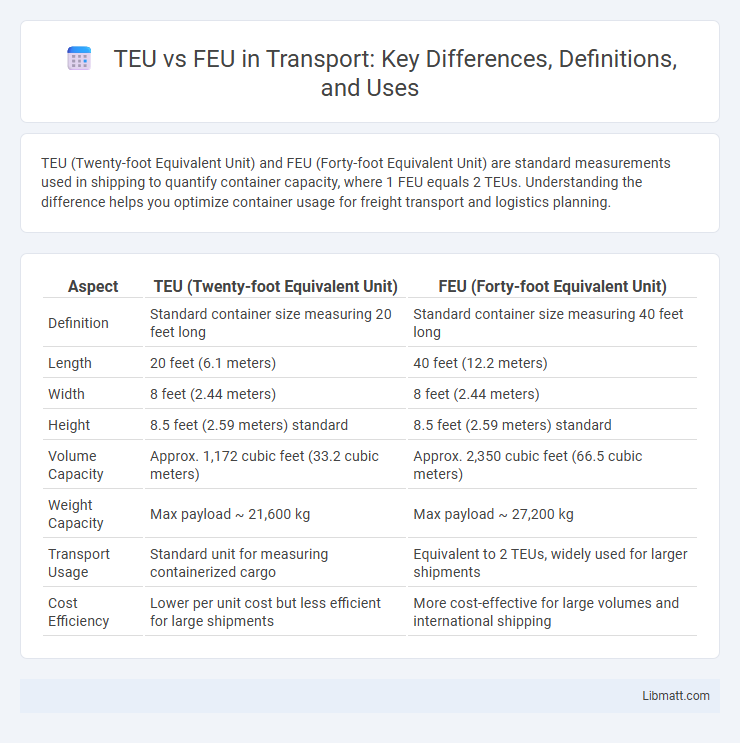
TEU (Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit) and FEU (Forty-foot Equivalent Unit) are standard measurements used in shipping to quantify container capacity, where 1 FEU equals 2 TEUs. Understanding the difference helps you optimize container usage for freight transport and logistics planning.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | TEU (Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit) | FEU (Forty-foot Equivalent Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standard container size measuring 20 feet long | Standard container size measuring 40 feet long |
| Length | 20 feet (6.1 meters) | 40 feet (12.2 meters) |
| Width | 8 feet (2.44 meters) | 8 feet (2.44 meters) |
| Height | 8.5 feet (2.59 meters) standard | 8.5 feet (2.59 meters) standard |
| Volume Capacity | Approx. 1,172 cubic feet (33.2 cubic meters) | Approx. 2,350 cubic feet (66.5 cubic meters) |
| Weight Capacity | Max payload ~ 21,600 kg | Max payload ~ 27,200 kg |
| Transport Usage | Standard unit for measuring containerized cargo | Equivalent to 2 TEUs, widely used for larger shipments |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower per unit cost but less efficient for large shipments | More cost-effective for large volumes and international shipping |
Understanding TEU and FEU: Definitions
TEU (Twenty-Foot Equivalent Unit) represents a standard measure of cargo capacity based on a 20-foot-long container, commonly used in shipping and logistics to quantify container volume. FEU (Forty-Foot Equivalent Unit) equals two TEUs and refers to a 40-foot-long container, reflecting a larger capacity used for international freight transport. Understanding these units is essential for accurately calculating shipping costs, container space utilization, and global trade logistics.
The Origins of TEU and FEU Standards
The TEU (Twenty-Foot Equivalent Unit) and FEU (Forty-Foot Equivalent Unit) standards originated from early 20th-century shipping practices to standardize container sizes for global maritime trade. The TEU, based on a 20-foot container, became the fundamental unit for measuring cargo capacity and vessel efficiency. The FEU, representing a 40-foot container, evolved to optimize space utilization and streamline handling, reflecting industry demands for larger, standardized containers.
