A plug connects electrical devices by fitting prongs into corresponding slots in an outlet, providing a secure and reliable connection, while a twist mechanism requires you to rotate the plug or connector to lock it in place, often used for added stability in power or mechanical connections. Your choice depends on the device's design and the need for a firm, twist-lock security versus a standard plug-in connection.
Table of Comparison
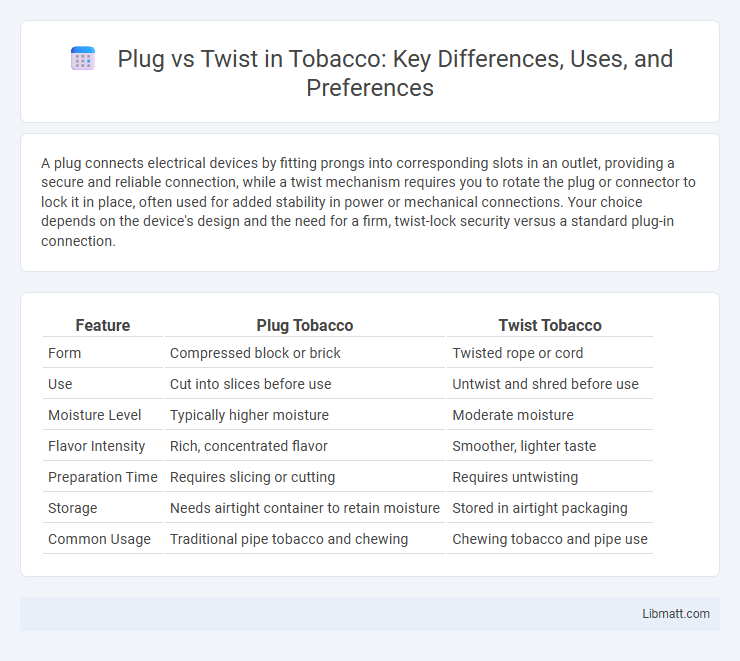
| Feature | Plug Tobacco | Twist Tobacco |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Compressed block or brick | Twisted rope or cord |
| Use | Cut into slices before use | Untwist and shred before use |
| Moisture Level | Typically higher moisture | Moderate moisture |
| Flavor Intensity | Rich, concentrated flavor | Smoother, lighter taste |
| Preparation Time | Requires slicing or cutting | Requires untwisting |
| Storage | Needs airtight container to retain moisture | Stored in airtight packaging |
| Common Usage | Traditional pipe tobacco and chewing | Chewing tobacco and pipe use |
Introduction to Plug vs Twist
Plug and twist mechanisms offer distinct approaches for securing devices and components, with plug systems emphasizing straightforward insertion and connection, while twist designs rely on rotational locking for stability. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right solution based on ease of use, security, and application context. Your choice between plug and twist can impact the efficiency and durability of the assembly.
Definition of Plug and Twist Mechanisms
Plug mechanisms involve inserting one component directly into another, creating a secure and straightforward connection often used in electrical and mechanical systems. Twist mechanisms rely on rotating one part to lock it into place within another, providing enhanced stability and resistance to accidental disconnection. Your choice between plug and twist mechanisms depends on the required ease of use and the level of connection security needed.
Historical Background and Development
The plug and twist locking mechanisms have evolved significantly since their inception in the late 19th century, initially developed for electrical connectors to improve safety and reliability. Early plug designs were simple, relying on friction or basic metal contacts, while twist mechanisms introduced a secure locking feature to prevent accidental disconnection. Modern implementations build on these innovations, incorporating advanced materials and precise engineering to enhance durability and user safety in various electrical applications.
Key Differences Between Plug and Twist
Plug connectors primarily rely on straight insertion for electrical connections, while twist connectors require a rotational action to secure the connection. Plug types are often favored for their quick connect and disconnect capabilities, whereas twist types provide enhanced stability and resistance to vibration. Material composition and use case scenarios further distinguish plug connectors, commonly found in household electronics, from twist connectors preferred in industrial and mechanical applications.
Advantages of Plug Connections
Plug connections offer superior ease of installation and removal, reducing labor time and minimizing the need for specialized tools. Their design ensures reliable electrical contact with high resistance to vibration and corrosion, enhancing long-term performance and safety. These connections also support modular setups, allowing quick reconfiguration and maintenance in complex systems.
Advantages of Twist Mechanisms
Twist mechanisms offer enhanced security and a more reliable connection compared to plug designs, reducing the risk of accidental disconnection in critical applications. Their locking feature ensures consistent electrical contact, which improves overall device performance and safety. You benefit from increased durability and stability, making twist mechanisms ideal for environments requiring robust and secure connections.
Common Applications for Plug vs Twist
Plug connectors are commonly used in household electronics, power tools, and audio-visual equipment where straightforward connectivity is essential. Twist connectors find application in industrial machinery, automotive wiring, and marine equipment due to their secure and vibration-resistant connection. Your choice depends on whether ease of use or enhanced stability suits your specific application needs.
Durability and Safety Considerations
Twist connectors provide enhanced durability through secure locking mechanisms that resist loosening over time, reducing the risk of electrical faults. Plug connectors offer ease of use but may wear out more quickly under frequent use, potentially compromising safety if contacts become loose. You should choose connectors based on your specific application needs, prioritizing those that maintain firm connections to ensure long-term electrical safety.
User Convenience and Installation
Twist connectors provide quick and secure wire connections ideal for residential and commercial electrical projects. Plug connectors offer greater user convenience with tool-free installation, making them perfect for fast updates and DIY tasks. Your choice depends on the balance between ease of use and long-term stability in electrical wiring.
Choosing the Right Option: Plug or Twist
Choosing the right option between plug and twist connectors depends on your specific application and ease of use. Plug connectors offer quick connections ideal for temporary setups, while twist connectors provide secure, vibration-resistant fastening suited for permanent installations. Assess your project requirements to select the option that ensures reliability and safety for your electrical or mechanical systems.
plug vs twist Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com