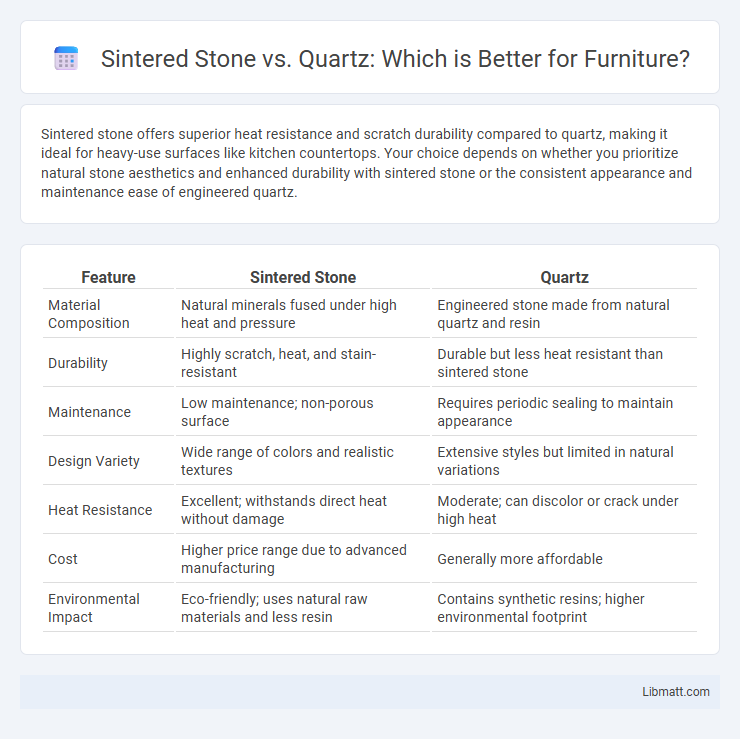
Sintered stone offers superior heat resistance and scratch durability compared to quartz, making it ideal for heavy-use surfaces like kitchen countertops. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize natural stone aesthetics and enhanced durability with sintered stone or the consistent appearance and maintenance ease of engineered quartz.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sintered Stone | Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural minerals fused under high heat and pressure | Engineered stone made from natural quartz and resin |
| Durability | Highly scratch, heat, and stain-resistant | Durable but less heat resistant than sintered stone |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; non-porous surface | Requires periodic sealing to maintain appearance |
| Design Variety | Wide range of colors and realistic textures | Extensive styles but limited in natural variations |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent; withstands direct heat without damage | Moderate; can discolor or crack under high heat |
| Cost | Higher price range due to advanced manufacturing | Generally more affordable |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; uses natural raw materials and less resin | Contains synthetic resins; higher environmental footprint |
Introduction to Sintered Stone and Quartz
Sintered stone is an engineered material created by compacting natural minerals at high temperatures and pressure, resulting in a durable, non-porous surface ideal for countertops and flooring. Quartz surfaces combine natural quartz crystals with resins and pigments, offering a versatile, low-maintenance option known for its scratch and stain resistance. Both materials provide aesthetic appeal and functional benefits, but sintered stone typically excels in heat resistance and UV stability.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Sintered stone is produced by compacting natural minerals like quartz, feldspar, and silica at extremely high temperatures and pressures, resulting in a highly durable and chemically stable material. Quartz countertops are engineered by combining approximately 90-95% natural quartz with resins and pigments, which are then cured and polished to create a non-porous surface. Understanding these distinct manufacturing processes helps you choose the right countertop based on durability, maintenance, and aesthetic preferences.
Appearance and Design Options
Sintered stone offers a wide range of natural hues and intricate patterns that mimic materials like marble, granite, and concrete, providing versatility for sophisticated and contemporary designs. Quartz surfaces feature consistent color and texture due to engineered composition, allowing for uniformity in large-scale applications and modern aesthetics. Your choice between sintered stone and quartz will depend on whether you prefer unique, nature-inspired patterns or consistent, customizable color palettes for your design projects.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Sintered stone exhibits superior durability and strength compared to quartz due to its manufacturing process that involves high heat and pressure, resulting in a dense, non-porous surface resistant to scratches, heat, and impact. Quartz, composed primarily of natural quartz crystals combined with resin, offers good hardness and resistance but is more prone to heat damage and surface scratches over time. Both materials are highly durable, but sintered stone's enhanced resistance to thermal shock and chemical exposure makes it ideal for heavy-use applications and outdoor environments.
Stain and Heat Resistance
Sintered stone offers superior stain and heat resistance compared to quartz, making it highly durable for kitchen and outdoor applications. Its manufacturing process involves high-temperature sintering, resulting in a non-porous surface that resists stains from oils, wine, and acidic substances more effectively than quartz. Your choice of sintered stone ensures enhanced longevity and minimal maintenance when exposed to heat and potential staining agents.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Sintered stone requires minimal maintenance due to its high resistance to stains, scratches, and heat, making it ideal for busy kitchens and bathrooms. Quartz surfaces also offer low maintenance but can be more susceptible to heat damage and require mild cleaning agents to preserve their resin binder. Your cleaning routine for both materials should involve non-abrasive cloths and pH-neutral cleaners to maintain their appearance and durability over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sintered stone offers a lower environmental impact than quartz due to its use of natural raw materials such as minerals, sand, and porcelain, processed with minimal water and energy consumption through advanced sintering technology. Quartz, while durable, relies heavily on resin binders and synthetic materials, which contribute to higher carbon emissions and challenges in recycling. The sustainability of sintered stone is enhanced by its longevity, resistance to wear, and ability to be recycled, making it a greener choice for eco-conscious construction and design projects.
Cost and Value Analysis
Sintered stone typically costs between $50 and $120 per square foot, offering superior durability and heat resistance compared to quartz, which ranges from $40 to $100 per square foot. While quartz provides a lower upfront price, sintered stone's enhanced scratch resistance and UV stability deliver greater long-term value, especially in high-traffic or outdoor applications. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement frequency, positions sintered stone as a more cost-effective investment over time.
Applications: Where to Use Each Material
Sintered stone excels in outdoor applications such as facades, exterior cladding, and countertops exposed to harsh weather due to its high resistance to UV rays and temperature fluctuations. Quartz is ideal for indoor surfaces like kitchen countertops, bathroom vanities, and backsplashes because of its non-porous nature and ease of maintenance. For your interior design projects, choose quartz for durability and stain resistance, while sintered stone offers unmatched durability and weather resistance for exterior uses.
Choosing the Right Surface for Your Needs
Sintered stone offers unmatched durability, resistance to heat, stains, and scratches, making it ideal for high-traffic kitchen countertops and outdoor applications. Quartz surfaces provide a non-porous, low-maintenance option with a wide variety of colors and patterns, perfect for indoor spaces requiring easy cleaning and stain resistance. Selecting between sintered stone and quartz depends on balancing the need for extreme durability with aesthetic versatility and maintenance preferences.
Sintered stone vs quartz Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com