Solar control glass reduces heat gain and glare by reflecting or absorbing solar radiation, making your interiors cooler and more comfortable. Thermal insulation glass provides superior energy efficiency by minimizing heat transfer through windows, helping maintain consistent indoor temperatures and lowering heating and cooling costs.
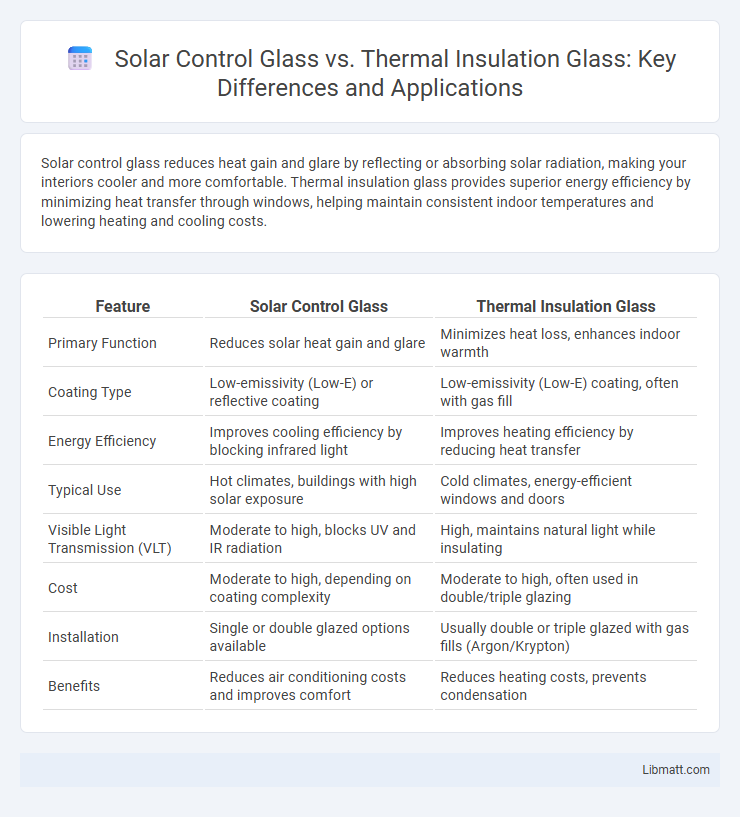
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solar Control Glass | Thermal Insulation Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reduces solar heat gain and glare | Minimizes heat loss, enhances indoor warmth |
| Coating Type | Low-emissivity (Low-E) or reflective coating | Low-emissivity (Low-E) coating, often with gas fill |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves cooling efficiency by blocking infrared light | Improves heating efficiency by reducing heat transfer |
| Typical Use | Hot climates, buildings with high solar exposure | Cold climates, energy-efficient windows and doors |
| Visible Light Transmission (VLT) | Moderate to high, blocks UV and IR radiation | High, maintains natural light while insulating |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on coating complexity | Moderate to high, often used in double/triple glazing |
| Installation | Single or double glazed options available | Usually double or triple glazed with gas fills (Argon/Krypton) |
| Benefits | Reduces air conditioning costs and improves comfort | Reduces heating costs, prevents condensation |
Introduction to Solar Control Glass and Thermal Insulation Glass
Solar control glass reduces heat gain by reflecting and absorbing solar radiation, enhancing indoor comfort and energy efficiency, especially in warm climates. Thermal insulation glass primarily minimizes heat transfer through conduction and convection, maintaining indoor temperatures by reducing heat loss in cold weather and heat gain in hot weather. Both types of glass improve building energy performance but target different aspects of thermal management.
How Solar Control Glass Works
Solar control glass works by reflecting and absorbing a significant portion of solar radiation to reduce heat transmission through windows, enhancing indoor comfort and energy efficiency. It typically incorporates special coatings or films that selectively filter infrared and ultraviolet rays while allowing visible light to pass through, minimizing glare and UV damage. Your choice of solar control glass can lower cooling costs and maintain a consistent indoor temperature compared to standard thermal insulation glass.
How Thermal Insulation Glass Functions
Thermal insulation glass functions by minimizing heat transfer between indoor and outdoor environments through multiple glass layers separated by inert gas fills, which reduce conductive and convective heat losses. Low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings on the glass surfaces reflect infrared radiation, further enhancing insulation performance by keeping heat inside during winter and outside during summer. This combination of gas fill and Low-E coatings results in superior energy efficiency compared to solar control glass, which primarily focuses on reducing solar heat gain rather than overall insulation.
Key Differences Between Solar Control and Thermal Insulation Glass
Solar control glass primarily reduces solar heat gain by reflecting and absorbing a significant portion of the sun's infrared radiation, enhancing indoor comfort and reducing cooling costs. Thermal insulation glass focuses on minimizing heat transfer through the window by using low-emissivity coatings and gas fills to improve energy efficiency during colder months. Your choice between these glasses depends on whether you prioritize blocking external heat for a cooler interior or retaining indoor heat to reduce heating expenses.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Solar control glass reduces heat gain by reflecting and absorbing solar radiation, significantly decreasing cooling loads in buildings. Thermal insulation glass enhances energy efficiency by minimizing heat transfer through multiple insulating layers, providing superior retention of indoor temperatures in diverse climates. Comparing both, solar control glass is more effective in hot environments for reducing air conditioning costs, while thermal insulation glass excels in maintaining warmth during colder periods, optimizing overall energy savings based on climate conditions.
Impact on Indoor Comfort and Climate
Solar control glass reduces indoor heat gain by reflecting and absorbing solar radiation, thereby maintaining cooler interior temperatures and minimizing reliance on air conditioning. Thermal insulation glass primarily limits heat transfer through conduction, preserving indoor warmth during winter and reducing heating costs. Both contribute to enhanced indoor climate control, with solar control glass focusing on summer comfort and thermal insulation glass optimizing year-round energy efficiency.
Cost Considerations and Long-Term Savings
Solar control glass typically has a higher upfront cost due to advanced coatings that reflect solar radiation, reducing cooling expenses over time. Thermal insulation glass focuses on minimizing heat transfer, resulting in lower heating and cooling bills, which can lead to significant long-term savings. Your choice should weigh initial investment against potential energy savings based on your climate and building needs.
Design and Aesthetic Options
Solar control glass offers a wide range of tinted, reflective, and patterned designs that enhance building aesthetics while reducing heat gain. Thermal insulation glass focuses on multi-layered constructions with Low-E coatings that prioritize energy efficiency without compromising transparency. Your choice depends on whether you value diverse visual styles typical of solar control glass or the sleek, clear look combined with superior thermal performance found in insulation glass.
Best Applications for Each Glass Type
Solar control glass is ideal for commercial buildings and facades in hot climates, reducing heat gain and minimizing cooling costs by reflecting and absorbing solar radiation. Thermal insulation glass suits residential and office environments in colder regions, enhancing energy efficiency by trapping indoor heat and reducing heat loss through windows. Both glass types improve occupant comfort but serve distinct functions based on climate and energy-saving priorities.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Building
Selecting the right glass for your building depends on balancing energy efficiency and comfort; solar control glass effectively reduces solar heat gain and glare, making it ideal for hot climates and buildings with large glazing areas. Thermal insulation glass minimizes heat transfer between interior and exterior environments, enhancing indoor temperature stability and reducing heating and cooling costs in colder regions. Understanding your building's climate, orientation, and energy goals is crucial to deciding between solar control and thermal insulation glass for optimal performance.
Solar control glass vs thermal insulation glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com