Scandinavian design emphasizes simplicity, functionality, and natural materials, creating a warm and inviting atmosphere with clean lines and light colors. Industrial design focuses on raw, unfinished elements like metal and wood, showcasing utilitarian structures and a rugged, urban aesthetic that complements loft and warehouse spaces.
Table of Comparison
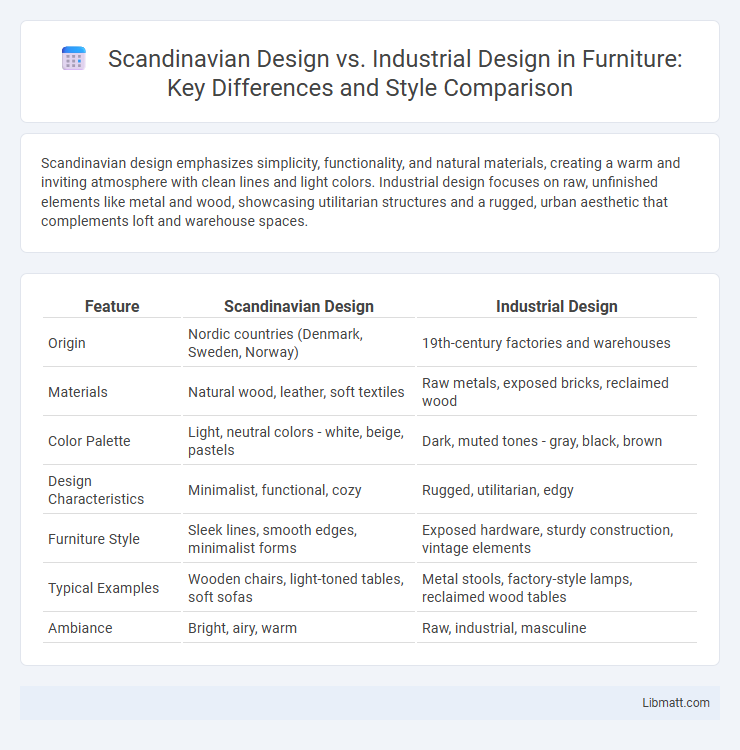
| Feature | Scandinavian Design | Industrial Design |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Nordic countries (Denmark, Sweden, Norway) | 19th-century factories and warehouses |
| Materials | Natural wood, leather, soft textiles | Raw metals, exposed bricks, reclaimed wood |
| Color Palette | Light, neutral colors - white, beige, pastels | Dark, muted tones - gray, black, brown |
| Design Characteristics | Minimalist, functional, cozy | Rugged, utilitarian, edgy |
| Furniture Style | Sleek lines, smooth edges, minimalist forms | Exposed hardware, sturdy construction, vintage elements |
| Typical Examples | Wooden chairs, light-toned tables, soft sofas | Metal stools, factory-style lamps, reclaimed wood tables |
| Ambiance | Bright, airy, warm | Raw, industrial, masculine |
Understanding Scandinavian Design: Key Principles
Scandinavian design emphasizes simplicity, functionality, and minimalism, often featuring natural materials like wood and neutral color palettes to create a calm and inviting atmosphere. It prioritizes clean lines, light-filled spaces, and practical aesthetics, making everyday objects both beautiful and useful. Your space benefits from this design by fostering a sense of openness and tranquility that enhances comfort and efficiency.
Defining Industrial Design: Core Characteristics
Industrial design emphasizes functionality, durability, and mass production with a focus on raw materials like metal, concrete, and exposed mechanical elements. It often features bold, utilitarian aesthetics that highlight structural components and manufacturing processes. Your choice between Scandinavian and industrial design depends on whether you prefer minimalist simplicity or rugged, industrial authenticity.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Scandinavian design originated in the early 20th century, emphasizing simplicity, functionality, and natural materials rooted in Nordic culture and craftsmanship. Industrial design emerged during the Industrial Revolution, focusing on mass production, durability, and utilitarian aesthetics driven by technological advancements. Your understanding of these styles reveals a contrast between Scandinavian elegance and warmth versus industrial ruggedness and efficiency.
Material Choices and Textures
Scandinavian design emphasizes natural materials like light woods, wool, and linen, creating warm, organic textures that promote simplicity and comfort. Industrial design favors raw, rugged materials such as exposed metal, concrete, and reclaimed wood, offering a gritty, utilitarian aesthetic with rough textures. Your choice between these styles will influence the tactile and visual impact of a space, balancing warmth and minimalism against edginess and functionality.
Color Palettes: Minimalism vs. Boldness
Scandinavian design emphasizes minimalism with a color palette dominated by soft neutrals, whites, and muted pastels, creating a calm and airy atmosphere. Industrial design favors boldness through the use of darker tones such as black, gray, and deep browns, often paired with raw materials like metal and exposed brick. This contrast highlights Scandinavian design's focus on simplicity and lightness, while industrial design conveys strength and ruggedness.
Functionality and Practicality in Both Styles
Scandinavian design emphasizes minimalism, clean lines, and functionality with a focus on creating practical, user-friendly furniture and spaces that optimize natural light and comfort. Industrial design prioritizes raw materials, exposed structures, and rugged textures, combining durability with practicality for urban environments and repurposed spaces. Both styles enhance functionality but Scandinavian design leans towards simplicity and coziness, while industrial design highlights robustness and visual storytelling through materials.
Furniture Forms and Iconic Pieces
Scandinavian design emphasizes clean lines, organic shapes, and functionality, with iconic pieces like Arne Jacobsen's Egg Chair and Alvar Aalto's plywood lounge chair highlighting natural materials and minimalism. Industrial design features raw, utilitarian forms with exposed metal, wood, and rivets, exemplified by classics such as the Tolix Marais chair and Jean Prouve's Standard chair, focusing on durability and industrial aesthetics. Both styles influence modern interiors but differ in their approach to material use and visual warmth.
Atmosphere and Emotional Impact
Scandinavian design creates a warm, inviting atmosphere through its use of natural materials, soft colors, and minimalist forms, fostering a sense of tranquility and comfort in your space. Industrial design evokes an edgy, urban feel with its exposed structures, raw metals, and bold lines, often generating a dynamic and energetic environment. Each style influences emotional impact differently, with Scandinavian design encouraging relaxation and calm, while industrial design sparks creativity and intensity.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Scandinavian design emphasizes sustainability through the use of natural, renewable materials like wood and wool, combined with minimalist aesthetics that reduce resource consumption. Industrial design often incorporates recycled metals and repurposed industrial materials but may prioritize function over environmental impact, leading to a broader environmental footprint. Both styles increasingly integrate eco-friendly practices, yet Scandinavian design remains more deeply rooted in long-term environmental responsibility.
Choosing the Right Style for Your Space
Scandinavian design emphasizes simplicity, functionality, and natural elements, featuring light colors, clean lines, and organic materials that create a calm and airy atmosphere. Industrial design incorporates raw materials like metal and exposed brick, with a rugged, utilitarian aesthetic that highlights architectural features and mechanical details. When choosing the right style for your space, consider whether you prefer the warmth and minimalism of Scandinavian design or the bold, edgy character of industrial design to reflect your personality and lifestyle.
Scandinavian design vs industrial design Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com