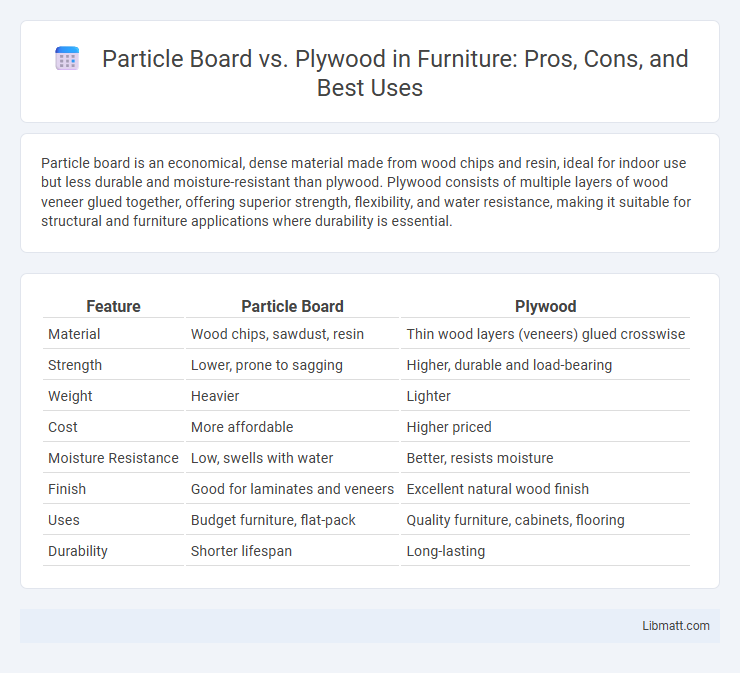
Particle board is an economical, dense material made from wood chips and resin, ideal for indoor use but less durable and moisture-resistant than plywood. Plywood consists of multiple layers of wood veneer glued together, offering superior strength, flexibility, and water resistance, making it suitable for structural and furniture applications where durability is essential.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Particle Board | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Wood chips, sawdust, resin | Thin wood layers (veneers) glued crosswise |
| Strength | Lower, prone to sagging | Higher, durable and load-bearing |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Cost | More affordable | Higher priced |
| Moisture Resistance | Low, swells with water | Better, resists moisture |
| Finish | Good for laminates and veneers | Excellent natural wood finish |
| Uses | Budget furniture, flat-pack | Quality furniture, cabinets, flooring |
| Durability | Shorter lifespan | Long-lasting |
Introduction to Particle Board and Plywood
Particle board is a manufactured wood product made from wood chips, sawdust, and resin compressed into sheets, offering an affordable and lightweight alternative for furniture and construction. Plywood consists of multiple layers of thin wood veneers glued together with grains alternating, providing superior strength, durability, and resistance to warping. Both materials are widely used in interior applications, but their structural properties and cost differences influence specific usage choices.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Particle board is composed of wood chips, sawdust, and resin, which are compressed and bonded under heat and pressure to form dense, uniform panels primarily used in furniture and cabinetry. Plywood consists of multiple thin layers of wood veneers, glued together with adjacent layers having their wood grain rotated up to 90 degrees, enhancing strength and reducing warping. The manufacturing process of particle board emphasizes cost-effectiveness and recyclability, while plywood focuses on durability and structural performance through its cross-laminated veneer construction.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Particle board offers lower strength and durability compared to plywood, making it more susceptible to chipping, swelling, and wear under heavy loads or moisture exposure. Plywood's layered construction with cross-grain veneers provides superior structural integrity, resistance to warping, and longer lifespan in furniture and construction applications. For high-stress environments, plywood's enhanced strength-to-weight ratio and moisture resistance make it the preferred material over particle board.
Cost Differences and Affordability
Particle board is generally more affordable than plywood due to its composition of compressed wood chips and resin, making it a cost-effective option for budget-conscious projects. Plywood, made from thin layers of wood veneer, typically costs more but offers superior strength and durability, which justifies the higher price for long-term investments. When choosing materials for your project, consider particle board for low-cost furniture or temporary use, while plywood is better suited for applications requiring enhanced structural integrity.
Moisture Resistance and Suitability
Particle board offers limited moisture resistance, making it less suitable for areas prone to humidity or water exposure compared to plywood. Plywood consists of multiple layers of wood veneer with better structural integrity and enhanced moisture resistance, ideal for bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor applications. Your choice should prioritize plywood when durability and moisture protection are critical for your project.
Weight and Ease of Handling
Particle board is generally heavier and denser than plywood, making it more challenging to handle and transport during construction or furniture assembly. Plywood is lighter and offers better strength-to-weight ratio, which simplifies your project by reducing fatigue and improving maneuverability. This ease of handling makes plywood the preferred choice for tasks requiring frequent adjustments or movement.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Particle board typically has a higher environmental impact due to the use of formaldehyde-based resins and lower durability, which leads to more frequent replacements and increased waste. Plywood, made from layers of solid wood veneers bonded with non-toxic adhesives, generally offers better sustainability through longer lifespan and recyclability. Both materials contribute to deforestation, but plywood sourced from certified sustainable forests reduces ecological harm compared to particle board made from mixed recycled wood fibers.
Common Applications in Construction and Furniture
Particle board is commonly used in low-cost furniture, cabinetry, and underlayment due to its affordability and smooth surface for laminates. Plywood is preferred in structural applications, flooring, roofing, and high-quality furniture for its superior strength, durability, and resistance to warping. Builders often choose plywood for load-bearing elements, while particle board suits budget-friendly, decorative projects with less structural demand.
Aesthetic Appeal and Finishing Options
Particle board offers a smooth, flat surface ideal for laminated finishes, providing a consistent and budget-friendly aesthetic appeal, though it lacks the natural grain texture found in plywood. Plywood features rich wood grain patterns and can be stained, varnished, or painted to enhance its natural beauty, making it preferable for visible furniture or decorative panels. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize cost-effective uniformity or the authentic wood appearance and finishing versatility.
Choosing Between Particle Board and Plywood
When choosing between particle board and plywood, consider factors such as strength, durability, and cost. Plywood offers superior structural integrity and moisture resistance, making it ideal for furniture and cabinetry that requires long-lasting support. Particle board is more budget-friendly and suitable for lightweight projects, but may not withstand heavy loads or moisture exposure as well as plywood.
Particle board vs plywood Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com