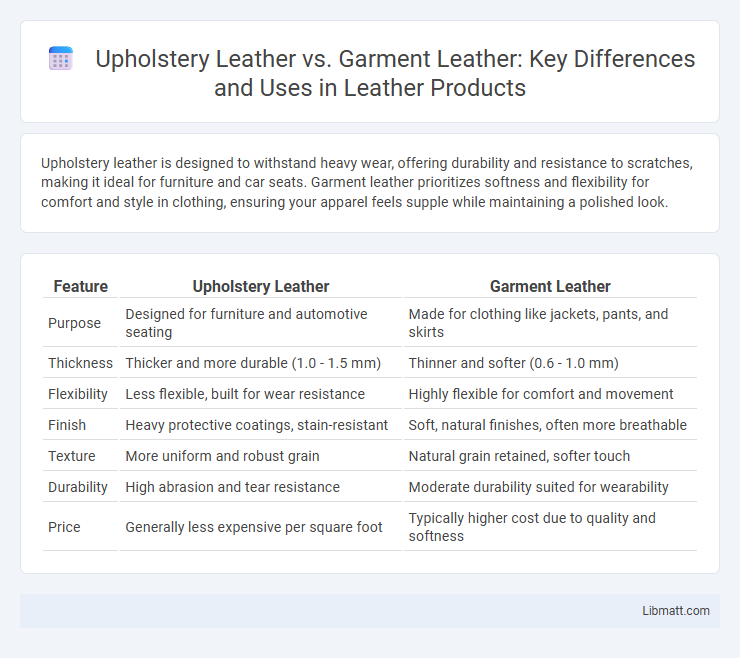
Upholstery leather is designed to withstand heavy wear, offering durability and resistance to scratches, making it ideal for furniture and car seats. Garment leather prioritizes softness and flexibility for comfort and style in clothing, ensuring your apparel feels supple while maintaining a polished look.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Upholstery Leather | Garment Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Designed for furniture and automotive seating | Made for clothing like jackets, pants, and skirts |
| Thickness | Thicker and more durable (1.0 - 1.5 mm) | Thinner and softer (0.6 - 1.0 mm) |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, built for wear resistance | Highly flexible for comfort and movement |
| Finish | Heavy protective coatings, stain-resistant | Soft, natural finishes, often more breathable |
| Texture | More uniform and robust grain | Natural grain retained, softer touch |
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Moderate durability suited for wearability |
| Price | Generally less expensive per square foot | Typically higher cost due to quality and softness |
Introduction to Upholstery Leather vs Garment Leather
Upholstery leather is specially treated to be durable, thick, and resistant to wear, making it ideal for furniture, car seats, and heavy-use applications. Garment leather, on the other hand, is softer, more flexible, and designed for comfort and style in clothing and accessories. Understanding the fundamental differences in texture, thickness, and finishing of these leathers helps you choose the right material for your project or product needs.
Key Differences Between Upholstery and Garment Leather
Upholstery leather is typically heavier, thicker, and more durable, designed to withstand frequent use and resist wear and tear on furniture surfaces. Garment leather is lighter, softer, and more flexible, tailored for comfort and ease of movement in clothing like jackets and gloves. The tanning processes also differ, with upholstery leather often treated for stain and abrasion resistance, while garment leather prioritizes suppleness and breathability.
Material Composition and Processing
Upholstery leather is typically made from thicker, more durable hides such as full-grain or top-grain cowhide, processed with heavy tanning and finishing techniques to enhance resistance to wear and stains. Garment leather, on the other hand, often uses softer, more flexible materials like lamb or goat leather, treated with lighter tanning processes to maintain suppleness and comfort for clothing. Your choice between upholstery leather and garment leather should consider these differences in material composition and processing to match the intended use and durability requirements.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Upholstery leather is engineered for high durability and strength, designed to withstand constant friction, heavy use, and environmental exposure, making it ideal for furniture and automotive seating. Garment leather prioritizes flexibility and softness, offering moderate strength but less resistance to abrasion compared to upholstery leather. When choosing for long-lasting use, your decision should account for upholstery leather's superior toughness and resistance to wear.
Texture and Aesthetic Appeal
Upholstery leather features a thicker, more durable texture designed to withstand wear and tear, often showcasing a matte or semi-gloss finish with natural grain patterns for a rich, classic aesthetic ideal for furniture. Garment leather is typically thinner and softer, emphasizing suppleness and flexibility with a smooth or lightly textured surface to enhance comfort and style in clothing. The contrasting textures directly influence their aesthetic appeal, with upholstery leather conveying robustness and timelessness, while garment leather offers elegance and a refined look suitable for fashion.
Common Uses and Applications
Upholstery leather is predominantly used for furniture, car seats, and interior decor due to its durability and resistance to wear and tear. Garment leather is designed for clothing items such as jackets, gloves, and pants, prioritizing softness, flexibility, and breathability. Both types of leather are treated differently during manufacturing to meet specific performance requirements in their respective applications.
Comfort and Breathability Factors
Upholstery leather is thicker and more durable, designed to withstand wear and provide firm support, which may reduce breathability and comfort during extended use. Garment leather, crafted to be lightweight and flexible, offers superior breathability and softness, enhancing your comfort when worn as clothing. Choosing garment leather ensures better moisture management and temperature regulation compared to the denser upholstery leather.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Upholstery leather requires regular maintenance with specialized leather cleaners and conditioners to prevent drying and cracking, especially in high-traffic areas. Garment leather demands more delicate care due to its softer, thinner texture, making it susceptible to stains and damage from moisture; spot cleaning with mild products is recommended. Both types benefit from avoiding direct sunlight and heat sources to maintain flexibility and appearance over time.
Cost Comparison: Upholstery vs Garment Leather
Upholstery leather typically costs more than garment leather due to its thicker, more durable hide and extensive finishing processes designed to withstand wear and tear in furniture. Garment leather, often sourced from thinner hides like lamb or goat, offers a softer feel at a lower price point, making it more affordable for clothing and accessories. Your choice should consider the intended use, balancing cost with durability and comfort requirements.
Choosing the Right Leather for Your Needs
Upholstery leather offers durability and thickness ideal for heavy-use furniture, resisting wear and stains over time. Garment leather is softer, thinner, and more flexible, designed for comfort and style in clothing and accessories. Selecting the right leather depends on the application's durability requirements, texture preference, and exposure to wear, ensuring functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Upholstery leather vs garment leather Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com