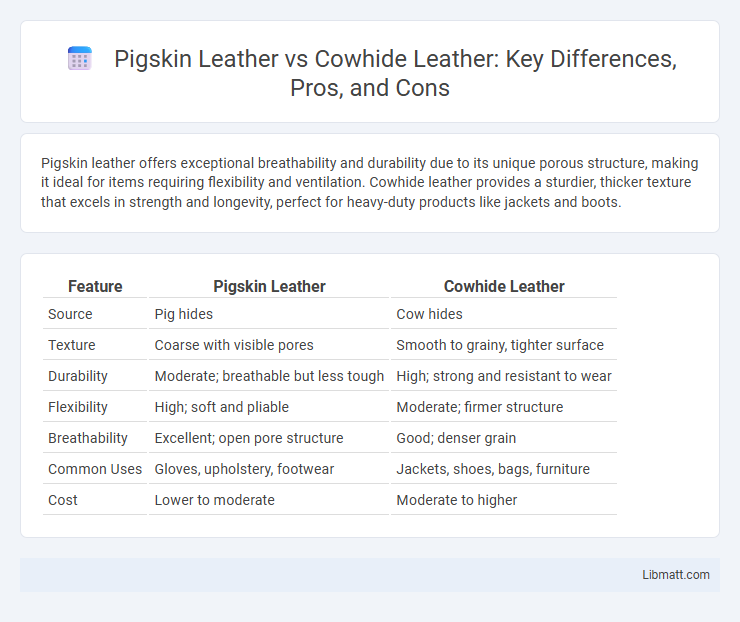
Pigskin leather offers exceptional breathability and durability due to its unique porous structure, making it ideal for items requiring flexibility and ventilation. Cowhide leather provides a sturdier, thicker texture that excels in strength and longevity, perfect for heavy-duty products like jackets and boots.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pigskin Leather | Cowhide Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Pig hides | Cow hides |
| Texture | Coarse with visible pores | Smooth to grainy, tighter surface |
| Durability | Moderate; breathable but less tough | High; strong and resistant to wear |
| Flexibility | High; soft and pliable | Moderate; firmer structure |
| Breathability | Excellent; open pore structure | Good; denser grain |
| Common Uses | Gloves, upholstery, footwear | Jackets, shoes, bags, furniture |
| Cost | Lower to moderate | Moderate to higher |
Introduction to Pigskin and Cowhide Leather
Pigskin leather, renowned for its softness and distinctive grain pattern, offers enhanced breathability and lightweight durability compared to cowhide leather. Cowhide leather, derived from mature cattle, is prized for its toughness, thickness, and long-lasting resilience, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Both materials serve different needs, with pigskin favored in fashion and apparel for comfort, while cowhide dominates in workwear and upholstery for strength.
Origins and Sources of Pigskin vs Cowhide
Pigskin leather originates from the hides of domestic pigs primarily raised in regions such as China, Europe, and the United States, making it a byproduct of the pork industry with a distinct porous texture. Cowhide leather, sourced from cattle raised worldwide including large-scale farms in the Americas, Australia, and India, is renowned for its durability and versatility due to the dense fiber structure. When choosing between pigskin and cowhide, understanding the origins helps you select leather tailored to your specific needs, whether for breathability or toughness.
Physical Characteristics: Texture and Appearance
Pigskin leather features a distinctive porous texture with visible follicles, giving it a unique grain pattern and a slightly rougher feel compared to cowhide. Cowhide leather is denser and smoother, offering a more uniform surface that can be polished to a high sheen and typically has fewer visible pores. These physical characteristics influence the leather's durability and aesthetic appeal, with pigskin prized for breathability and a rugged look, while cowhide is favored for its strength and classic, refined appearance.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Pigskin leather offers exceptional durability due to its dense fiber structure, making it resistant to wear and tear, while cowhide leather is renowned for its robust strength and long-lasting nature with a slightly thicker grain. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the flexibility and resilience of pigskin or the heavy-duty toughness of cowhide. Both materials provide excellent longevity, but cowhide may better withstand intense abrasion and heavy use over time.
Breathability and Comfort Levels
Pigskin leather offers superior breathability compared to cowhide leather due to its naturally porous structure that allows better air circulation. This enhanced airflow helps regulate temperature and reduces moisture buildup, resulting in increased comfort, especially in warm conditions. Cowhide leather tends to be thicker and less breathable, making pigskin a preferred choice for applications where lightweight, breathable material is essential.
Common Uses for Pigskin vs Cowhide Leather
Pigskin leather is commonly used for gloves, sportswear, and lightweight jackets due to its softness, breathability, and durability. Cowhide leather, known for its toughness and thickness, is preferred for heavy-duty items such as jackets, boots, belts, and furniture upholstery. Your choice between pigskin and cowhide leather depends on the desired texture, flexibility, and strength for the specific application.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Pigskin leather requires regular conditioning and gentle cleaning to maintain its softness and prevent dryness, as its porous texture is more susceptible to moisture absorption and staining. Cowhide leather is generally more durable and easier to care for, benefiting from occasional cleaning and conditioning to preserve its strength and water resistance. Both types demand prompt stain removal and avoidance of excessive heat to extend their lifespan.
Cost Differences Between Pigskin and Cowhide
Pigskin leather generally costs less than cowhide leather due to its availability and faster tanning process, making it a budget-friendly option for your leather goods. Cowhide, known for its durability and thickness, commands a higher price, reflecting its premium quality and longer processing time. Choosing between pigskin and cowhide ultimately depends on balancing cost with the leather's intended use and desired longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pigskin leather generally has a lower environmental impact than cowhide leather due to the smaller scale of pig farming and more efficient use of by-products from pork production. Cowhide leather contributes significantly to deforestation, methane emissions, and water consumption, making it less sustainable overall. Sustainable alternatives often involve sourcing pigskin from farms with responsible waste management and tanning practices that reduce chemical pollution.
Which Leather Is Best for Your Needs?
Pigskin leather offers a unique combination of softness, durability, and breathability, making it ideal for products requiring flexibility and comfort like gloves and jackets. Cowhide leather is known for its strength, toughness, and resistance to wear, perfect for heavy-duty items such as motorcycle gear and work boots. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize lightweight comfort and breathability with pigskin or robust durability and protection with cowhide.
Pigskin leather vs cowhide leather Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com