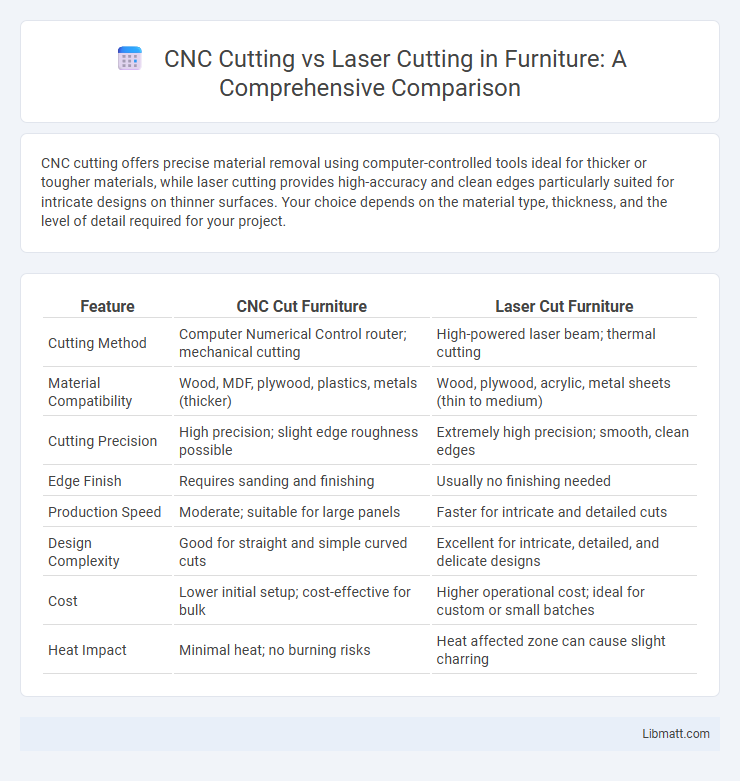
CNC cutting offers precise material removal using computer-controlled tools ideal for thicker or tougher materials, while laser cutting provides high-accuracy and clean edges particularly suited for intricate designs on thinner surfaces. Your choice depends on the material type, thickness, and the level of detail required for your project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | CNC Cut Furniture | Laser Cut Furniture |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | Computer Numerical Control router; mechanical cutting | High-powered laser beam; thermal cutting |
| Material Compatibility | Wood, MDF, plywood, plastics, metals (thicker) | Wood, plywood, acrylic, metal sheets (thin to medium) |
| Cutting Precision | High precision; slight edge roughness possible | Extremely high precision; smooth, clean edges |
| Edge Finish | Requires sanding and finishing | Usually no finishing needed |
| Production Speed | Moderate; suitable for large panels | Faster for intricate and detailed cuts |
| Design Complexity | Good for straight and simple curved cuts | Excellent for intricate, detailed, and delicate designs |
| Cost | Lower initial setup; cost-effective for bulk | Higher operational cost; ideal for custom or small batches |
| Heat Impact | Minimal heat; no burning risks | Heat affected zone can cause slight charring |
Introduction to CNC Cutting and Laser Cutting
CNC cutting uses computer numerical control to precisely shape materials by removing excess parts with tools like routers or mills, ideal for metals, plastics, and wood. Laser cutting employs a high-powered laser beam to vaporize or melt material, offering high precision and clean edges, especially suitable for thin metals and intricate designs. Both methods enhance manufacturing efficiency and accuracy but serve different material types and design complexities.
How CNC Cutting Works
CNC cutting operates through computer numerical control, guiding a motorized cutting tool over a material with precise movements based on programmed designs, enabling high accuracy in shaping metals, plastics, and wood. The process involves subtractive manufacturing where the cutting bit removes material by spinning or drilling, controlled by coordinates in the digital file. Unlike laser cutting, which uses a focused light beam to vaporize material, CNC cutting physically carves or mills the workpiece, allowing for varied tool types and depths in complex geometric patterns.
How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting works by directing a high-powered, focused laser beam onto a material, which melts, burns, or vaporizes specific sections to create precise shapes and designs. The process operates through computer numerical control (CNC), allowing for intricate cuts with minimal material waste and high repeatability. Your project benefits from laser cutting's ability to handle a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood, with exceptional accuracy and clean edges.
Material Compatibility in CNC and Laser Cutting
CNC cutting excels in processing a wide range of materials including metals, plastics, wood, and composites due to its versatile mechanical cutting tools. Laser cutting offers precise compatibility with thin metals, acrylics, wood, and certain fabrics but may struggle with reflective or thick materials. Your choice between CNC and laser cutting should consider the specific material properties and thickness to ensure optimal results in fabrication projects.
Precision and Accuracy: CNC vs Laser Cut
CNC cutting offers high precision through computer-controlled mechanical tools, often achieving tolerances as tight as +-0.001 inches, making it ideal for intricate metal and wood components. Laser cutting provides superior accuracy with its focused beam, capable of cutting materials with resolutions up to 0.001 inches and minimal kerf width, perfect for detailed designs in thinner materials. Both methods excel in precision, but laser cutting generally allows for finer detail and faster processing on thin-sheet applications.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
CNC cutting typically operates at a slower speed due to the mechanical process of carving or milling materials, making it ideal for thicker or harder substrates. Laser cutting achieves higher efficiency with rapid, non-contact beam technology enabling precise cuts at faster speeds, especially on thinner materials like plastics and metals. The choice between CNC and laser cutting depends on material type, thickness, and production volume requirements for optimal speed and efficiency.
Cost Analysis: CNC Cut vs Laser Cut
CNC cutting generally incurs higher initial costs due to expensive machinery and tooling but offers cost-efficiency for large production runs through reduced material waste and faster processing times. Laser cutting typically involves lower setup costs and excels in precision for detailed designs, making it more cost-effective for small batches or intricate work. Understanding your project volume and complexity will help determine whether CNC cut or laser cut provides the best value for your budget.
Edge Quality and Finish: Which is Better?
CNC cutting offers precise, clean edges with minimal burring, ideal for thicker materials requiring smooth finishes. Laser cutting excels in producing extremely fine, sharp edges with little to no mechanical stress, suitable for intricate designs on thinner materials. Your choice depends on the material thickness and desired edge quality, with laser cut providing superior finish in detailed work while CNC ensures robustness for heavy-duty applications.
Applications and Industries Using CNC and Laser Cutting
CNC cutting is widely utilized in industries like automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery for precise shaping of metals, plastics, and wood, excelling in tasks requiring deep cuts and complex geometries. Laser cutting finds extensive application in electronics, medical device manufacturing, and jewelry for its high accuracy and ability to cut intricate patterns on thin materials such as metals, plastics, and textiles. Your choice between CNC and laser cutting depends on the material thickness, desired precision, and specific industry requirements for production efficiency and quality.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
CNC cutting excels in precision and is ideal for thicker materials like metal, wood, and plastic, offering versatile options for intricate designs. Laser cutting provides superior detail and smooth edges, especially effective with thin materials such as acrylic, fabric, and paper. Selecting the right method depends on your project's material type, thickness, and the level of detail required to ensure optimal results and cost efficiency.
CNC cut vs laser cut Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com