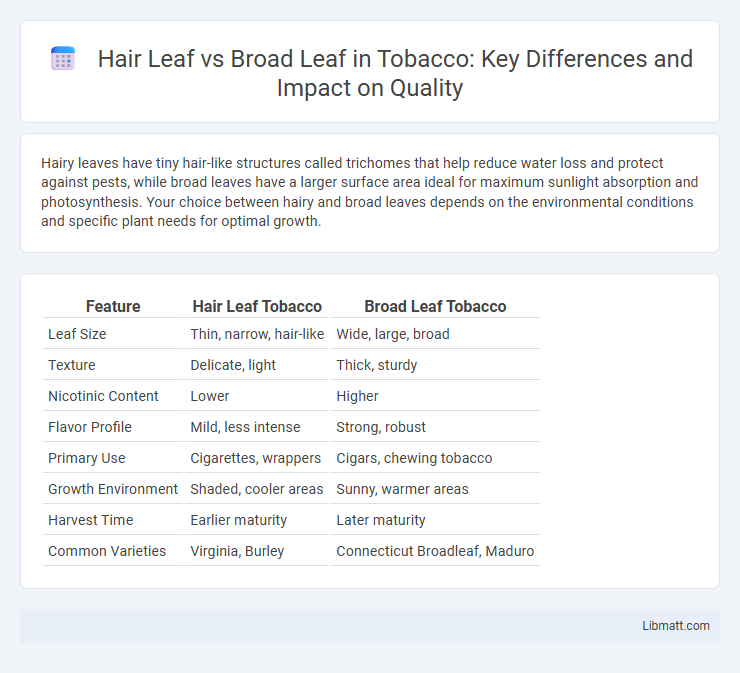
Hairy leaves have tiny hair-like structures called trichomes that help reduce water loss and protect against pests, while broad leaves have a larger surface area ideal for maximum sunlight absorption and photosynthesis. Your choice between hairy and broad leaves depends on the environmental conditions and specific plant needs for optimal growth.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hair Leaf Tobacco | Broad Leaf Tobacco |
|---|---|---|
| Leaf Size | Thin, narrow, hair-like | Wide, large, broad |
| Texture | Delicate, light | Thick, sturdy |
| Nicotinic Content | Lower | Higher |
| Flavor Profile | Mild, less intense | Strong, robust |
| Primary Use | Cigarettes, wrappers | Cigars, chewing tobacco |
| Growth Environment | Shaded, cooler areas | Sunny, warmer areas |
| Harvest Time | Earlier maturity | Later maturity |
| Common Varieties | Virginia, Burley | Connecticut Broadleaf, Maduro |
Introduction to Hair Leaf and Broad Leaf
Hair leaves feature fine, hair-like structures that aid in water retention and defense against pests, commonly found in arid environments. Broad leaves have a wider surface area optimized for maximum photosynthesis, typical in tropical and temperate regions. Understanding the differences between hair leaf and broad leaf types helps you choose suitable plants for specific climates and garden needs.
Defining Hair Leaf: Key Characteristics
Hair leaves are characterized by the presence of tiny, hair-like structures on their surface, which help reduce water loss and protect against pests. These leaves typically have a narrow shape with fine trichomes that enhance their ability to retain moisture in arid environments. Understanding the unique features of hair leaves can help you identify plant adaptations for survival in dry or harsh conditions.
Understanding Broad Leaf: Main Features
Broad leaves are characterized by their wide, flat surfaces which maximize photosynthesis efficiency by capturing more sunlight. These leaves often have complex vein patterns aiding in nutrient transport and structural support. Your understanding of broad leaves helps in distinguishing them from narrow or needle-like leaves, enhancing plant identification skills.
Anatomical Differences Between Hair Leaf and Broad Leaf
Hair leaves exhibit specialized epidermal structures called trichomes that reduce water loss and protect against herbivory, while broad leaves typically have a smoother surface with fewer trichomes. The mesophyll in hair leaves is often denser with more tightly packed cells to minimize transpiration, whereas broad leaves contain well-developed palisade and spongy mesophyll layers to maximize photosynthesis. Vein density tends to be higher in broad leaves to support larger surface areas and efficient nutrient transport, contrasting with the simpler vascular arrangement found in hair leaves.
Ecological Adaptations of Hair Leaf vs Broad Leaf
Hair leaves feature tiny hairs that reduce water loss and protect against herbivores, making them well-suited for arid and windy environments. Broad leaves have a larger surface area for photosynthesis, enhancing energy capture in shaded or moist habitats but increasing water loss risk. Your choice between hair leaf and broad leaf plants should consider these ecological adaptations to thrive in specific environmental conditions.
Common Plant Species with Hair Leaf and Broad Leaf
Common plant species with hair leaves include lamb's ear (Stachys byzantina), club moss (Lycopodiopsida), and various types of sage (Salvia spp.), which have fine hairs enhancing moisture retention and pest resistance. Broad-leaved plants such as maple (Acer spp.), oak (Quercus spp.), and magnolia (Magnolia spp.) typically feature wide, flat leaves optimized for maximum photosynthesis in diverse environments. Hair leaf species often thrive in arid or high-altitude regions, while broad-leaf species are more common in temperate and tropical forests.
Photosynthesis Efficiency: Hair Leaf vs Broad Leaf
Hair leaves with their narrow, elongated structures often exhibit reduced surface area, limiting light absorption but enhancing water retention, which can moderate photosynthesis under arid conditions. Broad leaves provide increased surface area that maximizes light capture and photosynthesis efficiency, particularly in environments with abundant sunlight and water. The presence of hair on leaves can reduce light intensity and temperature on the leaf surface, potentially decreasing photosynthesis rates compared to broad, smooth leaves optimized for light absorption.
Environmental Impact and Distribution Patterns
Hair leaf plants, typically found in arid and semi-arid regions, possess fine, narrow leaves that reduce evapotranspiration and enhance water conservation, thereby minimizing environmental stress in dry climates. Broad leaf species, prevalent in tropical and temperate forests, support higher photosynthetic rates but contribute to greater water loss and soil moisture depletion, influencing local hydrological cycles and biodiversity. The distinct leaf morphology drives their distribution patterns, with hair leaf plants dominating xeric environments and broad leaf species thriving in humid, resource-rich ecosystems.
Benefits and Uses in Agriculture and Horticulture
Hairy leaves enhance water retention and reduce transpiration, making them beneficial in drought-prone agricultural areas. Broad leaves increase photosynthetic capacity and nutrient absorption, supporting faster plant growth and higher crop yields in horticulture. Both leaf types contribute to pest deterrence, with hairy leaves providing a physical barrier and broad leaves offering more surface area for beneficial microbial colonies.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Hair Leaf and Broad Leaf Plants
Selecting between hair leaf and broad leaf plants depends on environmental conditions and aesthetic preferences. Hair leaf plants, with narrow, needle-like leaves, are well-suited for dry, windy habitats due to reduced water loss, while broad leaf plants offer greater photosynthetic capacity ideal for shaded or moist areas. Understanding these differences helps optimize plant health and landscape design choices.
Hair leaf vs broad leaf Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com