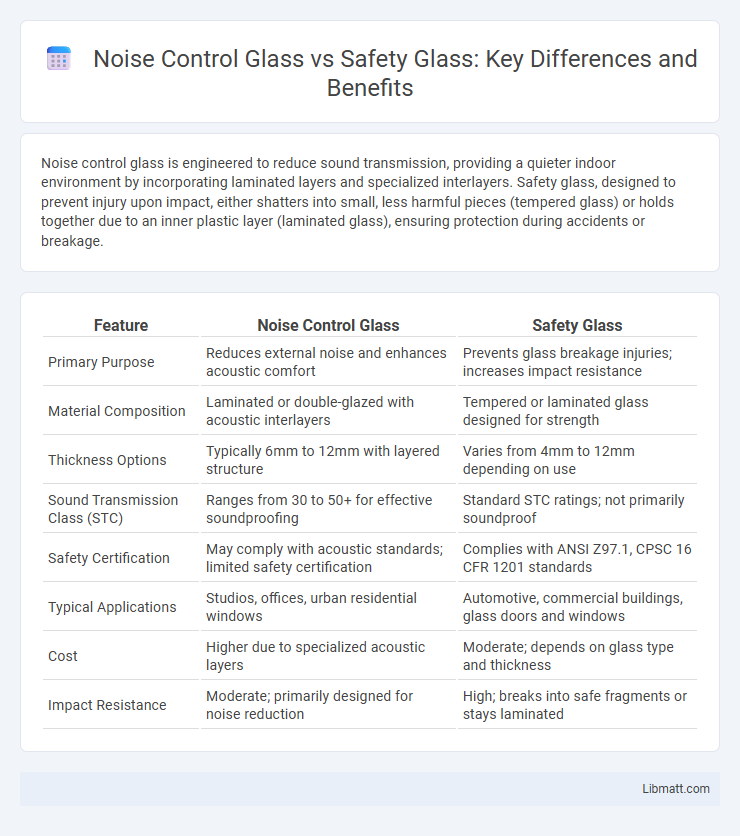
Noise control glass is engineered to reduce sound transmission, providing a quieter indoor environment by incorporating laminated layers and specialized interlayers. Safety glass, designed to prevent injury upon impact, either shatters into small, less harmful pieces (tempered glass) or holds together due to an inner plastic layer (laminated glass), ensuring protection during accidents or breakage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Noise Control Glass | Safety Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Reduces external noise and enhances acoustic comfort | Prevents glass breakage injuries; increases impact resistance |
| Material Composition | Laminated or double-glazed with acoustic interlayers | Tempered or laminated glass designed for strength |
| Thickness Options | Typically 6mm to 12mm with layered structure | Varies from 4mm to 12mm depending on use |
| Sound Transmission Class (STC) | Ranges from 30 to 50+ for effective soundproofing | Standard STC ratings; not primarily soundproof |
| Safety Certification | May comply with acoustic standards; limited safety certification | Complies with ANSI Z97.1, CPSC 16 CFR 1201 standards |
| Typical Applications | Studios, offices, urban residential windows | Automotive, commercial buildings, glass doors and windows |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized acoustic layers | Moderate; depends on glass type and thickness |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate; primarily designed for noise reduction | High; breaks into safe fragments or stays laminated |
Understanding Noise Control Glass
Noise control glass is engineered with laminated layers that absorb and reduce sound transmission, offering superior acoustic insulation compared to traditional safety glass. Unlike safety glass, which prioritizes impact resistance and shatter prevention through tempered or laminated construction, noise control glass specifically targets and minimizes noise pollution from external sources. This specialized glass is ideal for environments requiring both sound attenuation and clarity, such as recording studios, office spaces, and urban residences near heavy traffic.
What Is Safety Glass?
Safety glass is specially designed to minimize injury risk upon impact, featuring either laminated or tempered structures that prevent shards from causing harm. Laminated safety glass consists of two or more layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, holding fragments together when broken. You benefit from enhanced protection in environments prone to accidents or natural forces by choosing safety glass over standard noise control glass.
Key Differences Between Noise Control and Safety Glass
Noise control glass is engineered with multiple laminated layers designed to reduce sound transmission, enhancing acoustic insulation, while safety glass prioritizes strength and shatter resistance to protect against impact and breakage. Noise control glass typically contains special interlayers that absorb sound waves, whereas safety glass uses toughened or laminated materials to prevent shards from causing injury upon breaking. Understanding these key differences helps you select the right glass type based on whether your priority is soundproofing or physical safety.
Acoustic Performance: Which Glass Reduces Noise Better?
Noise control glass is specifically engineered with laminated layers and specialized interlayers to significantly reduce sound transmission, offering superior acoustic performance compared to safety glass. Safety glass, such as tempered or laminated types, primarily focuses on impact resistance and shatter prevention but provides less effective noise reduction. For your space where minimizing external noise is crucial, noise control glass delivers better sound insulation and improved acoustic comfort.
Safety Features: Impact Resistance Comparison
Noise control glass is designed primarily to reduce sound transmission but also offers moderate impact resistance, enhancing safety in environments where noise and minor impacts are concerns. Safety glass, including tempered and laminated types, is engineered with superior impact resistance, shattering into small, blunt pieces or remaining bonded to prevent injury upon breakage. Your choice should weigh noise reduction benefits against the higher impact safety standards provided by safety glass for maximum protection.
Typical Applications of Noise Control Glass
Noise control glass is predominantly used in environments requiring enhanced sound insulation such as recording studios, hospitals, and urban residential buildings near busy streets, where reducing external noise is critical. Unlike safety glass, which prioritizes impact resistance and shatter protection in applications like car windows and commercial storefronts, noise control glass focuses on acoustic performance to improve comfort and privacy. Your choice of glass should align with the need for soundproofing in spaces where noise disturbance can affect productivity, health, or daily living quality.
Where Is Safety Glass Commonly Used?
Safety glass is commonly used in automotive windshields, building windows, and glass doors to protect against impact and reduce injury risk. Unlike noise control glass, which focuses on reducing sound transmission, safety glass is designed to shatter into small, less harmful pieces upon breakage. Your choice between these glasses should consider where impact resistance is critical, such as in vehicles and high-traffic areas.
Installation Considerations for Both Glass Types
Installation of noise control glass requires precise sealing and adequate layering to maximize sound insulation, often involving laminated or double-glazed units. Safety glass installation prioritizes proper fitting and compliance with building codes to ensure it shatters safely under impact, commonly using tempered or laminated glass types. Your choice between these glasses should consider both acoustic performance and safety requirements during installation to achieve the desired functionality.
Cost Comparison: Noise Control vs Safety Glass
Noise control glass generally incurs higher costs due to its specialized laminated layers and acoustic interlayers designed to reduce sound transmission, whereas safety glass, including tempered and laminated variants, is typically less expensive as it prioritizes impact resistance and shatter prevention. The price differential reflects the advanced materials and manufacturing processes in noise control glass aimed at achieving enhanced sound insulation. Budget considerations often influence the choice between noise control glass and safety glass, with noise control glass favored in environments where noise reduction is critical despite its higher initial investment.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Noise control glass is designed with laminated layers and acoustic interlayers to significantly reduce sound transmission, making it ideal for environments requiring soundproofing. Safety glass, such as tempered or laminated glass, focuses on preventing injury by shattering into small, blunt pieces or holding together upon breakage. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize noise reduction or enhanced protection against impact and breakage.
noise control glass vs safety glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com