Grain-out occurs when excessive pressure on grains causes uneven extraction, leading to off-flavors, while split-out happens when water bypasses the coffee puck, resulting in weak and under-extracted brew. Understanding these processes helps you optimize grind size and tamping pressure for a balanced espresso shot.
Table of Comparison
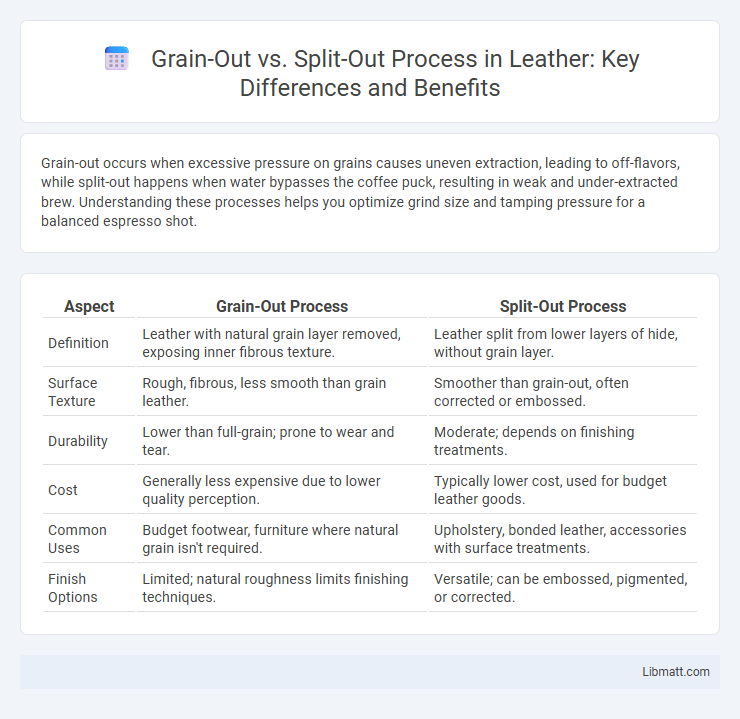
| Aspect | Grain-Out Process | Split-Out Process |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Leather with natural grain layer removed, exposing inner fibrous texture. | Leather split from lower layers of hide, without grain layer. |
| Surface Texture | Rough, fibrous, less smooth than grain leather. | Smoother than grain-out, often corrected or embossed. |
| Durability | Lower than full-grain; prone to wear and tear. | Moderate; depends on finishing treatments. |
| Cost | Generally less expensive due to lower quality perception. | Typically lower cost, used for budget leather goods. |
| Common Uses | Budget footwear, furniture where natural grain isn't required. | Upholstery, bonded leather, accessories with surface treatments. |
| Finish Options | Limited; natural roughness limits finishing techniques. | Versatile; can be embossed, pigmented, or corrected. |
Introduction to Grain-Out and Split-Out Processes
Grain-Out and Split-Out processes are essential techniques in semiconductor manufacturing used to improve wafer yield and device performance. Grain-Out refers to the controlled crystallization method that prevents defects by managing grain boundaries during thin-film deposition. Split-Out involves separating individual die from a wafer through precision dicing, reducing mechanical stress and enhancing chip quality.
Defining Grain-Out in Leather Production
Grain-out in leather production refers to the process of removing the grain layer from the hide, exposing the underlying corium layer, which results in a softer and more pliable leather but with a less natural surface texture. This method contrasts with split-out, where the hide is divided into multiple layers, allowing the use of both grain and corium parts separately for different leather products. Understanding grain-out is crucial for choosing the right leather type for your desired durability and aesthetic qualities.
What is Split-Out in Leather Processing?
Split-out in leather processing refers to the technique of dividing a hide or skin into multiple layers to achieve the desired thickness and quality for various leather products. This method enhances flexibility and texture control by separating the grain layer from the flesh side, enabling manufacturers to optimize material use and tailor the leather for specific applications. Your choice between grain-out and split-out depends on the required finish, durability, and end-use of the leather.
Key Differences Between Grain-Out and Split-Out
Grain-out and split-out are critical separation techniques used in mineral processing, with grain-out focusing on separating particles based on different grain sizes, while split-out divides materials into distinct fractions based on physical or chemical properties. Grain-out is primarily used to remove fine particles that may affect product quality, whereas split-out ensures precise material classification for optimized downstream processing. Understanding these key differences helps you select the most efficient method for improving recovery rates and product purity in your operations.
Advantages of the Grain-Out Process
The Grain-Out process offers enhanced material efficiency by maximizing grain utilization during milling, resulting in higher yield and reduced waste compared to the Split-Out process. It improves product uniformity by maintaining kernel integrity, which benefits both processing consistency and end-product quality. This method also reduces operational downtime as it requires fewer processing steps, lowering overall production costs.
Benefits of the Split-Out Technique
The split-out technique enhances product purity and quality by effectively separating impurities from the main grain feedstock, ensuring higher-grade output ideal for specialized applications. This process improves yield efficiency by minimizing material losses compared to traditional grain-out methods, resulting in better resource utilization and cost savings. Your production line benefits from increased flexibility, allowing for tailored processing adjustments that meet specific market demands and product specifications.
Common Applications of Grain-Out Leather
Grain-out leather is commonly used in footwear, upholstery, and automotive interiors due to its durable and textured surface that resists wear and scratches. The grain-out process retains the natural outer layer of the hide, making it ideal for products requiring a robust and attractive finish. Your choice of grain-out leather ensures longevity and a premium aesthetic for high-traffic applications.
Typical Uses for Split-Out Leather
Split-out leather is commonly used in applications requiring enhanced flexibility and reduced thickness, such as gloves, garment linings, and upholstery. This type of leather serves industries aiming for lightweight and soft materials without compromising durability. Automotive interiors and footwear manufacturers also rely on split-out leather to balance aesthetic appeal with functional performance.
Quality Considerations: Grain-Out vs Split-Out
Grain-out and split-out processes impact product quality differently due to variations in material properties and process control. Grain-out often results in localized defects or irregular grain structures affecting uniformity, while split-out tends to produce cleaner separations with less risk of internal stress or contamination. Understanding these quality considerations helps you select the appropriate process to maintain consistency and optimize final product performance.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Leather Needs
Grain-out and split-out refer to different leather processing techniques that affect texture, durability, and appearance. Grain-out leather retains the outer surface, providing a natural look and greater strength, while split-out leather comes from the inner layers, offering a softer feel but less durability. Choosing the right process for your leather needs depends on the intended use, desired finish, and longevity requirements.
Grain-out vs split-out process Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com