Civilian transport focuses on moving passengers and goods efficiently and safely for commercial or personal use, emphasizing comfort and cost-effectiveness. Military transport prioritizes the rapid and secure movement of troops, equipment, and supplies, often in challenging or hostile environments to support defense operations.
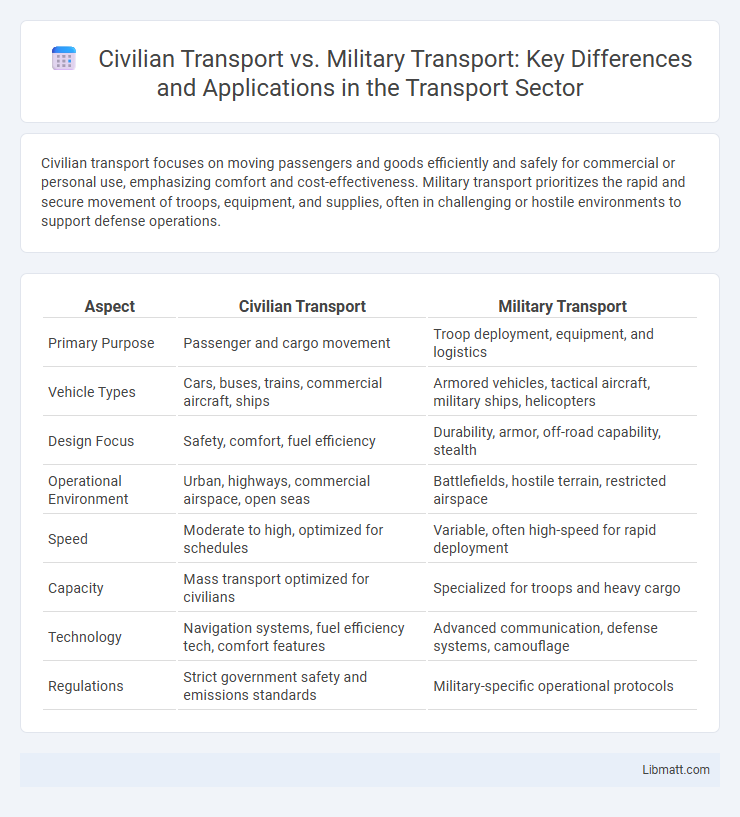
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Civilian Transport | Military Transport |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Passenger and cargo movement | Troop deployment, equipment, and logistics |
| Vehicle Types | Cars, buses, trains, commercial aircraft, ships | Armored vehicles, tactical aircraft, military ships, helicopters |
| Design Focus | Safety, comfort, fuel efficiency | Durability, armor, off-road capability, stealth |
| Operational Environment | Urban, highways, commercial airspace, open seas | Battlefields, hostile terrain, restricted airspace |
| Speed | Moderate to high, optimized for schedules | Variable, often high-speed for rapid deployment |
| Capacity | Mass transport optimized for civilians | Specialized for troops and heavy cargo |
| Technology | Navigation systems, fuel efficiency tech, comfort features | Advanced communication, defense systems, camouflage |
| Regulations | Strict government safety and emissions standards | Military-specific operational protocols |
Introduction to Civilian and Military Transport
Civilian transport systems prioritize passenger comfort, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, encompassing vehicles like buses, trains, and commercial airplanes designed for daily commuting and long-distance travel. Military transport emphasizes durability, versatility, and security, utilizing specialized vehicles such as armored personnel carriers, cargo aircraft, and amphibious ships engineered to operate in combat zones and harsh environments. Both sectors rely on advanced logistics and technology but differ fundamentally in purpose, design specifications, and operational requirements.
Key Differences Between Civilian and Military Transport
Civilian transport prioritizes passenger comfort, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, often focusing on commercial airlines, buses, and trains designed for mass transit. Military transport emphasizes durability, tactical capability, and the ability to operate in hostile environments, utilizing armored vehicles, cargo planes with heavy payload capacity, and amphibious transport. The key differences lie in design purpose, operational environment, and the level of security features integrated into each transport mode.
