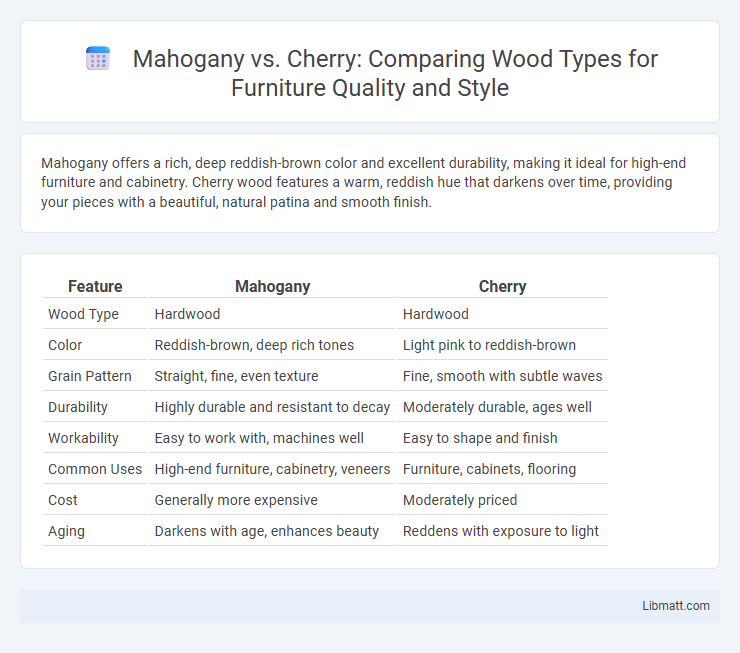
Mahogany offers a rich, deep reddish-brown color and excellent durability, making it ideal for high-end furniture and cabinetry. Cherry wood features a warm, reddish hue that darkens over time, providing your pieces with a beautiful, natural patina and smooth finish.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mahogany | Cherry |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Hardwood |
| Color | Reddish-brown, deep rich tones | Light pink to reddish-brown |
| Grain Pattern | Straight, fine, even texture | Fine, smooth with subtle waves |
| Durability | Highly durable and resistant to decay | Moderately durable, ages well |
| Workability | Easy to work with, machines well | Easy to shape and finish |
| Common Uses | High-end furniture, cabinetry, veneers | Furniture, cabinets, flooring |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Moderately priced |
| Aging | Darkens with age, enhances beauty | Reddens with exposure to light |
Introduction to Mahogany and Cherry Wood
Mahogany and cherry are premium hardwoods prized for their durability and rich color. Mahogany showcases deep reddish-brown hues and a fine, straight grain, making it ideal for high-end furniture and musical instruments. Cherry wood features warm, reddish tones that darken with age, offering a smooth texture perfect for elegant cabinetry and flooring, enhancing your interior spaces.
Botanical Origins and Species Differences
Mahogany primarily comes from the Swietenia genus, especially Swietenia macrophylla native to Central and South America, known for its straight grain and rich reddish-brown hue. Cherry wood, belonging to the Prunus genus with Prunus serotina as a key species native to North America, features a fine, smooth texture and deepens from light pink to reddish-brown as it ages. Understanding the botanical origins and species differences helps you choose the right wood based on grain pattern, color evolution, and regional availability.
Appearance and Color Comparison
Mahogany features a rich, reddish-brown hue with a fine, straight grain that deepens over time, creating a warm and elegant appearance. Cherry wood starts with a light pinkish tone that darkens to a rich reddish-brown, showcasing a smooth, satiny texture and subtle grain patterns. Your choice depends on whether you prefer mahogany's consistent warmth or cherry's dynamic color transformation and delicate grain.
Grain Patterns and Texture
Mahogany exhibits a straight, fine, and even grain pattern with a smooth texture, making it highly prized for its uniform appearance and workability. Cherry wood features a fine, straight grain with occasional waves or curls, offering a slightly more varied texture that enhances its rich, warm color. Both hardwoods provide excellent durability but differ in grain complexity, with mahogany's consistent pattern favored for elegance and cherry's subtle variations prized for character.
Durability and Hardness
Mahogany offers excellent durability with a Janka hardness rating of around 800-900, making it resistant to wear and everyday damage. Cherry wood, slightly softer with a Janka rating of about 950, tends to be more susceptible to dents but provides good long-term strength when properly maintained. Choosing between the two depends on your need for a balance between hardness and aesthetic aging, as cherry wood darkens beautifully over time while mahogany retains its rich tone.
Workability and Ease of Use
Mahogany offers excellent workability due to its straight grain and moderate hardness, making it easy to saw, plane, and carve with minimal blunting of tools. Cherry wood, while slightly harder, also carves smoothly and finishes well but may require sharper blades for intricate detailing. Both woods are favored by woodworkers for furniture and cabinetry, with mahogany prized for its ease in shaping and cherry valued for its fine, smooth finish.
Common Uses in Furniture and Cabinetry
Mahogany is prized for its deep, rich reddish-brown hue and durability, making it a top choice for high-end furniture, ornate cabinetry, and musical instruments. Cherry wood features a warm, reddish tone that darkens with age, commonly used in traditional and contemporary cabinetry, fine furniture, and interior millwork. Both woods offer excellent workability and finish quality, but mahogany is favored for its resistance to rot and decay, while cherry is valued for its smooth grain and elegant aging characteristics.
Pricing and Availability
Mahogany wood generally commands higher prices due to its rich color, durability, and limited availability, making it a premium choice for furniture and cabinetry. In contrast, cherry wood is more readily available and affordable while still offering a warm, elegant appearance that darkens beautifully with age. Availability of mahogany can be limited by regulations and sustainable harvesting practices, whereas cherry is widely sourced, contributing to its lower market cost.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mahogany and cherry wood differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability; mahogany, often sourced from tropical rainforests, faces challenges related to deforestation and habitat loss, making certified sustainable harvesting crucial. Cherry wood, primarily harvested from temperate forests in North America, generally has a lower ecological footprint due to better-regulated forestry practices and faster growth rates. Choosing FSC-certified mahogany or cherry supports responsible forestry, helping mitigate environmental degradation and promote sustainable wood production.
Choosing Between Mahogany and Cherry Wood
Selecting between mahogany and cherry wood depends on the desired grain appearance, durability, and color depth for a project. Mahogany offers a rich reddish-brown hue with a straight grain pattern and higher resistance to wear, ideal for high-end furniture and cabinetry. Cherry wood exhibits a smooth texture with a warm, reddish tone that darkens over time, making it suitable for elegant interior finishes and custom woodworking.
Mahogany vs Cherry Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com