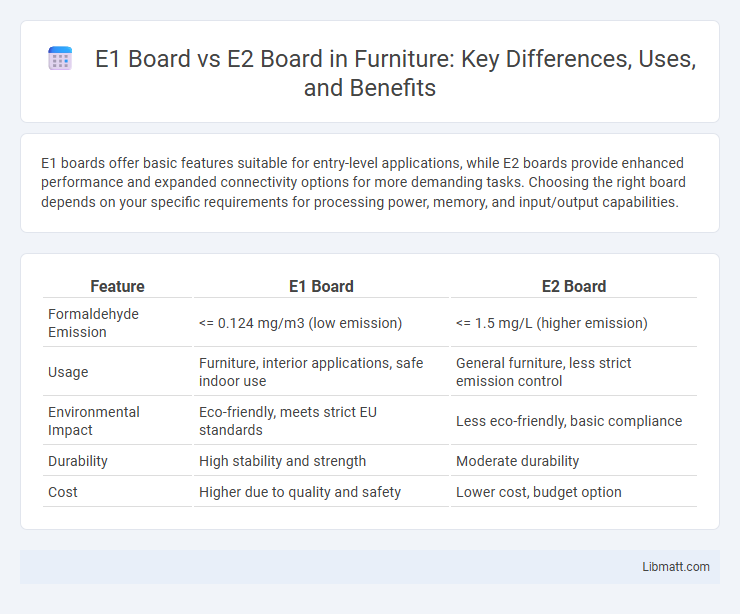
E1 boards offer basic features suitable for entry-level applications, while E2 boards provide enhanced performance and expanded connectivity options for more demanding tasks. Choosing the right board depends on your specific requirements for processing power, memory, and input/output capabilities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | E1 Board | E2 Board |
|---|---|---|
| Formaldehyde Emission | <= 0.124 mg/m3 (low emission) | <= 1.5 mg/L (higher emission) |
| Usage | Furniture, interior applications, safe indoor use | General furniture, less strict emission control |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, meets strict EU standards | Less eco-friendly, basic compliance |
| Durability | High stability and strength | Moderate durability |
| Cost | Higher due to quality and safety | Lower cost, budget option |
Introduction to E1 and E2 Boards
E1 and E2 boards represent fundamental types of electronic circuit boards designed for distinct applications in industrial and communication systems. The E1 board typically functions as a primary transmission interface supporting high-speed data transfer via E1 lines at 2.048 Mbps, crucial in telecommunications infrastructure. In contrast, the E2 board often extends capabilities by providing enhanced processing power, additional interfaces, or improved signal integrity, tailored for complex networking environments.
Differences in Formaldehyde Emission Standards
E1 boards exhibit formaldehyde emissions below 0.1 ppm (parts per million), aligning with strict European standards for indoor air quality, whereas E2 boards allow higher emissions, typically up to 1.5 ppm. This significant difference impacts their suitability for applications requiring low-emission materials, such as residential furniture and interior fittings. Manufacturers prioritize E1 boards to meet eco-friendly certifications and regulatory compliance in markets with stringent formaldehyde limits.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
E1 boards are primarily made from formaldehyde-based adhesives with controlled emission levels compliant with European standards, while E2 boards use higher formaldehyde content resulting in less stringent environmental performance. The manufacturing process for E1 emphasizes advanced resin formulations and curing techniques to minimize harmful emissions, ensuring safety and durability. Your choice between E1 and E2 boards affects indoor air quality due to these differences in composition and production methods.
Health and Environmental Impacts
E1 boards have lower formaldehyde emissions, meeting stringent European standards for indoor air quality and reducing health risks such as respiratory issues and allergies. E2 boards exhibit higher levels of formaldehyde, which can contribute to indoor air pollution and pose greater environmental concerns due to increased chemical off-gassing. Choosing E1 boards supports sustainable building practices by minimizing toxic emissions and enhancing long-term environmental safety.
Performance and Durability Comparison
E1 boards typically feature lower processing power and fewer input/output options compared to E2 boards, resulting in modest performance suited for basic applications. E2 boards offer enhanced CPU speeds, greater memory capacity, and improved thermal management, facilitating higher performance and extended operational longevity. Durability-wise, E2 boards are often built with advanced materials and robust circuit designs, providing superior resistance to wear, heat, and environmental stress compared to the more basic construction of E1 boards.
Applications in Furniture and Construction
E1 boards, known for their low formaldehyde emissions, are widely used in furniture manufacturing, providing a safer indoor environment and compliance with health standards. E2 boards, with slightly higher emission levels, are often employed in construction for non-visible structural purposes where cost-effectiveness is prioritized over strict emission control. Your choice between E1 and E2 boards should consider the specific application's exposure and regulatory requirements in furniture or building projects.
Cost Analysis: E1 vs E2 Boards
E1 boards generally offer a cost-effective solution with lower initial investment compared to E2 boards, making them ideal for budget-sensitive projects. E2 boards provide enhanced features and higher performance, which justify their higher price through long-term value and reduced maintenance costs. Your decision should balance upfront expenses with expected operational efficiency and project requirements.
Global Regulations and Certifications
E1 boards comply with strict global regulations such as UL94 V-0 for flammability and RoHS for hazardous substances, ensuring safe and environmentally friendly performance in electronics manufacturing. E2 boards often feature extended certifications including IPC-4101 for high-performance laminates, meeting rigorous standards for aerospace and military applications. Understanding these certifications ensures your products meet international safety and quality requirements, reducing risk and enhancing market acceptance.
Choosing the Right Board for Your Project
Selecting the right board for your project depends on the specific requirements of your application; E1 boards typically offer basic functionality suitable for straightforward tasks, while E2 boards provide enhanced performance with advanced features and greater processing power. Understanding the complexity of your project, including computational needs and peripheral interfaces, will guide your choice toward better efficiency and future scalability. Your project benefits from aligning board capabilities with technical demands to optimize cost-effectiveness and operational success.
Future Trends in Engineered Wood Boards
E1 boards, characterized by low formaldehyde emissions, are increasingly preferred for eco-friendly construction, while E2 boards offer higher durability and moisture resistance for industrial applications. Future trends indicate a growing demand for composite wood products integrating nanotechnology to enhance strength and reduce environmental impact. Innovations in bio-based adhesives and digital manufacturing processes will further drive the evolution and sustainability of engineered wood boards.
E1 board vs E2 board Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com