Purposes and Objectives of Each Transport Type
Civilian transport primarily focuses on the safe and efficient movement of passengers and goods for commercial, personal, and public use, emphasizing convenience, comfort, and cost-effectiveness. Military transport aims to rapidly deploy troops, equipment, and supplies, prioritizing strategic mobility, security, and readiness in diverse and often hostile environments. Your understanding of these distinct purposes highlights the tailored designs and operational protocols that differentiate each transport type.
Vehicle Types Used in Civilian vs Military Sectors
Civilian transport relies heavily on passenger cars, buses, and commercial trucks designed for efficiency and comfort in urban and suburban environments. Military transport prioritizes armored vehicles, tactical trucks, and specialized aircraft engineered for durability, off-road capability, and mission-specific requirements. The distinct vehicle types reflect the contrasting demands of civilian mobility and military operational effectiveness.
Infrastructure Requirements for Civilian and Military Transport
Civilian transport infrastructure demands extensive networks of airports, highways, and railways optimized for continuous passenger and cargo flow, emphasizing accessibility, safety, and efficiency in urban and rural areas. Military transport infrastructure requires specialized facilities such as secure airbases, heavy-duty ports, and rapid deployment roads designed to support tactical operations, armored vehicles, and large-scale troop movements under diverse and often hostile conditions. Your planning for transport systems must consider these distinct infrastructure needs to ensure operational effectiveness and security for both civilian and military purposes.
Safety and Security Considerations
Civilian transport prioritizes passenger safety through stringent regulatory compliance, advanced navigation systems, and emergency preparedness protocols designed to minimize accidents and ensure comfort. Military transport emphasizes security measures, including armored vehicles, secure communication systems, and tactical maneuvering to protect personnel and sensitive cargo in hostile environments. Both sectors implement rigorous maintenance and training standards, but military transport integrates combat readiness and threat mitigation strategies that surpass civilian safety protocols.
Technology and Innovations in Transport
Military transport incorporates advanced technologies such as stealth design, autonomous navigation, and enhanced durability to operate in extreme environments, surpassing the capabilities of most civilian transport systems. Civilian transport innovations prioritize energy efficiency, passenger comfort, and environmental sustainability, utilizing electric propulsion, smart traffic management, and connected vehicle technologies. Your understanding of these technological differences highlights how military and civilian sectors drive specialized innovation tailored to distinct operational needs.
Cost Factors and Funding Sources
Civilian transport relies heavily on public funding, including government subsidies, passenger fares, and private investments, which influences its cost structure toward affordability and accessibility. Military transport costs are significantly higher due to advanced technology, specialized equipment, and rigorous operational requirements, typically funded through defense budgets and taxpayer allocations. Cost factors in military transport also include maintenance of durability and security standards not prioritized in civilian transport systems.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Civilian transport primarily relies on commercial aviation, private vehicles, and public transit systems, which contribute significantly to global carbon emissions, with aviation alone accounting for roughly 2-3% of global CO2 emissions. Military transport, including aircraft, ships, and ground vehicles, operates with high fuel consumption and lower efficiency, often using specialized fuels and older technology, resulting in disproportionate greenhouse gas emissions relative to its scale. Efforts to reduce the environmental impact of both sectors focus on improving fuel efficiency, adopting alternative energy sources like biofuels and electrification, and implementing stricter emissions regulations for civilian use while balancing operational readiness and mission requirements for military applications.
Future Trends in Civilian and Military Transport
Future trends in civilian transport emphasize electric and autonomous vehicles, with advancements in battery technology and AI driving efficiency and sustainability. Military transport focuses on enhanced mobility through hybrid propulsion systems, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and improved logistics networks to increase operational flexibility. Both sectors are investing heavily in smart infrastructure and cybersecurity to support connected and resilient transport ecosystems.
civilian transport vs military transport Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com