TEU vs FEU: Key Differences
TEU (Twenty-Foot Equivalent Unit) and FEU (Forty-Foot Equivalent Unit) are standard shipping container measurements with TEU representing a 20-foot container and FEU equaling 40 feet, effectively two TEUs. TEU measures volume and capacity for smaller shipments, while FEU is used for larger, more cost-effective cargo transport, doubling the TEU unit size. Understanding TEU vs FEU is crucial for logistics planning, freight cost calculation, and maximizing container space efficiency in international shipping.
Container Dimensions and Capacity Comparison
A Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit (TEU) measures 20 feet long, 8 feet wide, and 8.5 feet high with a capacity of approximately 1,360 cubic feet, while a Forty-foot Equivalent Unit (FEU) doubles the length to 40 feet but maintains the same width and height, offering around 2,720 cubic feet of volume. The FEU can carry twice the cargo volume of a TEU, making it more efficient for larger shipments. Shipping logistics prioritize FEUs for maximizing load capacity without increasing the container's footprint on transport vessels.
Common Uses of TEU and FEU Containers
TEU (Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit) containers are commonly used for shipping smaller volumes, individual cargo shipments, and goods requiring easier handling or storage, while FEU (Forty-foot Equivalent Unit) containers accommodate larger or bulkier loads such as machinery, automotive parts, and bulk commodities, maximizing container space efficiency. Your choice between TEU and FEU depends on the specific volume and type of cargo, with TEUs favored for flexibility and FEUs preferred for cost-effective transport of larger shipments. Both TEU and FEU containers are standard in global shipping, ensuring compatibility across different transport modes and simplifying logistics coordination.
Cost Implications: TEU vs FEU
Understanding the cost implications between TEU (Twenty-Foot Equivalent Unit) and FEU (Forty-Foot Equivalent Unit) is crucial for optimizing shipping expenses. FEUs often offer better cost efficiency per container since they double the capacity of a TEU while incurring less than double the shipping fees, reducing your overall freight cost per cubic meter. However, TEUs provide more flexibility in cargo handling and may be preferable for smaller shipments or routes with container size restrictions.
Shipping Efficiency: Which Container Is Better?
TEU (Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit) and FEU (Forty-foot Equivalent Unit) significantly differ in shipping efficiency, with FEUs offering greater capacity and cost-effectiveness per unit. FEUs can carry double the volume of TEUs, reducing handling and shipping costs, and improving space utilization on vessels and trucks. Shipping with FEUs enhances operational efficiency by minimizing the number of containers needed, leading to lower fuel consumption and faster loading and unloading times.
Global Trade and Container Preference
Twenty-foot Equivalent Units (TEUs) and Forty-foot Equivalent Units (FEUs) represent standard container sizes critical to global trade logistics, with TEUs measuring 20 feet in length and FEUs measuring 40 feet, effectively double the size of a TEU. Shipping companies and freight forwarders often prefer FEUs for their efficiency in maximizing cargo volume while minimizing handling costs, significantly impacting container preference in international shipping routes. The choice between TEU and FEU containers influences port infrastructure, container fleet management, and overall supply chain optimization, reflecting strategic decisions based on trade volume, destination, and commodity type.
Choosing the Right Container for Your Cargo
Selecting the right container between TEU and FEU depends on the volume and nature of your cargo; TEU (Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit) suits smaller shipments, while FEU (Forty-foot Equivalent Unit) accommodates larger loads more efficiently. FEUs offer nearly double the capacity of TEUs, making them cost-effective for heavy or bulky goods that maximize economized shipping space. Understanding your cargo dimensions, weight, and shipping frequency is critical to optimize storage, transport costs, and logistics efficiency when deciding between TEU and FEU containers.
TEU and FEU: Future Trends in Container Shipping
TEU (Twenty-Foot Equivalent Unit) and FEU (Forty-Foot Equivalent Unit) remain essential metrics in container shipping, with rising global trade driving demand for larger, more efficient containers like FEUs. Innovations in sustainable shipping practices and digital tracking are enhancing the optimization of TEU and FEU usage, reducing costs and environmental impact. Your logistics strategy should account for these trends to maximize capacity and streamline container management in future maritime operations.
TEU vs FEU Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com