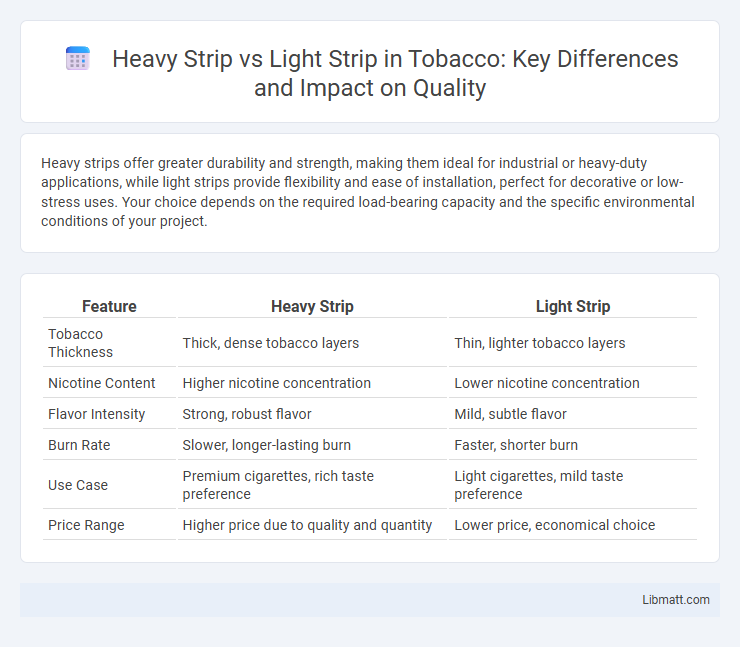
Heavy strips offer greater durability and strength, making them ideal for industrial or heavy-duty applications, while light strips provide flexibility and ease of installation, perfect for decorative or low-stress uses. Your choice depends on the required load-bearing capacity and the specific environmental conditions of your project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heavy Strip | Light Strip |
|---|---|---|
| Tobacco Thickness | Thick, dense tobacco layers | Thin, lighter tobacco layers |
| Nicotine Content | Higher nicotine concentration | Lower nicotine concentration |
| Flavor Intensity | Strong, robust flavor | Mild, subtle flavor |
| Burn Rate | Slower, longer-lasting burn | Faster, shorter burn |
| Use Case | Premium cigarettes, rich taste preference | Light cigarettes, mild taste preference |
| Price Range | Higher price due to quality and quantity | Lower price, economical choice |
Introduction to Heavy Strip and Light Strip
Heavy strip steel features a thicker gauge and higher tensile strength, making it ideal for structural applications and heavy-duty manufacturing. Light strip steel is thinner and more flexible, suited for automotive panels, appliances, and lighter fabrication work. Your choice depends on the required durability, weight considerations, and the specific industrial application.
Defining Heavy Strip vs Light Strip
Heavy strip steel refers to thicker, more robust metal sheets typically used in structural applications requiring high strength and durability, such as construction beams and industrial machinery components. Light strip steel, by contrast, consists of thinner sheets designed for applications that prioritize flexibility and lightweight characteristics, commonly found in automotive panels and household appliances. The primary distinction lies in the gauge thickness, weight per unit area, and intended mechanical properties aimed at meeting different performance criteria.
Key Differences Between Heavy and Light Strips
Heavy strips typically have a thicker gauge and higher mass per unit length, providing greater strength and durability compared to light strips. Light strips are thinner, more flexible, and easier to work with, making them suitable for applications requiring less structural support. Your choice between heavy and light strips depends on the specific load-bearing requirements and environmental conditions of your project.
Material Composition and Thickness Comparison
Heavy strips are typically made from thicker gauge metals such as stainless steel or carbon steel, with thicknesses ranging from 0.5 mm to over 3 mm, providing enhanced strength and durability for industrial applications. Light strips, often composed of aluminum or thinner steel grades, usually measure below 0.5 mm in thickness, allowing for greater flexibility and ease of fabrication in consumer goods and electronics. The difference in material composition and thickness directly impacts the mechanical properties, weight, and cost-efficiency of each strip type in manufacturing processes.
Applications of Heavy Strips
Heavy strips are primarily used in structural applications such as shipbuilding, bridges, and heavy machinery where high strength and durability are critical. Their thickness and robustness make them suitable for manufacturing components that must withstand significant stress and load. Your projects requiring enhanced mechanical performance benefit from the superior toughness and rigidity of heavy strips.
Uses and Benefits of Light Strips
Light strips offer versatility for accent lighting, decorative purposes, and creating ambiance in residential and commercial spaces. Their energy-efficient LED technology provides long-lasting illumination with minimal heat output, making them ideal for tight or enclosed areas. Easy installation and flexible design enable customization for various surfaces, enhancing aesthetics without the bulk or weight of heavy strips.
Performance and Durability Analysis
Heavy strips exhibit superior performance and durability due to their increased thickness and density, which enhance load-bearing capacity and resistance to wear, making them ideal for applications requiring high mechanical strength. Light strips offer greater flexibility and lighter weight, providing ease of handling and reduced installation costs but may suffer from lower resistance to deformation and shorter lifespan under heavy-duty conditions. Material composition, surface treatment, and application environment significantly influence the long-term durability and performance efficiency between heavy and light strips.
Cost Implications: Heavy Strip vs Light Strip
Heavy strip generally incurs higher costs due to increased material usage and manufacturing complexity, impacting your overall production budget. Light strip offers cost savings through reduced weight and easier handling, which can lower transportation and installation expenses. Choosing between heavy and light strip depends on balancing initial material costs with long-term efficiency and application requirements.
Selection Criteria for Specific Industries
Heavy strips offer superior strength and durability, making them ideal for industries like automotive and construction where load-bearing applications and structural integrity are critical. Light strips, characterized by their flexibility and easier handling, are preferred in electronics and packaging sectors where precision and lightweight materials enhance performance and reduce costs. Selection depends on factors such as mechanical stress, corrosion resistance, and manufacturing processes specific to each industry's requirements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Strip for Your Needs
Heavy strip steel offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications and structural components. Light strip steel is more flexible and easier to form, suited for consumer goods and lighter manufacturing processes. Selecting the right strip depends on balancing load requirements, material performance, and production methods to optimize efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Heavy strip vs light strip Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com