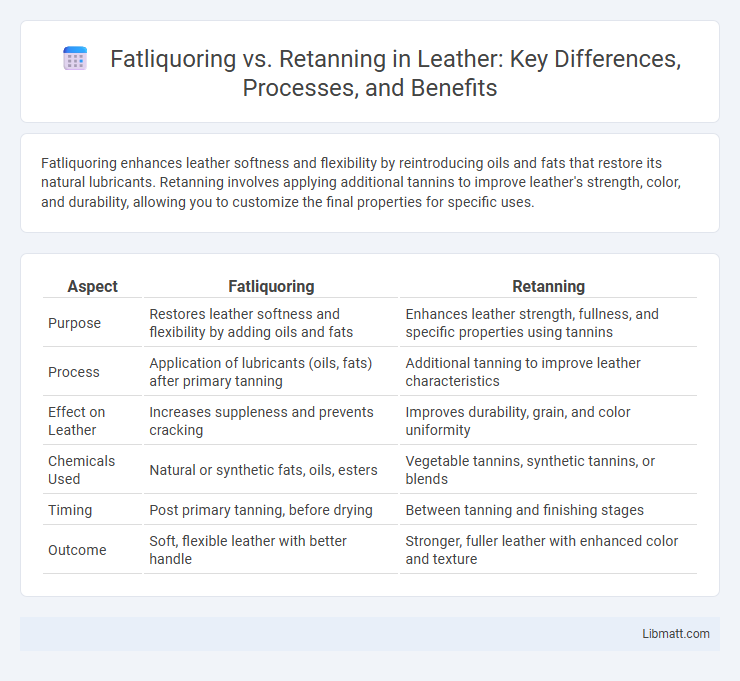
Fatliquoring enhances leather softness and flexibility by reintroducing oils and fats that restore its natural lubricants. Retanning involves applying additional tannins to improve leather's strength, color, and durability, allowing you to customize the final properties for specific uses.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fatliquoring | Retanning |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Restores leather softness and flexibility by adding oils and fats | Enhances leather strength, fullness, and specific properties using tannins |
| Process | Application of lubricants (oils, fats) after primary tanning | Additional tanning to improve leather characteristics |
| Effect on Leather | Increases suppleness and prevents cracking | Improves durability, grain, and color uniformity |
| Chemicals Used | Natural or synthetic fats, oils, esters | Vegetable tannins, synthetic tannins, or blends |
| Timing | Post primary tanning, before drying | Between tanning and finishing stages |
| Outcome | Soft, flexible leather with better handle | Stronger, fuller leather with enhanced color and texture |
Introduction to Fatliquoring and Retanning
Fatliquoring and retanning are essential leather processing steps that enhance softness and durability. Fatliquoring involves infusing leather with oils and fats to restore flexibility and prevent stiffness, while retanning strengthens leather by introducing additional tanning agents to improve its texture and resistance. Understanding these processes helps optimize your leather's quality and lifespan.
Defining Fatliquoring: Process and Purpose
Fatliquoring is a crucial leather processing step involving the infusion of oils and fats into the leather fibers to restore softness, flexibility, and water resistance. This process prevents leather from becoming stiff and brittle after tanning, ensuring durability and comfort in the final product. Your leather goods benefit from fatliquoring as it enhances suppleness and maintains the desired texture throughout their lifespan.
Retanning Explained: Techniques and Benefits
Retanning incorporates techniques such as chrome, vegetable, and synthetic tannins to enhance leather's properties, improving softness, fullness, and color fastness. This process refines the leather's physical characteristics, making it more durable and suitable for specific end uses like footwear and upholstery. Your leather gains improved strength and aesthetic appeal through carefully controlled retanning methods tailored to achieve desired qualities.
Key Differences between Fatliquoring and Retanning
Fatliquoring primarily involves the application of oils and fats to leather to restore softness, flexibility, and water resistance, while retanning uses alternative tanning agents such as synthetic chemicals or vegetable tannins to modify the leather's properties after initial chrome tanning. Fatliquoring enhances the leather's lubrication and prevents stiffness, whereas retanning adjusts color, durability, and texture, providing specific performance characteristics and improved resistance. The processes differ in chemical composition and purpose: fatliquoring focuses on lubrication and softness, retanning aims to enhance physical and aesthetic qualities of the leather.
Chemical Agents Used in Fatliquoring
Fatliquoring involves the use of chemical agents such as sulfated oils, synthetic oils, and emulsified fats to lubricate and soften leather fibers, enhancing flexibility and durability. Common agents in fatliquoring include sulfated castor oil, adipic acid esters, and mineral oils, which penetrate the leather matrix to replace natural fats lost during tanning. Retanning chemical agents, by contrast, typically consist of synthetic tannins, chromium salts, and aldehydes designed to improve leather firmness, colorfastness, and fullness rather than fiber lubrication.
Common Materials and Agents for Retanning
Retanning commonly employs materials such as synthetic tannins, aldehydes, and oil-based agents to enhance leather's firmness, fullness, and grip, while improving color uniformity. These agents penetrate the leather fibers to modify the physical and chemical properties, making it suitable for specific end-use requirements. Your choice of retanning materials directly influences the leather's durability, texture, and appearance.
Impacts on Leather Properties: Softness, Strength, and Color
Fatliquoring significantly enhances leather softness and flexibility by reintroducing oils and fats, improving tensile strength and preventing stiffness, while retanning primarily refines leather color depth and uniformity without markedly affecting softness. Retanning contributes to increased leather firmness and density by adding new tanning agents, which augment durability and resistance but can reduce pliability if overused. Together, fatliquoring and retanning balance the trade-off between softness and strength while achieving desired color stability and aesthetic appeal.
Industrial Applications: When to Choose Each Process
Fatliquoring is essential in industrial leather processing when flexibility, softness, and waterproofing are critical, especially in footwear and garment manufacturing. Retanning suits applications requiring enhanced leather firmness, improved grain quality, or specific chemical properties, often utilized in upholstery and automotive leather production. Choosing between fatliquoring and retanning depends on the desired end-use characteristics, balancing moisture resistance with structural integrity.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Fatliquoring enhances leather softness and flexibility by reintroducing oils and fats, often utilizing biodegradable and eco-friendly materials that reduce environmental impact. Retanning typically involves synthetic chemicals and heavy metals, posing challenges for waste management and increasing carbon footprint in leather production. Your choice between fatliquoring and retanning can significantly influence the sustainability profile of leather goods, with fatliquoring trending towards greener, more sustainable practices.
Innovations and Trends in Fatliquoring and Retanning
Innovations in fatliquoring emphasize eco-friendly and bio-based oils that enhance leather softness while reducing environmental impact. Advances in retanning incorporate novel synthetic and vegetable tannins to improve leather durability and texture with sustainable practices. The trend towards integrating nanotechnology and smart additives in both processes boosts performance and creates innovative leather qualities for diverse applications.
Fatliquoring vs retanning Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com