrive in temperate regions of Europe, Asia, and North America, while birch trees have a broader distribution extending across the Northern Hemisphere, including cold and boreal climates. Your choice between beech and birch depends on the specific environmental conditions and geographic location suitable for each genus.
Appearance: Bark, Leaves, and Wood Grain
Beech trees feature smooth, gray bark with thin, ovate leaves that have fine serrations, while birch trees are known for their distinctive white or silver bark that often peels in papery layers and triangular, toothed leaves. Beech wood exhibits a tight, straight grain with a uniform pale color, making it ideal for furniture, whereas birch wood has a finer, more pronounced grain pattern with a creamy white to light brown hue, favored for plywood and cabinetry. The contrasting bark textures and leaf shapes between beech and birch are key identifiers, while their wood grain differences influence their practical applications in woodworking.
Wood Hardness and Durability Comparison
Beech wood typically exhibits a higher Janka hardness rating around 1,300 lbf, making it harder and more resistant to dents compared to birch, which has a Janka rating near 1,260 lbf. In terms of durability, beech wood is dense and strong but less resistant to outdoor elements and moisture than birch, which possesses better natural resistance to decay and is often preferred for environments with higher humidity. Both woods are suitable for indoor furniture and flooring, but beech excels in wear resistance while birch offers improved longevity in variable conditions.
Common Uses in Furniture and Carpentry
Beech wood is highly favored in furniture making for its strength, fine grain, and smooth finish, making it ideal for chairs, tables, and cabinetry. Birch is commonly used in carpentry for plywood and veneer applications due to its hardness and uniform texture, offering durability and an attractive appearance. Both woods provide excellent workability, but beech's shock resistance makes it preferable for bending and turning projects.
Workability and Finishing Qualities
Beech wood offers excellent workability with its fine, even grain, making it easy to machine, sand, and carve for smooth finishes. Birch also works well but tends to be slightly harder, requiring more effort for intricate detailing, yet it achieves a durable surface with a polished appearance. Both woods respond well to staining and finishing, but beech's consistent texture allows for more uniform finishes in furniture and cabinetry.
Color, Texture, and Grain Distinctions
Beech wood typically features a light, creamy color with a fine, even texture and straight grain, making it smooth and uniform, ideal for furniture and cabinetry. Birch wood exhibits a pale yellow to warm reddish-brown hue, with a slightly coarser texture and a more pronounced, wavy grain pattern, adding visual interest to flooring and plywood. Color differences between beech and birch influence their aesthetic applications, while texture and grain distinctions affect their workability and finish quality.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Beech trees are highly sustainable due to their fast growth rate and ability to regenerate naturally, supporting biodiversity and soil health in temperate forests. Birch trees also contribute to sustainability by thriving in poor soil conditions, aiding in land reclamation and carbon sequestration. Both species offer ecological benefits, but beech wood's density and longevity often result in a lower overall environmental impact over time compared to the softer, less durable birch wood.
Cost and Availability Differences
Beech wood generally costs more than birch due to its denser grain and higher durability, making it a premium choice for furniture and flooring. Birch is more readily available and widely sourced, which often results in lower prices and easier accessibility for your projects. Both types of wood vary regionally in cost and availability, so considering local market conditions can help optimize your purchasing decision.
Choosing Between Beech and Birch: Key Considerations
Beech wood features a tight, uniform grain and a pale cream color, making it ideal for furniture requiring durability and a smooth finish, while birch offers a fine grain with a slightly yellow hue suited for cabinetry and plywood applications. Your choice between beech and birch depends on factors like resistance to wear, workability, and the desired aesthetic for your project. Understanding these characteristics helps ensure you select the perfect hardwood to match durability needs and design preferences.
Beech vs Birch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com